What is hydatid cyst
Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease caused by infection with tiny tapeworms of the genus Echinocococcus.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Hydatid cyst is a parasitic infection that primarily affects the liver but which can be found anywhere in the body. This case involves spontaneous dissemination of hydatid cyst disease, a rare occurrence in the absence of any intervention or trauma. A year-old male patient complained of abdominal pain of 10 years' duration. He was apparently asymptomatic until 10 years ago, at which point he developed abdominal pain and vomiting. He was hospitalized at that time and confirmed to have hydatid cyst in the liver; he was treated with oral Albendazole for six months.
What is hydatid cyst
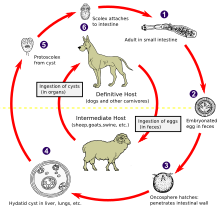
Hydatid disease is caused by infection with a small tapeworm parasite called Echinococcus granulosus. In Australia, most infections are passed between sheep and dogs, although other animals including goats, horses, kangaroos, dingoes and foxes may be involved. The hydatid parasite is carried by dogs in their bowel, without any symptoms of infection. Sheep become infected while grazing in areas contaminated with dog faeces. Dogs become infected by eating the uncooked organs of infected sheep. People become infected by ingesting eating eggs of the parasite, usually when there is hand-to-mouth transfer of eggs in dog faeces. This can occur when handling dogs or objects including food and water soiled with dog faeces. Person-to-person or sheep-to-person transmission does not occur. The parasites form slowly enlarging fluid-filled cysts which may become very large. Cysts occur most commonly in the liver or lungs, but may occur in any organ, including the heart, brain and bones. Cysts often do not cause symptoms unless they become very large or break. Hydatid cysts are diagnosed by x-ray, ultrasound, CT or MRI scans and may sometimes be confirmed by a blood test. Occasionally, microscopic examination of the cyst fluid is required.
Figure 3.
Category: Infections and parasites. Topic: Parasites. Hydatid disease also known as hydatidosis or echinococcosis is a potentially serious, sometimes fatal, condition caused by cysts containing the larval stages of the Echinococcus granulosus E. Adult E. People become infected by ingesting swallowing the eggs. This can occur via hand-to-mouth transfer after handling dogs or objects contaminated with the eggs, or from consuming contaminated food or water.
Ever since Hippocrates described Hydatid disease, physicians all over the world have encountered it in various organs. Hydatid disease is also referred to as echinococcosis or echinococcal disease. It results from an infection due to a tapeworm of genus Echinococcus. Human echinococcosis is a zoonotic infection i. This microscopic tapeworm is found in foxes, dogs and cats. Human cases are rare. The disease may produce cysts in the liver, lungs, brain and other organs liver being the most common followed by lung. It is common all over India, especially in Kashmir. Any race can be affected and it is common in both men and women.
What is hydatid cyst
Most are harmless, but they should be removed when possible because they occasionally may change into malignant growths, become infected, or obstruct a gland. There are four main types of cysts: retention cysts , exudation cysts , embryonic cysts , and parasitic cysts. Baker cyst a swelling on the back of the knee, due to escape of synovial fluid that has become enclosed in a sac of membrane. Bartholin cyst a mucus-filled cyst of a Bartholin gland, usually developing as a consequence of an obstruction of the duct by trauma, infection, epithelial hyperplasia, or congenital atresia or narrowing. See also cystic disease of breast. An example is a branchial cyst. Called also enterocyst and enterocystoma.
Video de zodofilia
The case described here is in the transitional stage. You will lie on a bed that will move in and out of the hole in the middle of the ring. Open toolbar Accessibility Tools. Tuzun M, Hekimoglu B. In this phase, HD cannot spread, and in the absence of mass effect or other complications, there is no need for surgery. Hence we attribute the spread of disease to possible spontaneous intraperitoneal seeding. Infectious period time during which an infected person can infect others There is no direct person-to-person transmission. Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease caused by infection with tiny tapeworms of the genus Echinocococcus. The infected liver: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Daughter vesicles brood capsules , small spheres that contain the protoscolices, are formed from the germinal layer. There is disseminated echinococcus disease in the peritondal cavity. Magnetic resonance imaging MRI reveals a homogeneous hypointense lesion on T1-weighted images and a homogeneous hyperintense lesion on T2-weighted images. Another mode of spread other organs is cyst rupture into neighboring organs or peritoneum.
Or you're spending too much time in the bathroom. Perhaps heartburn seems like a constant companion. No matter the issue, this is the place to find information about digestive health.
Talk to your doctor about which option will be best for you. Before you leave the hospital make sure you talk to your doctors about pain relief and what you should and should not be doing. The scanner looks like a ring doughnut. But this just means treatment with medicines. A CT scan takes about half an hour. Diagnosis of hydatid disease Hydatid cysts are diagnosed by x-ray, ultrasound, CT or MRI scans and may sometimes be confirmed by a blood test. Computed tomography CT of the abdomen confirmed the ultrasound findings. So you will probably have tests to rule out a lot of other things before you can be diagnosed. An MRI scan uses magnets and radio waves to build up a picture of the inside of your body. Other complications include internal and external rupture of HCs, secondary site involvement due to invasion of various anatomic barriers e. The CT density of the mother cyst is higher than the daughter cysts Figure 3. Note daughter cysts in two HCs. The movement of fluid in this circulatory pathway is produced by the movement of the diaphragm and peristalsis of bowel. The diagnosis is relatively easy in endemic regions and in solitary HC. Magnetic resonance imaging MRI reveals a homogeneous hypointense lesion on T1-weighted images and a homogeneous hyperintense lesion on T2-weighted images.

I am final, I am sorry, but, in my opinion, this theme is not so actual.
While very well.