Peptidase
Federal government websites often end in.
Protease and peptidase are two types of enzymes with a few significant differences between them. Papain-like peptidases: structure, function, and evolution. Navigation Menu. AAT Bioquest. Cart 0. Sign In. What are the differences between protease and peptidase?
Peptidase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Peptidases represent a large family of hydrolases present in all living organisms, which catalyze the degradation of peptide bonds in different biological processes [ 1 ]. Peptidases are involved in the degradation of off-function proteins in lysosomes, cytosol, plasma membranes, or in extracellular space; however, they may also have regulatory roles controlling biological processes crucial for cell homeostasis. In addition to being involved in normal protein turnover, their irregular function has been associated with a number of pathological processes, including cancer, neurodegenerative, immune and cardiovascular disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, atherosclerosis, periodontitis, pancreatitis, osteoporosis, diseases of the insufficient lysosomal degradation of proteins, and more. In view of the recent COVID pandemic, the function of peptidases in viral uptake and replication has been exposed, and several approaches to targeting viral or host peptidases are suggested as tools for the prevention and treatment of disease. In this Special Issue, Geiger et al. In the paper, they analyzed the impact of these compounds on viral replication and demonstrated that they act in a cell-line-specific way. They further investigated three compounds in human precision-cut lung slices and observed donor-dependent antiviral activity. The results show that not only host cell proteolytic profile but also the sensitivity of viral peptidases for inhibition determine the viral uptake and replication in certain cell types. In addition to viral infection and promotion, the peptidases are involved in several other parasites, such as the protozoan Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense , which causes Human African Trypanosomiasis, also known as sleeping sickness, leading to meningoencephalitis.
Ouwendijk for technical assistance. In addition, peptidase, infection of primary bronchiolar epithelial cells was blocked by the DPP4 antibodies in a dose-dependent manner Fig.
A protease also called a peptidase , proteinase , or proteolytic enzyme [1] is an enzyme that catalyzes proteolysis , breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids , and spurring the formation of new protein products. Proteases are involved in numerous biological pathways, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism breakdown of old proteins , [3] [4] and cell signaling. In the absence of functional accelerants, proteolysis would be very slow, taking hundreds of years. They have independently evolved multiple times , and different classes of protease can perform the same reaction by completely different catalytic mechanisms. Proteases can be classified into seven broad groups: [6]. Proteases were first grouped into 84 families according to their evolutionary relationship in , and classified under four catalytic types: serine , cysteine , aspartic , and metallo proteases.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Mitochondrial proteins are encoded by both nuclear and mitochondrial DNA. While some of the essential subunits of the oxidative phosphorylation OXPHOS complexes responsible for cellular ATP production are synthesized directly in the mitochondria, most mitochondrial proteins are first translated in the cytosol and then imported into the organelle using a sophisticated transport system. These proteins are directed mainly by targeting presequences at their N-termini. These presequences need to be cleaved to allow the proper folding and assembly of the pre-proteins into functional protein complexes. Their proper functioning is essential for mitochondrial homeostasis as the disruption of any of them is lethal in yeast and severely impacts the lifespan and survival in humans.
Peptidase
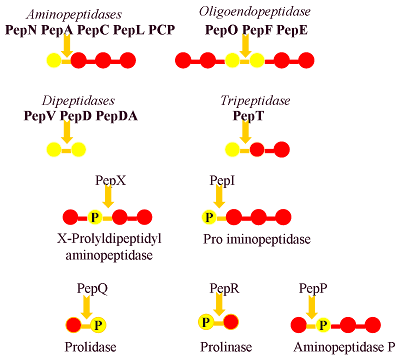
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Peptidases are enzymes capable of cleaving, and thereby often inactivating, small peptides. They are widely distributed on the surface of many different cell types, with the catalytic site exposed only at the external surface. In addition, some peptidases may have functions that are not based on their enzymatic activity. Peptidases are classified according to the location of the cleavage site in the putative substrate Table 1. Endopeptidases recognize specific amino acids in the middle of the peptide, whereas exopeptidases recognize one or two terminal amino acids. The closed circle can be any amino acid. It soon became apparent that NEP was similar to enkephalinase, originally discovered in the brain.
Adengo mısır ot ilacı fiyatı
Plant genomes encode hundreds of proteases, largely of unknown function. Published online Apr Their tropism is primarily determined by the ability of the spike S entry protein to bind to a cell surface receptor. Regul Pept ; 70 USA 88 , — Expression of APN may be used as a marker for myeloid leukaemia. Each family may contain many hundreds of related proteases e. Wu, K. Acknowledgements We gratefully acknowledge Mr T. However, no effect of glucocorticoids was observed in another study using the same bronchial epithelial cell line. Reduced serum DPP IV activity has also been described in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and in oral cancer patients. Cigarette smoke induces bronchoconstrictor hyperresponsiveness to substance P and inactivates airway neutral endopeptidase in the guinea pig. Dijkman, R. There is a Summary page for each family and clan, and these again have indexes. Thus, APN is expressed on renal proximal tubular epithelial cells, small intestinal epithelium, biliary canaliculae, synaptic membranes of the central nervous system, bone marrow stromal cells, fibroblasts, osteoclasts, placenta, and granulocytes [ 5 ].
Enjoy free shipping today! Peptidase is an enzyme that makes sure we absorb the most nutrients from the food we consume.
Although ECE may play a role in modulating biologically active peptides, it remains to be determined whether it is involved in the pathogenesis of asthma. Cell Stem Cell 6 , — Nucleic Acids Res 46 , DD Lambeir, A. Lancet ; By a complex cooperative action, proteases can catalyze cascade reactions, which result in rapid and efficient amplification of an organism's response to a physiological signal. The role of these peptidases in the metabolism of susceptible peptides has been little investigated, but it may be hypothesized that these enzymes are involved in the final hydrolysis of a variety of substrates, with or without initial cleavage by an endopeptidase. Exposure to ozone also results in increased responsiveness for SP, and this effect could not be enhanced by inhibition of NEP [ 41 ]. J Biol Chem ; DPP4 also has a major role in glucose metabolism by its degradation of incretins and has been further implicated in T-cell activation, chemotaxis modulation, cell adhesion, apoptosis and regulation of tumorigenicity 16 , PowerPoint slides PowerPoint slide for Fig. Gene structure The APN gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 15 q25—26 and exists of 20 exons [ 13 ]. The cathepsin L-like cysteine peptidase in the parasite is involved in the penetration of the blood—brain barrier, and its activity is modulated by the chagasin-family endogenous inhibitor of cysteine peptidases ICP. SARS-CoV replication and pathogenesis in an in vitro model of the human conducting airway epithelium.

0 thoughts on “Peptidase”