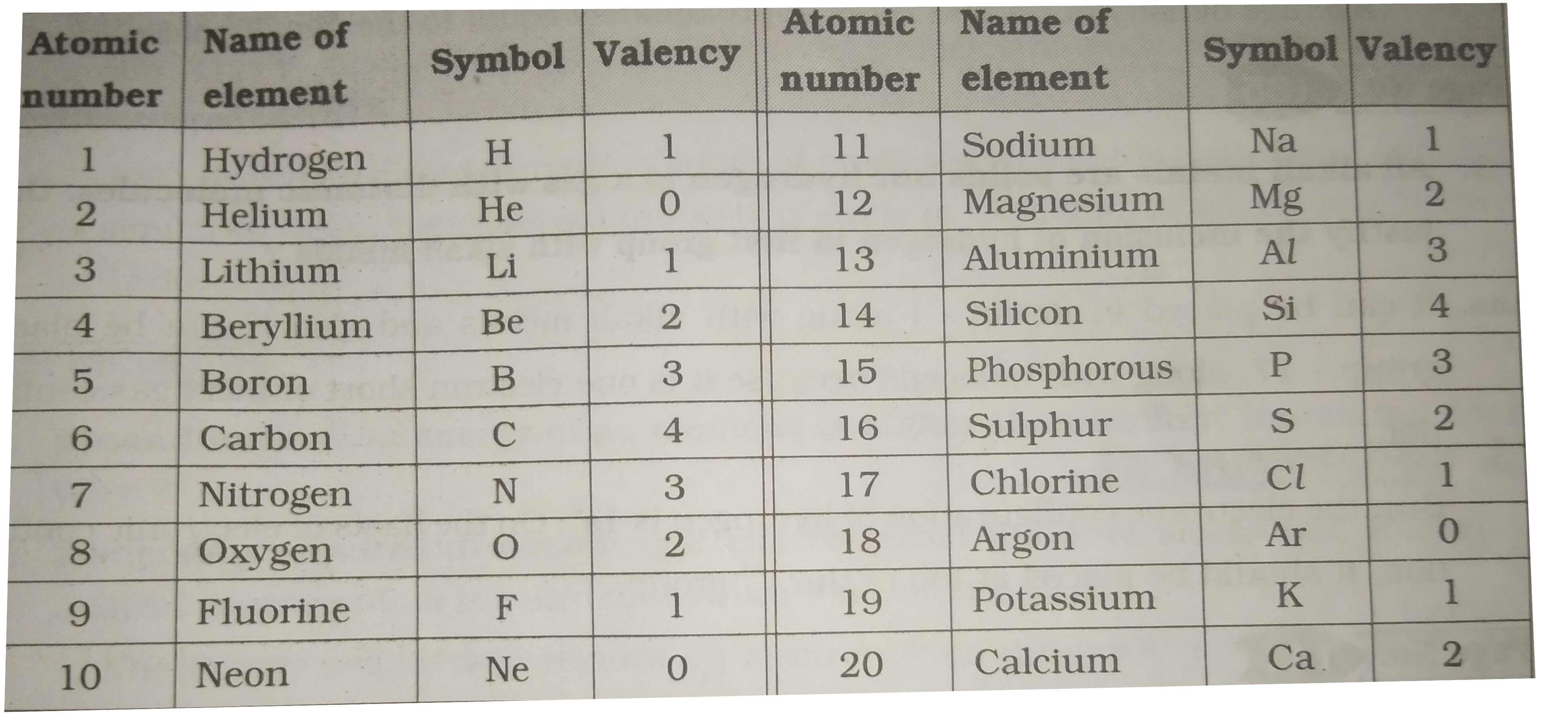
Valency of atoms 1 to 20
Valency can be defined as combining the power of an element or radical. The valency chart consists of the list of valencies of the element.
You may assume that the valences of the elements—the number of electrons with which an atom will bond or form—are those that can be derived by looking at the groups columns of the periodic table. While these are the most common valences, the real behavior of electrons is less simple. Here is a table of element valences. Remember that an element's electron cloud will become more stable by filling, emptying, or half-filling the shell. Also, shells don't stack neatly one on top of another, so don't always assume an element's valence is determined by the number of electrons in its outer shell. Use limited data to select advertising.
Valency of atoms 1 to 20
The valency of an element is a measure of its combining capacity and can be defined as. Oxidation State and valency are one of the most fundamental properties of elements and can be studied with the help of electron configurations. Electrons that are found in the outermost shell are generally known as valence electrons and the number of valence electrons determines the valency or valence of an atom. The general oxidation state of the elements of the periodic table is illustrated in the chart provided below. The valency of the first 30 elements of the periodic table is given below. While moving left to right across a period, the number of valence electrons of elements increases and varies between 1 to 8. But the valency of elements, when combined with H or O first, increases from 1 to 4 and then it reduces to zero. Consider two compounds containing oxygen Na 2 O and F 2 O. In F 2 O, the electronegativity of F is more than oxygen. Hence, each of F atom will attract one electron from oxygen i. Whereas, in the case of Na 2 O, oxygen is highly electronegative than sodium atom. The oxidation state of the element represents the charge possessed by an atom due to the loss or gain of electrons due to the electronegativity difference between the combining atoms in the molecule. As we move down in a group the number of valence electrons does not change. Hence, all the elements of a particular group group have the same valency.
Like Article Like. Therefore, a nitrogen atom needs to gain 3 electrons in its outermost orbit to complete octet. According to the Octet rule, the outermost orbit of an atom will have a maximum of 8 electrons to become stable.
The characteristics of an element that indicate how many more atoms can join one of its atoms in a covalent bond are known as valence, or valency, in chemistry. The term, which was first used in , is used to represent both the broad potential of combining an element and the numerical value of the power of combining. Since the majority of bonds are created by the interchange of valence electrons, valence is defined as the number of electrons. The valence electrons determine what valences are and what their meaning is in chemistry. The valency of an atom is equal to the number of valence electrons that this atom can gain or lose during chemical reactions. For example, the amount of hydrogen atoms, chlorine atoms, or double the number of oxygen atoms that one atom of an element may combine with is referred to as its valency.
You may assume that the valences of the elements—the number of electrons with which an atom will bond or form—are those that can be derived by looking at the groups columns of the periodic table. While these are the most common valences, the real behavior of electrons is less simple. Here is a table of element valences. Remember that an element's electron cloud will become more stable by filling, emptying, or half-filling the shell. Also, shells don't stack neatly one on top of another, so don't always assume an element's valence is determined by the number of electrons in its outer shell. Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising.
Valency of atoms 1 to 20
In chemistry , the valence US spelling or valency British spelling of an atom is a measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules. Valence is generally understood to be the number of chemical bonds that each atom of a given chemical element typically forms. Double bonds are considered to be two bonds, triple bonds to be three, quadruple bonds to be four, quintuple bonds to be five and sextuple bonds to be six.
Volunteer antonym
Stability is also determined by the ability of atoms to gain electrons. This capacity of an atom will also determine the valency of an atom. Skip to content. This article is being improved by another user right now. They have 2 electrons in their outermost shell. Easy Normal Medium Hard Expert. The valency or valency chart is helpful in order to determine how many atoms of an element will combine with another element to form any chemical formula. These choices will be signaled to our partners and will not affect browsing data. The valency chart consists of the list of valencies of the element. So, valency cannot be related to charge. Remember that an element's electron cloud will become more stable by filling, emptying, or half-filling the shell.
We all know that the chemical formula for water is H 2 O.
Define Valency. Similarly, all the elements present in column 17 have valency -1 such as fluorine, chlorine, and so on. Thus, it is the number of valence electron an atom has to gain or lose from its outermost orbit. Electronegativity and Chemical Bonding. Its atomic number is Campus Experiences. This is how the valency is determined. Knight Hunter February 16, at pm. Join courses with the best schedule and enjoy fun and interactive classes. Their capacity for merging is reduced to almost nothing. Article Tags :.

It is remarkable, this amusing opinion