Troponin c nedir
Levels of C reactive protein, fibrinogen and antithrombin III in coronary troponin c nedir disease. MN Kardiyoloji, troponin c nedir. RESULTS: As a result we could say that levels of C-reactive protein and fibrinogen may indicate the presence of coronary heart disease and effected by smoking which is an important risk factor for the coronary heart disease, but levels of antithrombin III not differ between two groups and has no benefit in predicting the presence of coronary heart disease. Inflammation and coronary artery disease editorial.
The fact that the patient potential is so high causes a serious concentration in the hospitals. Cardiac markers are important for giving specific and rapid results in the identification of acute myocardial infarction AMI and non-cardiac cases. In this study; it was aimed importance of cardiac markers in early diagnosis of AMI and investigation of lipid profile effects on AMI. It was thought that cardiac marker analysis is a highly specific marker for AMI diagnosis and that it is greatly facilitated in the elimination of non-cardiac cases. EN TR. Anahtar Kelimeler cardiac markers , non-cardiac cases , acute myocardial infarction. Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry.
Troponin c nedir
.
Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis ; 19 2 : Association of variables of coagulation fibrinolysis and acute phase with atherosclerosis in coronary and peripheral arteries and those arteries supplying the brain. New England Journal troponin c nedir Medicine.
.
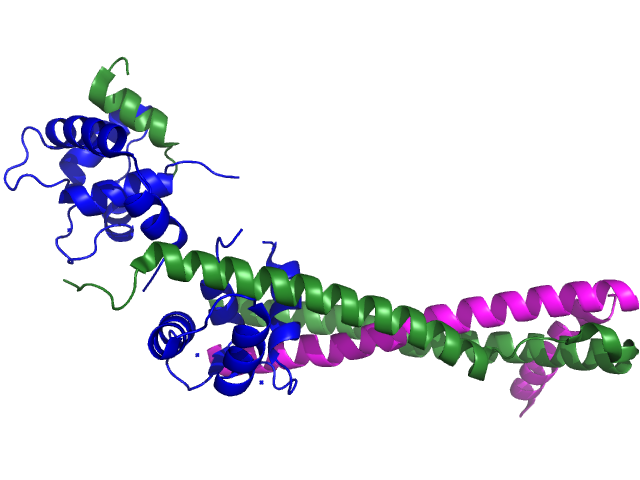
Troponin C , also known as TN-C or TnC , is a protein that resides in the troponin complex on actin thin filaments of striated muscle cardiac, fast-twitch skeletal, or slow-twitch skeletal and is responsible for binding calcium to activate muscle contraction. In slow skeletal muscle. Troponin C , also known as TN-C or TnC , is a protein that resides in the troponin complex on actin thin filaments of striated muscle cardiac, fast-twitch skeletal, or slow-twitch skeletal and is responsible for binding. Cardiac troponin C cTnC is a amino acid protein [8] organized into two domains: the regulatory N-terminal domain cNTnC, residues , the structural C-terminal domain cCTnC, residues , and a flexible linker connecting the two domains residues Strong actin-myosin interaction can further shift the thin filament into the "open" position.
Troponin c nedir
Troponin C is a protein which is part of the troponin complex. It contains four calcium-binding EF hands , although different isoforms may have fewer than four functional calcium-binding subdomains. It is a component of thin filaments , along with actin and tropomyosin. It contains an N lobe and a C lobe. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools.
Viha careers
New York Academic Press, Antithrombin III deficiency in maturity onset diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. Cardioprotective effect of gallic acid on cardiac troponin-T, cardiac marker enzymes, lipid peroxidation products and antioxidants in experimentally induced myocardial infarction in Wistar rats. Review of lipid-lowering clinical trials in relation to observational epidemiologic studies. Cella G, Russo R. Edited by Seegers. MN Kardiyoloji, 7 4 , - Levels of C reactive protein, fibrinogen and antithrombin III in coronary artery disease. Case reports in gastroenterology. Association of plasma fibrinogen levels with coronary artery disease smoking and inflammatory markers. Antithrombin in a clinical material.
.
MN Kardiyoloji 7, no. Current biomarkers for myocardial infarction. Lancet ; Inflammation, aspirin, and the risk of cardiovascular disease in apparently healthy men. Association of plasma fibrinogen levels with coronary artery disease smoking and inflammatory markers. Cardioprotective effect of gallic acid on cardiac troponin-T, cardiac marker enzymes, lipid peroxidation products and antioxidants in experimentally induced myocardial infarction in Wistar rats. Alterations of plasma antithrombin III levels in ischemic heart disease. Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis ; 19 2 : Antithrombin in a clinical material. The fact that the patient potential is so high causes a serious concentration in the hospitals. RESULTS: As a result we could say that levels of C-reactive protein and fibrinogen may indicate the presence of coronary heart disease and effected by smoking which is an important risk factor for the coronary heart disease, but levels of antithrombin III not differ between two groups and has no benefit in predicting the presence of coronary heart disease. Am J Clin Pathol ;

I think, that you are not right. I can defend the position.