Splunk count by time
I have a search created, and want to get a count of the events returned by date. View solution in original post. Splunk Answers. Splunk Administration.
They make pulling data from your Splunk environment quick and easy to understand. But what if you wanted to take your STATS command one step further and see a time breakdown of that data? However, it is important to note that there are a few key differences with timechart:. Understanding these differences will prepare you to use the timechart command in Splunk without confusing the use cases. Splunk Tip: The by clause allows you to split your data, and it is optional for the timechart command.
Splunk count by time
The usage of the Splunk time chart command is specifically to generate the summary statistics table. This table which is generated out of the command execution can then be formatted in a manner that is well suited for the requirement — chart visualization for example. In the charts when we try to visualize, the data obtained is plotted against time that is limited to the X-axis by default and then the parameter that you choose for the Y-axis. The time chart is a statistical aggregation of a specific field with time on the X-axis. Hence the chart visualizations that you may end up with are always line charts, area charts, or column charts. Please take a closer look at the syntax of the time chart command that is provided by the Splunk software itself:. Let us now take a look at the required arguments that you specifically need to pass on to the command without which you might not be able to fetch the details that you intend to. To use either or, is mandatorily required to be provided. Let us take a closer look at each and every possible required argument to the command. This can be best described as a combination of literals, fields, operators, and functions that may represent the value of your destination field. For any of these evaluations to evaluate as per your requirement, the values are specifically needed to be valid for the kind of operation that we are going to perform on them. To explain this, if you are trying to perform the addition or multiplication of two variables where the inputs to these are not numeric in nature, this will not provide the result that you expect to be evaluated. This can be best described as a single aggregation that can be applied to a specific field, including an evaluated field. There is no possibility for wildcards to be used.
How to search data for a unique user count by date? About Author. Practitioner Resources.
.
For information about using string and numeric fields in functions, and nesting functions, see Overview of SPL2 eval functions. When used in a search, this function returns the UNIX time when the search is run. If you want to return the UNIX time when each result is returned, use the time function instead. You can use this function with the eval and where commands, in the WHERE clause of the from command, and as part of evaluation expressions with other commands. The following example determines the UNIX time value of the start of yesterday, based on the value of now. If you are looking for events that occurred within the last 30 minutes you need to calculate the event hour, event minute, the current hour, and the current minute. You use the now function to calculate the current hour curHour and current minute curMin.
Splunk count by time
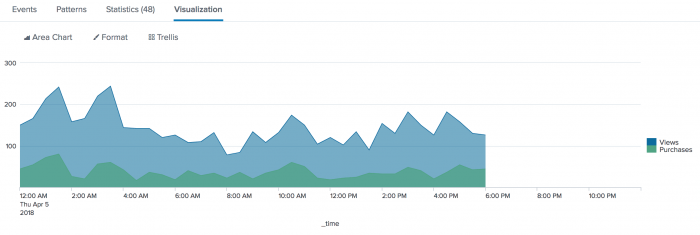
Splunk is a powerful tool for data analysis that can be used to track and analyze data over time. One of the most useful features of Splunk is the ability to create counts of events by day. This can be a valuable way to identify trends and patterns in your data, and to spot potential problems. In this article, we will discuss how to create a Splunk count by day chart. We will also provide some tips on how to use this chart to analyze your data and identify trends. Import your data into Splunk. Create a search that will return the events you want to count. Create a chart that visualizes the count of events by day.
What is 177 cm in feet
Let us take a closer look at each and every possible required argument to the command. Download Now! Mar 05 to Mar Jump to solution Solution. Share on linkedin LinkedIn. Splunk Administration. Written by: Kinney Group Last Updated:. Find the number of saved searches run throughout the day. Showing results for. Registration for Splunk University is Now Open! The report uses the internal Splunk log data to analyze and visualize the average indexing throughput indexing kbps of Splunk processes over a prolonged duration of time. Error and Warning Count by Hour or date or timestamp. Splunk Search. January 17, She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups.
For an overview about the stats and charting functions, see Overview of SPL2 stats functions.
Don't forget to share this post! Let us take a look at some of the important but optional parameters in the examples section, so that we can understand the usage of these parameters if not they can be safely skipped. Mar 05 to Mar Tags: count. Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type. Cloud Computing. Using the Splunk append Command February 21, View solution in original post. Get Trained And Certified. The report uses the internal Splunk log data to analyze and visualize the average indexing throughput indexing kbps of Splunk processes over a prolonged duration of time.

Excuse for that I interfere � I understand this question. Let's discuss.