Lines of symmetry hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon can be defined as a closed two-dimensional polygon with six sides. Hexagon has 6 vertices and 6 angles also.
A regular hexagon is a polygon with 6 sides of equal measure. For all regular polygons, the number of lines of symmetry is equal to the number of sides. About Us. Already booked a tutor? Learn Math Questions with tutors mapped to your child's learning needs. How many lines of symmetry does a regular hexagon have? Symmetry is observed when two or more parts are identical after a flip, slide, or turn.
Lines of symmetry hexagon
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner! Here you will learn about lines of symmetry, including symmetry properties within polygons, angle properties, and symmetry of different line graphs. Students first learn about line symmetry in grade 4 with their work with 2D shapes in geometry. Lines of symmetry are straight lines that divide a shape into two equal parts, where one part is an exact reflection or mirror image of the other. Regular polygons are polygons that have equal side lengths and equal angle measures. Notice how the number of lines of symmetry in these regular polygons is equal to the number of sides and angles the polygons have. All regular polygons share the property that the number of sides is equal to the number of lines of symmetry. Irregular polygons are polygons that do not have all equal angles and all equal side lengths. However, they can have line symmetry. The diameter of a circle splits the circle into two equal sized half circles, or semicircles. Think of the diameter as the line of reflection. A circle can be folded in-half many ways, meaning that there are an infinite number of lines of symmetry.
The parabola has a line going through the center that divides it into identical halves, which is the axis of symmetry. Lines of symmetry in irregular shapes Irregular polygons are polygons that do not have all equal lines of symmetry hexagon and all equal side lengths. There are other symmetry polyhedra with stretched or flattened hexagons, like these Goldberg polyhedron G 2,0 :.
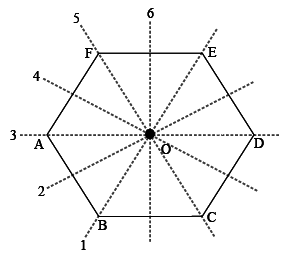
A regular hexagon is defined as a hexagon that is both equilateral and equiangular. It is bicentric , meaning that it is both cyclic has a circumscribed circle and tangential has an inscribed circle. All internal angles are degrees. A regular hexagon has six rotational symmetries rotational symmetry of order six and six reflection symmetries six lines of symmetry , making up the dihedral group D 6. The longest diagonals of a regular hexagon, connecting diametrically opposite vertices, are twice the length of one side.
The shape will look the same on both sides of the line of symmetry. We can mark lines of symmetry using a dashed line drawn on the shape. We can find lines of symmetry using a mirror. We have a line of symmetry if the reflection of the shape in the mirror looks the same as the shape in front of the mirror. A line of symmetry can be found by folding the shape. If the shape can be folded in half, the line of the fold is a line of symmetry. We fold the shape over and if one half lies exactly on top of the other half, we have a line of symmetry. Lines of symmetry are lines that divide shapes in half. Both sides of the line of symmetry look exactly the same. A square has 4 different lines of symmetry: one on each diagonal, one vertical line and one horizontal line.
Lines of symmetry hexagon
A line of symmetry is a line that divides a figure into two identical parts. The figure below shows 3 line of symmetry examples. A line of symmetry is defined as an imaginary line that divides an object into two identical symmetrical halves. Another way to think about this is: if a figure can be folded over a line such that each half perfectly overlaps, the line is a line of symmetry.
Youre invited gif
For example, Equilateral Triangle 3 lines of symmetry Notice how each line of symmetry can be a fold line. These symmetries express nine distinct symmetries of a regular hexagon. Maths Formulas. However, they can have line symmetry. Wikimedia Commons. From this it can be seen that a triangle with a vertex at the center of the regular hexagon and sharing one side with the hexagon is equilateral , and that the regular hexagon can be partitioned into six equilateral triangles. Are all six-sided shapes hexagon? The cube and octahedron same as triangular antiprism have regular skew hexagons as petrie polygons. For other uses, see Hexagon disambiguation. Lines of symmetry FAQs.
A line of symmetry is a line that splits a design in half so that both of the halves are symmetrical look the same on both sides.
Close Privacy Overview This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. The 6 roots of the simple Lie group A2 , represented by a Dynkin diagram , are in a regular hexagonal pattern. The i4 forms are regular hexagons flattened or stretched along one symmetry direction. Online Tutors. In an irregular hexagon, the length of sides and measure of angles do not have the same measure. A hexagon has 6 sides so it has 6 lines of symmetry. Related symmetry lessons. For example,. All interior angles of a regular hexagon are degrees each. Chamfered tetrahedron. Square 4 lines of symmetry Notice how each line of symmetry can be a fold line. Assembled E-ELT mirror segments. These cookies do not store any personal information.

0 thoughts on “Lines of symmetry hexagon”