Raid disk calculator
Provides access to product training, sales and marketing resources, deal registration, and more to our VARs, Integrators, Resellers and other channel partners. Use the Lyve Cloud portal to configure and manage your object storage and services. Register, access, raid disk calculator, and manage Lyve Mobile services, subscriptions and projects.
Therefore it allows you to make an informed choice about the configuration of your next RAID array. It compares the following RAID levels:. If this is your first time configuring a RAID array, you might be unsure as to exactly what one is. Let's explain. In the early days of computing, mainframes used large and expensive hard disks , designed to be highly reliable. The thing is that when they fail everything fails eventually , all of the data would be lost unless you had a backup , and the expensive disk would need to be replaced. Soon cheaper hard drives came along, but they were not very reliable at all, with failures being all too common.
Raid disk calculator
RAID 0 splits data across drives, resulting in higher data throughput. The performance of this configuration is extremely high, but a loss of any drive in the array will result in data loss. This level is commonly referred to as striping. Compared to a single drive, this mode tends to be faster on reads, slower on writes. This is a good entry-level redundant configuration. However, since an entire drive is a duplicate, the cost per megabyte is high. This is commonly referred to as mirroring. RAID 5 stripes data at a block level across several drives, with parity equality distributed among the drives. The parity information allows recovery from the failure of any single drive. Write performance is rather quick, but because parity data must be skipped on each drive during reads, reads are slower. The low ratio of parity to data means low redundancy overhead.
All rights reserved.
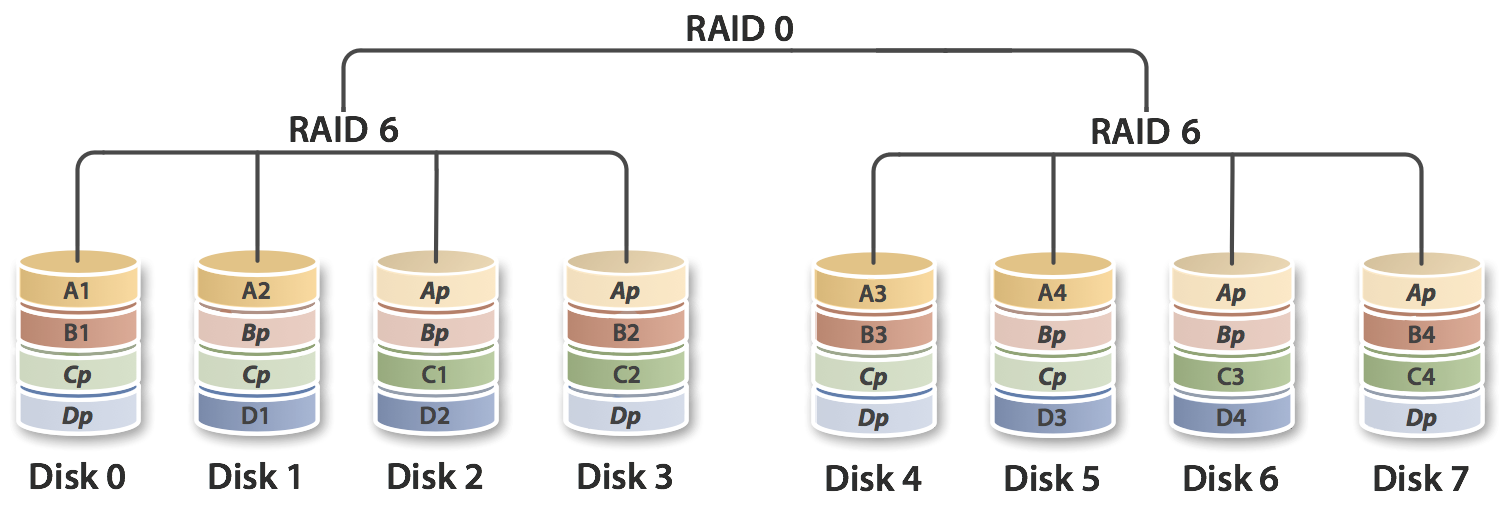
Explore RAID products. Note that this setup results in a nested RAID. This means you're creating at least two RAID sets that sit within another. This calculator assumes you are creating a typical setup with two subsets, though it would be possible to create more with enough disks. Each drive is individual of each other and mounts as such. With Spanning, separate disks are "merged" into a single "logical" volume, so your system only mounts one volume. This is similar in capacity to RAID 0, although the data is not split across the drives.
Paste the code to your website and the calculator will appear on that spot automatically! Find the page to which you want to add the calculator, go to edit mode, click 'Text', and paste the code to there. This RAID calculator computes array characteristics by calculating the disk capacity, number, and type of the array. File download time calculator helps you to calculate how long it takes to download a file based on the internet download speed. Enter a Color: rgb , , - Hex The KD calculator helps with calculating your kill to death ratio. This tool can be used in the calculator mode for performing algebraic operations using hex numbers add subtract multiply divide hexadecimals. Binary is a numerical number system that functions in a similar way to the decimal numbers system. This system is likely more familiar to most people. These include possible network addresses and usable host ranges.
Raid disk calculator
Mousing over a table cell loads the relevant data into the walkthrough section below. You can click table cells to freeze or unfreeze that cell for the walkthrough. Its on-disk structure is far more complex than that of a traditional RAID implementation. This complexity is driven by the wide array of data protection features ZFS offers.
Remote control app for insignia tv
Embed Share via. JBOD storage pools do not offer data redundancy. This process is called striping in RAID terminology. Don't worry, the helpful calculator messages will guide you. Select options. RAID 0 is all about performance. Please refer to individual device specifications to confirm RAID support, drive quantity allowed, and capacity support. RAID 6 is an upgrade from 5 : data is striped at a block level across several drives with double parity distributed among the drives. Just make sure there is a complete copy of the data somewhere else. RAID 6 uses two parity blocks per data stripe. Each written stripe is mirrored to one of the remaining disks in the array. The low ratio of parity to data means low redundancy overhead. That's much better than RAID 6, which had no increase. Capacity is calculated based on parameters selected in the tool.
It provides increased data reliability and performance by combining multiple drives into a single storage unit.
How much speed do I gain from raid 0? Let's explain. What is RAID 10? Therefore it allows you to make an informed choice about the configuration of your next RAID array. You can use the above images to better understand the intputs and outputs of the RAID calculator. For writing, we can write to half the number of disks at once, so that means a maximum write speed gain of 3x. If even one disk failed in a RAID 0 array, you would lose all your data. RAID 10 allows a total of 2 disk failures, one per mirrored set. However, since an entire drive is a duplicate, the cost per megabyte is high. In our online calculator you can select between four types of storage units: classic binary terabytes and gigabytes and SI terabytes and gigabytes. That's much better than RAID 6, which had no increase. The performance of both reads and writes approaches the sum of throughputs of every drive in the set and is a big benefit of this spanned configuration.

And where at you logic?
In it something is. Many thanks for the information, now I will not commit such error.
Excuse, the question is removed