Ti plasmid is obtained from
Ti-plasmid, short for tumour-inducing plasmid, is an extrachromosomal molecule of DNA found commonly in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It is also found in other species of Agrobacterium such as A. Agrobacterium is a gram negative bacteria that belongs to the class Alphaproteobacteria. It is one of the pathogenic species belonging to this class.
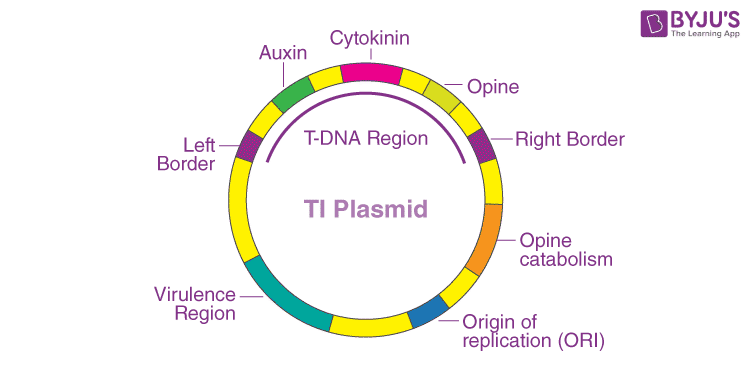
A tumour inducing Ti plasmid is a plasmid found in pathogenic species of Agrobacterium , including A. Evolutionarily, the Ti plasmid is part of a family of plasmids carried by many species of Alphaproteobacteria. Members of this plasmid family are defined by the presence of a conserved DNA region known as the repABC gene cassette, which mediates the replication of the plasmid, the partitioning of the plasmid into daughter cells during cell division as well as the maintenance of the plasmid at low copy numbers in a cell. The presence of this Ti plasmid is essential for the bacteria to cause crown gall disease in plants. These regions have features that allow the delivery of T-DNA into host plant cells, and can modify the host plant cell to cause the synthesis of molecules like plant hormones e.
Ti plasmid is obtained from
See all related overviews in Oxford Reference ». A tumor- inducing hence the acronym plasmid found in the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens q. It is these hormones that cause gall formation. Only a small part of the plasmid actually enters the plant; the rest stays in the bacterium, where it has other functions. The wild-type plasmid produces tumor cells, but it can be modified so that it can carry foreign genes into cells without making the recipient cells tumorous. Ti-mediated tumorigenesis is the first case of a horizontal mobile element q. See Chronology, , Zaenen et al. From: Ti plasmid in A Dictionary of Genetics ». Subjects: Science and technology — Life Sciences. View all related items in Oxford Reference ».
Suzuki, K.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Agrobacterium -mediated plant transformation has been used widely, but there are plants that are recalcitrant to this type of transformation. It is desirable to develop strains that can broaden the host range. A large number of Agrobacterium strains have not been tested yet to determine whether they can be used in transformation. In order to improve the disarming method and to obtain strains disarmed and ready for the plant transformation test, we developed a simple scheme to make certain Ti plasmids disarmed and simultaneously maintainable in Escherichia coli and mobilizable between E.
Ti-Plasmid is also known as an extrachromosomal genetic material found in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. The crown ball disease that affects dicot plants is caused by this phytopathogen. The size of the Ti Plasmid is kb. These are large plasmids that typically have a size between kbp and 2 Mbp. Ti Plasmid is an extrachromosomal genetic material found in the dicot plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. This phytopathogen causes crown ball disease, which is a problem for dicot plants. A useful tool for transferring desired genes to different plant species, the Ti Plasmid was initially discovered in These Plasmids can range in size from Kbps to 2 Mbps, which is often rather large.
Ti plasmid is obtained from
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a plant pathogen with the capacity to deliver a segment of oncogenic DNA carried on a large plasmid called the tumor-inducing or Ti plasmid to susceptible plant cells. These large replicons typically code for functions essential for cell physiology, pathogenesis, or symbiosis. Most of these elements rely on a conserved gene cassette termed repABC for replication and partitioning, and maintenance at only one or a few copies per cell 1.
Selcuksportshd giris 26
To our knowledge, the present study represents the first demonstration of a close correlation between the Ti plasmid type of A. Gelvin, S. It seems likely that bacteria with these chromosomal backgrounds are common in rose cultivation areas and are good recipients for Ti plasmids. However, the large size of Ti and Ri plasmids, approximately kbp, makes structural analysis and modification difficult. See all related overviews in Oxford Reference ». E-mail: pj. Only a small part of the plasmid actually enters the plant; the rest stays in the bacterium, where it has other functions. They digested the fragments with Hae III and found that the profiles H1 and H3 always correlated with strains from biovar 1, while biovar 2 strains gave rise to profile H2. Tanaka, Y. Priefer, and A.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The trb operon from pTiC58 is one of three loci that are required for conjugal transfer of this Ti plasmid.
The site is secure. Two samples had the rarely observed galls on scions Fig. Van Veen, P. Stability of the modified Ti plasmids. Virulence of Agrobacterium. Uraji, M. The presence of the opine molecules in crown galls therefore provides an ecological niche favoring pathogen development and Ti plasmid dissemination 2. These opines cannot be utilized by the plant host, and will instead be exported out of the plant cell where it can be taken up by the Agrobacterium cells. Substitution of low-copy-number oriV for high copy-number-number oriV is likely to be effective for stable maintenance in E. December They are also often termed replicons , as their replication begins at a single site.

I consider, that you are mistaken. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
Also that we would do without your magnificent idea