Velocity is equal to
The terms velocity and speed give us an idea of how fast or slow an object is moving, velocity is equal to. Quite often, we come across situations where we need to identify which of the two or more objects is moving faster. One can easily tell the faster of velocity is equal to two if they are moving in the same direction on the same road. However, if their direction of motion is in the opposite direction, then it is difficult to determine the fastest.
In distance-speed relations, we will learn about the Distance formula. We will also see velocity formula. The problems that are from this section base themselves on the concepts and definitions of terms that measure distance , speed and time. Here we will see many examples from this section, we will introduce the important concepts like the Distance formula, the velocity formula etc. We will also solve questions based on the Distance formula and the other relevant formulae. Let us start! First, we will collect all the formulae that we shall use to solve the examples ahead.
Velocity is equal to
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Displacement, velocity, and time. About About this video Transcript. Although speed and velocity are often words used interchangeably, in physics, they are distinct concepts. Created by Sal Khan. Want to join the conversation? Log in. Sort by: Top Voted.
I'm confused, velocity is equal to, because in this article, it says average speed is written as Vavg V with a lowercase "avg"but in Sal's video, he writes average velocity as the same thing. A car travels along a straight road to the east for meters in 5 seconds, then goes west for 60 meters in 1 second. We also know that it took him three seconds to cover the gap between his starting and ending points.
Before understanding average speed and average velocity , we must first understand the distinction between distance and displacement. The scalar quantity "distance" represents how much ground an object has covered. The shortest distance between two points is represented by displacement, which is a vector quantity. If a particle moves in a circle, for example, the distance travelled after one revolution equals the circumference of the circle, but the displacement is zero. Let's have a look at the definitions of speed and velocity. To know about average speed and average velocity, first, we must know of some terms and their meanings.
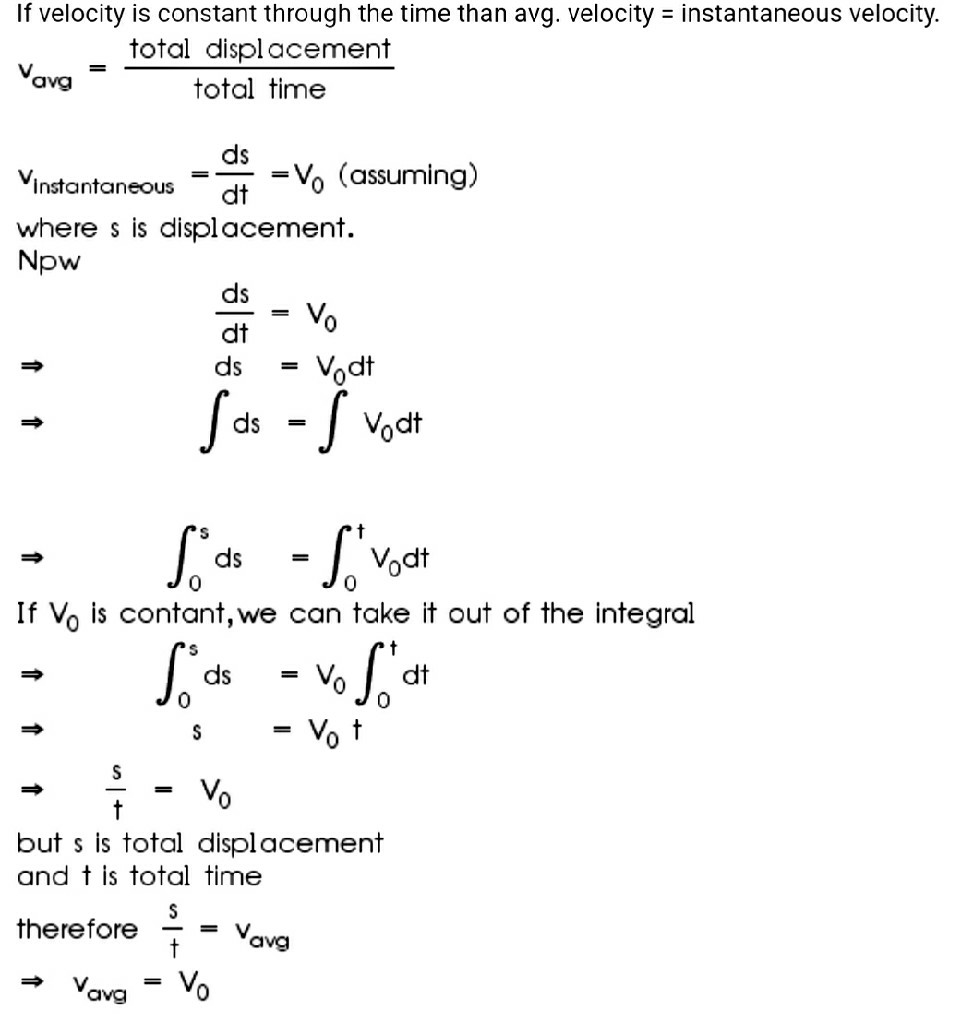
Velocity is the speed in combination with the direction of motion of an object. Velocity is a fundamental concept in kinematics , the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies. Velocity is a physical vector quantity : both magnitude and direction are needed to define it. For example, "5 metres per second" is a scalar, whereas "5 metres per second east" is a vector. If there is a change in speed, direction or both, then the object is said to be undergoing an acceleration. The instantaneous velocity of an object is the limit average velocity as the time interval approaches zero. From this derivative equation, in the one-dimensional case it can be seen that the area under a velocity vs. In calculus terms, the integral of the velocity function v t is the displacement function s t. In the figure, this corresponds to the yellow area under the curve. Although the concept of an instantaneous velocity might at first seem counter-intuitive, it may be thought of as the velocity that the object would continue to travel at if it stopped accelerating at that moment.
Velocity is equal to
Imagine something moving back and forth very fast: it has a high speed, but a low or zero velocity. A km is m, and there are seconds in an hour, so we can convert like this see Unit Conversion Method to learn more :. The examples so far calculate average speed : how far something travels over a period of time. But speed can change as time goes by. A car can go faster and slower, maybe even stop at lights. So there is also instantaneous speed : the speed at an instant in time. We can try to measure it by using a very short span of time the shorter the better.
El tiempo en vera por horas
These are essentially saying the same thing. Hagay Onn. What is the total distance that Khan covers? Im struggling to find the Avg. First the iguana walks 12 meters to the right in a time of 20 seconds. Note that the velocity for the return trip is negative. The smaller the time intervals considered in a motion, the more detailed the information. For instance, a car traveling on a circular track that begins and ends at the same position. Mobile Newsletter chat close. Hope you have understood the velocity meaning, unit of velocity, constant velocity and the difference between speed and velocity in brief. Speed is a prime indicator of the rapidity of the object. However, velocity is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Please leave a comment below if you have any questions. So over 1 hour. Time Taken — The time taken by the object to move the given distance.
Velocity in physics is defined as a vector measurement of the direction and rate of the motion. In simple words, the term velocity gives us an idea of the speed at which an object is moving in a particular direction.
Another way of visualizing the motion of an object is to use a graph. Stop thumbtack 2 wherever you want in the circle you're creating, and stick it in. Just as we need to distinguish between instantaneous velocity and average velocity, we also need to distinguish between instantaneous speed and average speed. Distance is the scalar. Login To View Results. Average speed is a rate that is a quantity divided by the time taken to get that quantity. This means the average velocity is also equal to zero. In a way, you are asking the question "what is the point in vectors? Video transcript Now that we know a little bit about vectors and scalars, let's try to apply what we know about them for some pretty common problems you'd, one, see in a physics class, but they're also common problems you'd see in everyday life, because you're trying to figure out how far you've gone, or how fast you're going, or how long it might take you to get some place. Covering Ground What, pray tell, is "displacement? State And Prove Bernoulli's Theorem. Posted 5 years ago.

Excuse, that I can not participate now in discussion - there is no free time. But I will be released - I will necessarily write that I think on this question.
Between us speaking, in my opinion, it is obvious. I would not wish to develop this theme.