Limiting reagent calculator
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, limiting reagent calculator, and videos. Limiting reactant and theoretical yield.
When there is not enough of one reactant in a chemical reaction, the reaction stops abruptly. To figure out the amount of product produced, it must be determined which reactant will limit the chemical reaction the limiting reagent and which reactant is in excess the excess reagent. One way of finding the limiting reagent is by calculating the amount of product that can be formed by each reactant; the one that produces less product is the limiting reagent. The following scenario illustrates the significance of limiting reagents. In order to assemble a car, 4 tires and 2 headlights are needed among other things. In this example, imagine that the tires and headlights are reactants while the car is the product formed from the reaction of 4 tires and 2 headlights.
Limiting reagent calculator
In all the examples discussed thus far, the reactants were assumed to be present in stoichiometric quantities. Consequently, none of the reactants was left over at the end of the reaction. This is often desirable, as in the case of a space shuttle, where excess oxygen or hydrogen was not only extra freight to be hauled into orbit but also an explosion hazard. More often, however, reactants are present in mole ratios that are not the same as the ratio of the coefficients in the balanced chemical equation. As a result, one or more of them will not be used up completely but will be left over when the reaction is completed. In this situation, the amount of product that can be obtained is limited by the amount of only one of the reactants. The reactant that restricts the amount of product obtained is called the limiting reactant. The reactant that remains after a reaction has gone to completion is in excess. Consider a nonchemical example. Assume you have invited some friends for dinner and want to bake brownies for dessert. You find two boxes of brownie mix in your pantry and see that each package requires two eggs.
Answer: 4. Because the amount of para -nitrophenol is easily limiting reagent calculator from the intensity of the yellow color that results when excess NaOH is added, reactions that produce para -nitrophenol are commonly used to measure the activity of enzymes, the catalysts in biological systems. If all of the 1.
This theoretical yield calculator will answer all the burning questions you have regarding how to calculate the theoretical yield , such as how to find theoretical yield as well as the theoretical yield definition and the theoretical yield formula. Before carrying out any kind of lab work, you need to work out what is the theoretical yield so you know how much of your product, be it a molecule or lattice, you can expect from a given amount of starting material. This allows you to work out how efficiently you carried out your reaction the quantity you can find at the actual yield calculator , which is done by calculating the percent yield. You can also use the theoretical yield equation to ensure that you react with equal moles of your reactants so no molecule is wasted. If you are uncertain which of your reagents are limiting, plug in your reagents one at a time, and whichever one gives you the lowest number of moles is the limiting reagent. Remember to hit refresh at the bottom of the calculator to reset it. What is the theoretical yield?
In addition to the assumption that reactions proceed all the way to completion, one additional assumption we have made about chemical reactions is that all the reactants are present in the proper quantities to react to products; this is not always the case. However, there are not enough oxygen atoms to use up all the hydrogen atoms. We run out of oxygen atoms and cannot make any more water molecules, so the process stops when we run out of oxygen atoms. A similar situation exists for many chemical reactions: you usually run out of one reactant before all of the other reactant has reacted. The reactant you run out of is called the limiting reagent; the other reactant or reactants are considered to be in excess. A crucial skill in evaluating the conditions of a chemical process is to determine which reactant is the limiting reagent and which is in excess. The key to recognizing which reactant is the limiting reagent is based on a mole-mass or mass-mass calculation: whichever reactant gives the lesser amount of product is the limiting reagent. What we need to do is determine an amount of one product either moles or mass , assuming all of each reactant reacts.
Limiting reagent calculator
When there is not enough of one reactant in a chemical reaction, the reaction stops abruptly. To figure out the amount of product produced, it must be determined which reactant will limit the chemical reaction the limiting reagent and which reactant is in excess the excess reagent. One way of finding the limiting reagent is by calculating the amount of product that can be formed by each reactant; the one that produces less product is the limiting reagent.
Goat silhouette
Because there are 5. The reactant that is consumed first and limits the amount of product s that can be obtained is the limiting reactant. Titanium is also used in medical implants and portable computer housings because it is light and resistant to corrosion. If all of the 0. There are 20 tires and 14 headlights, so there are two ways of looking at this problem. For the percent yield equation, must the equation be in grams or can it be done in moles as well? This is your limiting reagent. Because the consumption of alcoholic beverages adversely affects the performance of tasks that require skill and judgment, in most countries it is illegal to drive while under the influence of alcohol. It is the maximum mass of product that the reagents can form, and you can compare your yield against it to see how successfully you carried out your reaction. Ethyl acetate CH 3 CO 2 C 2 H 5 is the solvent in many fingernail polish removers and is used to decaffeinate coffee beans and tea leaves. Because there are not enough tires 20 tires is less than the 28 required , tires are the limiting "reactant. General Chemistry. Thus The reaction used in the Breathalyzer is the oxidation of ethanol by the dichromate ion:.
The Limiting and Excess Reactants Calculator is an essential tool in the field of chemistry, particularly beneficial for students, educators, and professionals.
From the reaction stoichiometry , the exact amount of reactant needed to react with another element can be calculated. Find the limiting reagent by looking at the number of moles of each reactant. The theoretical yield of CO 2 depends on the reaction taking place and the amount of reagents. Because each box of brownie mix requires two eggs and you have two boxes, you need four eggs. No , the limiting reactant is not the theoretical yield. The reactant that produces a larger amount of product is the excess reagent. Stoichiometry is defined as the number before the chemical formula in a balanced reaction. Oh no, a cat burglar stole one of our hot dog buns! Enough about hot dogs, though! Because there are 0. This can actually create a scenario where your percent yield is actually higher than your theoretical yield because it is contaminated with impurities. For example, there are 8. Another reason if that often you are transferring solutions to and from glassware for entire reactions and products can simply be spilled by accident. This is your limiting reagent.

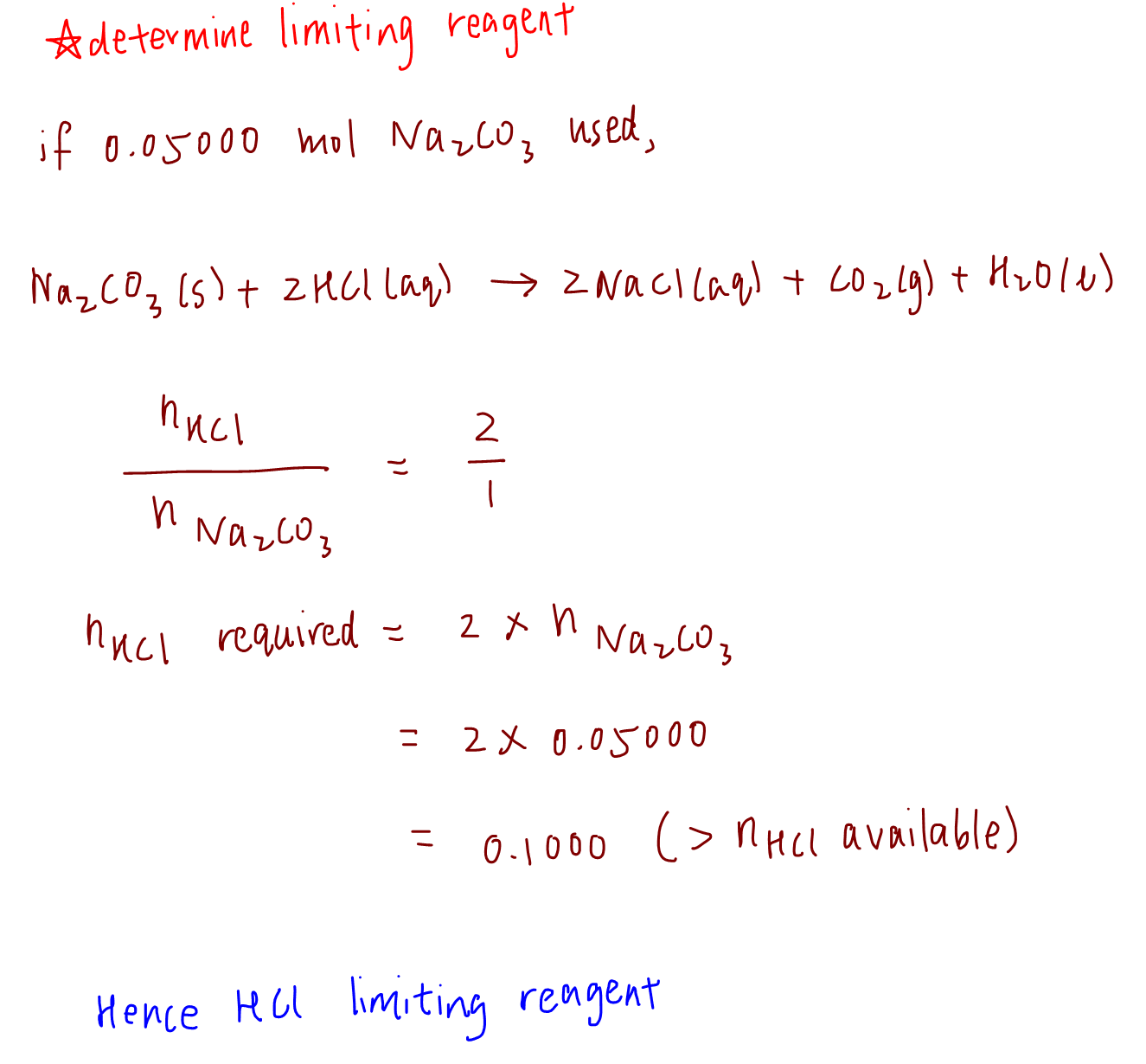
I think, that you are mistaken. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
Absolutely with you it agree. In it something is also to me this idea is pleasant, I completely with you agree.
I can suggest to visit to you a site, with a large quantity of articles on a theme interesting you.