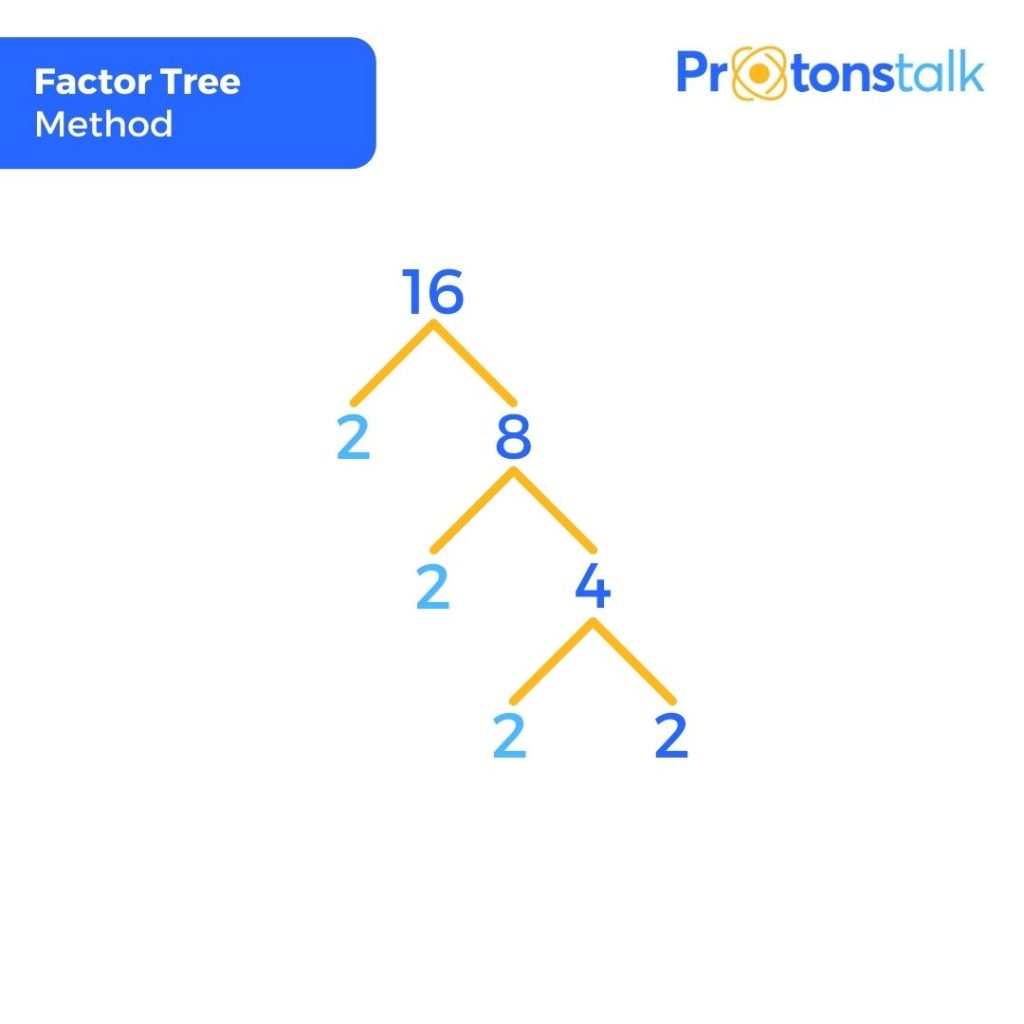
What are all of the factors of 16
Szukanie zaawansowane. Pokaż uproszczony widok rekordu Zobacz statystyki.
The deciduous dentition is made up of primary teeth in humans. These teeth are shed and then replaced by permanent successors. This process of shedding the deciduous teeth and replacement by the permanent teeth is called exfoliation. Exfoliation begins 2 or 3 years after the deciduous root is completely formed. At this time the root begins to resorb at its apical end, and resorption continues in the direction of the crown until the entire root is resorbed and the tooth finally falls out. The primary or deciduous dentition consists of 20 teeth, each quadrant containing two incisors, one canine, and two molars Fig. The first deciduous teeth to erupt, about 8 months after birth, are the mandibular central incisors.
What are all of the factors of 16
.
The cervical convexity buccocervical ridge on the buccal surface does not continue onto the distal surface.
.
The Factoring Calculator finds the factors and factor pairs of a positive or negative number. Enter an integer number to find its factors. For positive integers the calculator will only present the positive factors because that is the normally accepted answer. For example, you get 2 and 3 as a factor pair of 6. If you also need negative factors you will need to duplicate the answer yourself and repeat all of the factors as negatives such as -2 and -3 as another factor pair of 6. On the other hand this calculator will give you negative factors for negative integers.
What are all of the factors of 16
Also, if we divide 16 by one of its factors, we will get another factor of Let us brush up a little. Any number can be a factor of a number if it divides the number without leaving any remainder behind.
L&s nude
As the bone continues to grow, the deciduous teeth develop spaces between them called primate spaces. Instead of two lingual fossae, one is present. The ordinal numbers. Primitive roots of unity and cyclotomic polynomials. Permanent teeth have more yellow, grey, or brown tones. They have a whiter color with a bluish cast. Grooves originating at the distal pit are the distofacial triangular, the distolingual, and the distal marginal grooves. Finite sets. Formalized Mathematics, 12 1 , The deciduous anteriors are smaller than their permanent successors in both their crown and root proportions. It is very narrow and is also conical in shape. These teeth are shed and then replaced by permanent successors.
The factors of 16 are the numbers that produce the result as 16 when two numbers are multiplied together.
The buccocervical ridges on the deciduous molars are much more pronounced, especially on first molars. Frattini subgroup. The deciduous teeth are usually lighter in color than the permanent teeth. The mesial, mesiofacial triangular, mesial marginal, and mesiolingual triangular grooves originate in the mesial pit. Labiolingually the lateral incisors are also wider. Mesial and distal aspects From the proximal aspects Fig. These roots also flare apically to allow room for the permanent teeth to develop between them Fig. Subgroup and cosets of subgroups. The crown appears to be narrower distally than mesially. Mandibular Central Incisors Fig. The buccolingual measurement of a deciduous maxillary first molar at the cervical third is greater than the same measurement at the occlusal third.

I consider, that you commit an error. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.