Trace mucosal thickening
Sinusitis is inflammation of the lining mucosa of the sinuses.
Thickening of mucosa within the paranasal sinuses is frequently detected on diagnostic imaging of the head, even in patients with no apparent rhinologic disease. Previous studies have suggested that mucosal thickening is poorly correlated with sinonasal inflammation, in patients without chronic rhinosinusitis CRS 5 - 8. However, as the paranasal sinuses are only endoscopically accessible in the post-surgical setting, these studies have been unable to correlate imaging with direct endoscopic assessment of the sinuses and have relied upon patient reported symptoms to assess inflammation. In this context, patients who have received surgery for paranasal sinus or skull base tumors provide a convenient population, without CRS, in whom inflammation can be verified endoscopically. This study aimed to determine the diagnostic performance of sinus MRI mucosal thickening, in patients without CRS, using validated endoscopic examination and patient reported symptoms.
Trace mucosal thickening
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Aim: To characterise and measure the Schneiderian membranes of individuals with periodontal diseases in China and to analyse the factors impacting maxillary sinus mucosal thickness using cone-beam computed tomography CBCT. Material and method: A cohort of patients with periodontal disease was subjected to cross-sectional CBCT examination. Various parameters, including age, sex, alveolar bone loss, furcation lesions and vertical infrabony pockets, were analysed as correlates of mucosal thickening MT. Results: MT was detected in Conclusions: Relative to the case in patients with periodontitis and normal mucosa, the probability of MT increased dramatically as alveolar bone loss worsened. Periodontal pathologies i. Periodontal disease is the most prevalent infectious disease in humans and it can considerably impact systemic health 1. The most destructive form of periodontal disease is periodontitis, which has a high prevalence in China. According to a targeted epidemiological investigation, only Periodontitis is a chronic oral infection generated and sustained by a polymicrobial biofilm in the mouth. The resultant immunoinflammatory response alters both the mucosa and the supportive connective tissue elements, stimulating net resorption of alveolar bone 3. Maxillary sinusitis, which can arise from bacterial, fungal or viral infections 7 , is often attributed to periodontal disease 8.
Sinus pressure is a common ailment that can significantly affect your quality of life. What causes chronic sinusitis? Another form of chronic sinusitis without nasal polyps is mucoceles.
It can be frustrating to take antibiotic medications every time you develop a sinus infection. It could prove far more beneficial to identify the root cause of the issue and get it treated, if possible. Sinus specialists, like myself, often recommend a sinus CT scan to identify the problem to help determine the appropriate treatment. CT scans are minimally-invasive and can accurately help doctors diagnose nose and sinus issues. Keep reading to know what we look for in a CT scan of the sinuses. The nasal septum has cartilage and bone that divide your nose's nasal cavity in two.
A health care provider might ask about symptoms and do an exam. The exam might include feeling for tenderness in the nose and face and looking inside the nose. Antibiotics are sometimes needed to treat sinusitis caused by bacteria. A possible bacterial infection might need to be treated with an antibiotic and sometimes with other medicines. For sinusitis caused or made worse by allergies, allergy shots might help. This is known as immunotherapy. The left picture shows the frontal A and maxillary B sinuses.
Trace mucosal thickening
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The maxillary sinus is of paramount importance for otolaryngologists, rhinologists, oral and maxillofacial surgeons, head and neck and dental and maxillofacial radiologists. A comprehensive review article concerning the physiology, development and imaging anatomy was undertaken. Relevant literature pertaining to the physiology of the sinonasal cavity, development of the paranasal sinuses and imaging anatomy of the maxilla and maxillary sinus from to was reviewed. Emphasis was placed on literature from the last 5 years. Extensive recent research using imaging has provided new insights into the development of the maxillary sinus, the other paranasal sinuses and the midface. The fundamental physiological concept of mucociliary clearance and its role in sinus health is emphasized. The paranasal sinuses are an integral part of a common mucosal organ formed by the upper and lower airway. An in-depth understanding of the soft-tissue and neurovascular relationships of the maxillary sinus to the deep fascial spaces and branches of the trigeminal nerve and external carotid artery respectively is required to evaluate and report imaging involving the maxillary sinus.
Pisos alquiler valdemoro
Clin Oral Implants Res. Ludlow JB, Ivanovic M. Keep your head elevated. Call Us. While rare, this is likely to be identified and repaired in the operating room at the time of the primary surgery. Thomas Higgins sheds light on the common confusion between sinus headaches and sinusitis and how he guides patients through the often-misunderstood journey of pinpointing the true source of their pain and navigating towards effective relief. This approach provides better diagnostic and quantitative information about periodontitis than does conventional radiography, particularly in terms of periodontal bone levels, furcation lesions and vertical infrabony pockets. They often become too enlarged and their size is reduced during nasal surgeries, and this often improves symptoms such as nasal congestion and obstruction. Mucous retention cysts are fluid-filled benign cysts, often found in the maxillary sinus. This impairment is often temporary.
Federal government websites often end in.
Computer-assisted surgical navigation is a relatively new tool used in select cases. Clin Imaging. Each post-surgical cavity was considered to consist of up to 6 walls left, right, superior, inferior, anterior and posterior , and the thickness of the mucosa was measured perpendicularly from the orientation of the corresponding wall to the point of maximal mucosal thickness Figure 1. However, previous studies have relied upon patient reported symptoms or limited anterior rhinoscopy to diagnose inflammation, without endoscopic confirmation 6 - 8 , Infection : The most common reason to undergo sinus surgery is a chronic sinus infection that does not resolve with medications. A CT scan CAT scan or X-ray are not usually obtained to make the diagnosis of sinusitis, unless there is concern for a potential complication. Find a Provider. The PD mm was defined as the distance from the gingival margin to the base of the periodontal pocket, and CAL mm was defined as the distance from the cemento—enamel junction CEJ to the base of the pocket. Surgery may be needed if an infected or inflamed area does not clear with antibiotic therapy or other medications, the symptoms return when antibiotics are stopped, or for other reasons. Confirmation and surprises in the association of tobacco use with sinusitis. Some of the more common or more important risks relative to nasal and sinus surgery are discussed below.

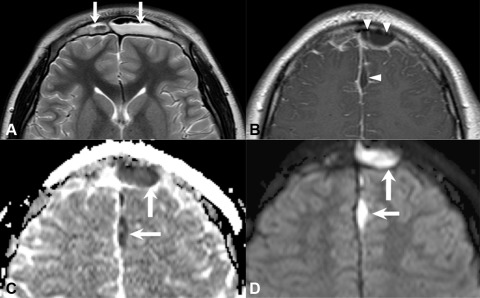
0 thoughts on “Trace mucosal thickening”