Significance of nernst equation
The Nernst equation is one of the two central equations in electrochemistry, significance of nernst equation. In more precise words: The Nernst Equation tells us what the potential of an electrode is when the electrode is surrounded by a solution containing a redox-active species with an activity of its oxidized and reduced species. The complete Nernst Equation is:.
This article provides an explanation of Nernst equation formula and its applications. It also gives details about Nernst distribution law, cell potential, limitation of Nernst equation, etc. The Nernst equation formula establishes a relationship between the reaction quotient, electrochemical cell potential, temperature, and the standard cell potential. A German chemist, Walther Hermann Nernst, proposed the equation. Nonetheless, the cell potential fluctuates due to concentration, temperature, and pressure. According to the Nernst Equation, the reaction quotient affects the overall potential of an electrochemical cell. The consumption of reactants and the formation of products throughout the reaction cause the cell potential to decrease slowly.
Significance of nernst equation
In electrochemistry , the Nernst equation is a chemical thermodynamical relationship that permits the calculation of the reduction potential of a reaction half-cell or full cell reaction from the standard electrode potential , absolute temperature , the number of electrons involved in the redox reaction , and activities often approximated by concentrations of the chemical species undergoing reduction and oxidation respectively. It was named after Walther Nernst , a German physical chemist who formulated the equation. The reaction quotient Q r , also often called the ion activity product IAP , is the ratio between the chemical activities a of the reduced form the reductant , a Red and the oxidized form the oxidant , a Ox. The chemical activity of a dissolved species corresponds to its true thermodynamic concentration taking into account the electrical interactions between all ions present in solution at elevated concentrations. So, if the concentration C , also denoted here below with square brackets [ ] of all the dissolved species of interest are sufficiently low and that their activity coefficients are close to unity, their chemical activities can be approximated by their concentrations as commonly done when simplifying, or idealizing, a reaction for didactic purposes:. At chemical equilibrium , the ratio Q r of the activity of the reaction product a Red by the reagent activity a Ox is equal to the equilibrium constant K of the half-reaction:. The Nernst equation is frequently expressed in terms of base logarithms i. Therefore, its value is a conditional value, i. Because molar and molal concentrations were once referred as formal concentrations , it could explain the origin of the adjective formal in the expression formal potential. The formal potential is thus the reversible potential of an electrode at equilibrium immersed in a solution where reactants and products are at unit concentration. When the formal potential is measured under standard conditions i. In this case, as for the standard reduction potentials, the concentrations of dissolved species remain equal to one molar M or one molal m , and so are said to be one formal F.
If these concentrations or pressures have other values, the cell potential will change in a manner that can be predicted from the principles you already know. Not to be confused with Ernst equation. Clear All Compare Now.
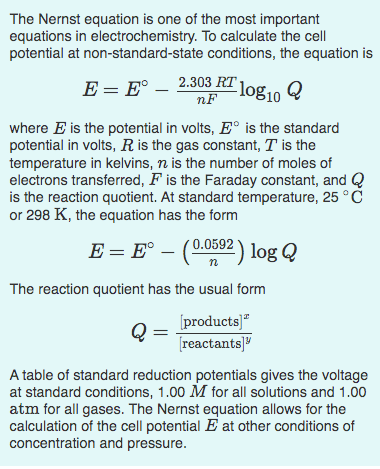
Make sure you thoroughly understand the following essential ideas. It is especially important that you know the precise meanings of all the highlighted terms in the context of this topic. The standard cell potentials we discussed in a previous section refer to cells in which all dissolved substances are at unit activity , which essentially means an "effective concentration" of 1 M. Similarly, any gases that take part in an electrode reaction are at an effective pressure known as the fugacity of 1 atm. If these concentrations or pressures have other values, the cell potential will change in a manner that can be predicted from the principles you already know. We begin with the equation derived previously which relates the standard free energy change for the complete conversion of products into reactants to the standard potential. This is the Nernst equation that relates the cell potential to the standard potential and to the activities of the electroactive species.
The Nernst equation describes how the equilibrium potential for an ion species also known as its Nernst potential is related to the concentrations of that ion species on either side of a membrane permeable to the ion. The membrane potential is the electric potential difference that exists across a membrane which is permeable to an ionic species and which separates solutions of the ionic species at differing concentrations. For example, cell membranes are often permeable to potassium, and the concentration of potassium inside the cell is greater than the concentration outside the cell. Negatively changed anions balance out the positive charge of potassium ions so that the charge inside and outside the cell is neutral, and the membrane is assumed to be impermeable to the anions Fig. Synonyms Equilibrium potential. Definition The Nernst equation describes how the equilibrium potential for an ion species also known as its Nernst potential is related to the concentrations of that ion species on either side of a membrane permeable to the ion. Detailed Description Physical Basis of the Equilibrium Potential The membrane potential is the electric potential difference that exists across a membrane which is permeable to an ionic species and which separates solutions of the ionic species at differing concentrations. Nernst Equation, Fig. A cell containing high, balanced concentrations of potassium ions and
Significance of nernst equation
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Cell potentials under nonstandard conditions. About About this video Transcript. Using the Nernst equation to calculate the cell potential when concentrations are not standard conditions. Created by Jay.
71 marta bus schedule
The Nernst equation has a physiological application when used to calculate the potential of an ion of charge z across a membrane. JEE Important Formulas. Share via. We have thus related the standard electrode potential and the equilibrium constant of a redox reaction. Out of these cookies, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. The pH of a solution is defined by the activity of the hydrogen ion rather than its concentration. The term formal concentration F is now largely ignored in the current literature and can be commonly assimilated to molar concentration M , or molality m in case of thermodynamic calculations. It is especially important that you know the precise meanings of all the highlighted terms in the context of this topic. Pourbaix diagram for iron. Nitrate ions must also pass between the cells to maintain electroneutrality. The Nernst equation allows the calculation of the extent of reaction between two redox systems and can be used, for example, to assess whether a particular reaction will go to completion or not. In electrochemistry , the Nernst equation is a chemical thermodynamical relationship that permits the calculation of the reduction potential of a reaction half-cell or full cell reaction from the standard electrode potential , absolute temperature , the number of electrons involved in the redox reaction , and activities often approximated by concentrations of the chemical species undergoing reduction and oxidation respectively. Allotment of Examination Centre. The number of states must vary linearly with the volume V of the system here an idealized system is considered for better understanding, so that activities are posited very close to the true concentrations. Highlight Differences.
Make sure you thoroughly understand the following essential ideas. It is especially important that you know the precise meanings of all the highlighted terms in the context of this topic. The standard cell potentials we discussed in a previous section refer to cells in which all dissolved substances are at unit activity , which essentially means an "effective concentration" of 1 M.
The equation Nernst can be described as:. When the membrane is permeable to more than one ion, as is inevitably the case, the resting potential can be determined from the Goldman equation, which is a solution of G-H-K influx equation under the constraints that total current density driven by electrochemical force is zero:. Get all the important information related to the JEE Exam including the process of application, important calendar dates, eligibility criteria, exam centers etc. Huizenga claimed their original calculation was affected by a misinterpretation of the Nernst equation. The complete Nernst Equation is:. Iron Stability diagrams are able to condense a great amount of information into a compact representation, and are widely employed in geochemistry and corrosion engineering. Quantities here are given per molecule, not per mole , and so Boltzmann constant k and the electron charge e are used instead of the gas constant R and Faraday's constant F. However, solid M concentration is taken as unity, and the above equation may be represented as:. This article provides an explanation of Nernst equation formula and its applications. Quote : A formal potential is defined as the potential of a half-cell, measured against the standard hydrogen electrode, when the total concentration of each oxidation state is one formal. Learn more topics related to Chemistry. This Pourbaix diagram has special relevance to electrochemical corrosion of metals. To determine approximate values of formal reduction potentials, neglecting in a first approach changes in activity coefficients due to ionic strength, the Nernst equation has to be applied taking care to first express the relationship as a function of pH. Note that equilibria between species separated by diagonal lines are dependent on both E and pH, while those separated by horizontal or vertical lines are affected by pH only or E only, respectively.

Has casually found today this forum and it was specially registered to participate in discussion.
I confirm. I agree with told all above. Let's discuss this question.