Coagulase negative staphylococcus
There's more to see -- the rest of this topic is available only to subscribers. Renew my subscription. Not now - I'd like more time to decide.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. The definition of the heterogeneous group of coagulase-negative staphylococci CoNS is still based on diagnostic procedures that fulfill the clinical need to differentiate between Staphylococcus aureus and those staphylococci classified historically as being less or nonpathogenic.
Coagulase negative staphylococcus
Distinguishing true infection from contamination can be difficult; this is discussed separately. See "Infection due to coagulase-negative staphylococci: Epidemiology, microbiology, and pathogenesis", section on 'Distinguishing infection from contamination'. General issues related to antimicrobial resistance and treatment of CoNS infections will be reviewed here. Issues related to treatment of Staphylococcus lugdunensis are discussed separately. See "Staphylococcus lugdunensis". The epidemiology, microbiology, pathogenesis, and clinical manifestations of CoNS are discussed separately. See "Infection due to coagulase-negative staphylococci: Epidemiology, microbiology, and pathogenesis" and "Infection due to coagulase-negative staphylococci: Clinical manifestations". Why UpToDate? Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you. View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large. Infection due to coagulase-negative staphylococci: Treatment. Formulary drug information for this topic.
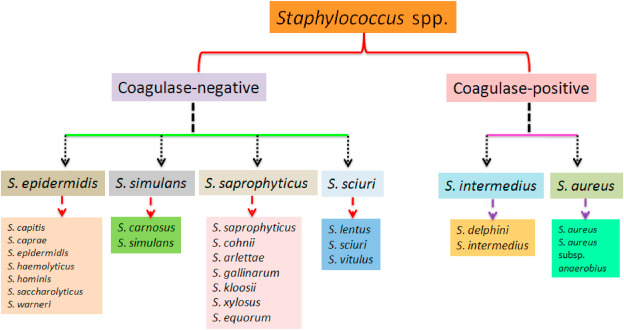
However, this does not necessarily translate into a reduced clinical significance. Figure 1 displays an overview of CoNS known thus far, their attributable clinical relevance, frequency, coagulase negative staphylococcus, and the associated infectious syndrome.
The epidemiology, microbiology, and pathogenesis of CoNS will be reviewed here. Issues related to clinical manifestations and treatment of CoNS infections are discussed separately. See "Infection due to coagulase-negative staphylococci: Clinical manifestations" and "Infection due to coagulase-negative staphylococci: Treatment". Patients at particular risk for CoNS infection include those with prosthetic devices eg, pacemakers, intravascular catheters, prosthetic heart valves, orthopedic implants and immunocompromised hosts. Species — There are currently 47 species recognized in the genus Staphylococcus [ 2 ]. Staphylococci are aerobic and facultatively anaerobic gram-positive cocci that produce catalase and have a tendency to form irregular clusters.
Doctors typically consider CoNS bacteria harmless when it remains outside the body. However, the bacteria can cause infections when present in large amounts, or when present in the bloodstream. Doctors often divide staph bacteria into coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative types. Coagulase is an enzyme needed to make blood clot. This enzyme is present in Staphylococcus aureus S.
Coagulase negative staphylococcus
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The definition of the heterogeneous group of coagulase-negative staphylococci CoNS is still based on diagnostic procedures that fulfill the clinical need to differentiate between Staphylococcus aureus and those staphylococci classified historically as being less or nonpathogenic. Due to patient- and procedure-related changes, CoNS now represent one of the major nosocomial pathogens, with S. They account substantially for foreign body-related infections and infections in preterm newborns. While S. In addition to CoNS found as food-associated saprophytes, many other CoNS species colonize the skin and mucous membranes of humans and animals and are less frequently involved in clinically manifested infections. This blurred gradation in terms of pathogenicity is reflected by species- and strain-specific virulence factors and the development of different host-defending strategies. Clearly, CoNS possess fewer virulence properties than S.
Alexandra daddario hot pics
Introduction Coagulase-negative staphylococci CoNS form a large group of Gram-positive cocci united by their mutual lack of the virulence factor coagulase [ 1 ]. As described above, significant interspecies differences in clinical relevance, pathogenicity, and even antimicrobial susceptibility exist [ 50 , 51 ]. Leveraging sequencing or genotyping data to characterize the pathogenic potential of CoNS constitutes another approach that has been applied recently [ 58 ]. Staphylococcus lugdunensis infections: high frequency of inguinal area carriage. Vancomycin, the oldest glycopeptide antibiotic, offers a broad Gram-positive coverage through inhibiting cell wall synthesis [ 74 ]. Duke University Medical Center. Pappas, et al. Beekmann S. Reporting and Interpreting the Isolation and Identification of CoNS The main question to be answered in the reporting of CoNS recovered from a clinical specimen is whether their detection reflects a true infection or only contamination or colonization. This was confirmed by a multitude of clinical studies that considered certain entities and patient groups. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Apart from this, additional criteria can be considered. Emerging Staphylococcus species as new pathogens in implant infections.
The following discussion will emphasize the issues specific to both native valve endocarditis and prosthetic valve endocarditis caused by CoNS.
One might assume that difficult-to-detect CoNS species may be underdiagnosed, at least in infections of immunocompromised patients 96 , Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. Colonization of different parts of the skin and mucous membranes of the host is the key source of endogenous infections by CoNS. Email address. Antibiotic Ointment May Reduce Staph Infections for Newborn Infants Infants, especially those in intensive care units, are vulnerable to staph infections. Irrespective of the species, the SCV phenotype is characterized by drastic changes in cellular metabolism, reflected by a reduced growth rate and substantial quantitative and qualitative modifications of the transcriptome, metabolome, and proteome , — Sufficient controlled clinical study data on the efficacy of antimicrobial agents for S. Infection due to coagulase-negative staphylococci: Epidemiology, microbiology, and pathogenesis. Contact Support If you need further assistance, please contact Support. A case of bone marrow infection by Staphylococcus saccharolyticus. Subsequently, in , Shaw et al. Staphylococcus edaphicus sp. The skin microbiome. Infection types.

In my opinion it is very interesting theme. I suggest all to take part in discussion more actively.