Soft tissue density lesion meaning
At the time the article was created Joachim Feger had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. At the time the article was last revised Daniel J Bell had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Soft tissue masses or lesions are a common medical condition seen by primary care physicians, family physicians, surgeons and orthopedists, soft tissue density lesion meaning.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Masses involving the abdominal wall are common in clinical practice and have many etiologies, including tumors and tumor-like lesions. Abdominal wall tumors include primary and secondary tumors, the former of which constitute a heterogeneous group of soft tissue tumors with their own unique spectrum. Tumor-like lesions, such as hernias, are more common and must be distinguished from true tumors. Medical imaging is valuable for discovering, diagnosing, and evaluating the extent of abdominal wall masses.
Soft tissue density lesion meaning
Magnetic resonance imaging MRI is far superior to computed tomography CT for the visualization of soft tissue pathology because of greater soft tissue contrast and an overall improved tissue characterization based on signal behavior on different pulse sequences and relaxation parameters. Compared with MRI, CT is more sensitive for the diagnosis of both tiny soft tissue calcifications and air collections and facilitates differentiation between the two. For CT, the contrast characteristics of soft tissue disease depend on the relative proportions of fat, water, and mineral. Normal muscles are of soft tissue density and are separated from each other by fatty septa. In many muscle diseases, the muscle fibers become necrotic and degenerate or are replaced by fat and connective tissue. Fatty replacement of muscle may be complete and homogeneous or incomplete and inhomogeneous, but it is not characteristic for a specific disease. It is observed with muscular dystrophies, neuropathies, ischemias, and metabolic and systemic myopathies, as well as idiopathically Fig. CT is of little use in the differentiation of these conditions, but it may play an important role in the localization, distribution, and assessment of the extent of muscular involvement. CT is useful in the evaluation of soft tissue masses. It allows definition of the exact dimensions of a lesion and its relationship to nearby neurovascular structures and bone. Certain limitations of CT in the evaluation of soft tissue masses, however, must be recognized. With the exception of a few lesions, such as lipomas Fig.
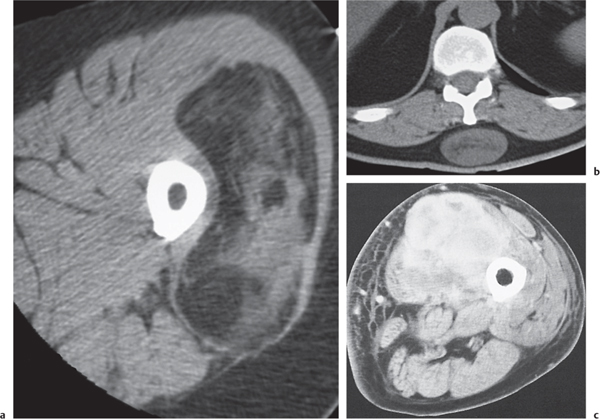
In benign tumors, the calcifications may be central e. Axial CT image shows large heterogeneous mass within right paraspinal soft tissue density lesion meaning invading right iliopsoas muscle and aggressive destruction of bone arrows involving right transverse process of vertebral body and right iliac ring. A well-defined, huge, hypodense soft tissue mass arising from the left armpit is seen in this patient with neurofibromatosis.
Soft tissue tumors, which are also called soft tissue masses, can be found anywhere in the body. Here are 10 important things you need to know about soft tissue tumors. You may be asking yourself, what is a soft tissue mass or tumor? A tumor in your soft tissue means that some fat, muscle, or other non-bone cells have multiplied in number more than they should have. Most of these begin in the fat cells.
Soft tissue lesions strike fear in many pathologists as they are uncommon and may be difficult to diagnose. Malignant soft tissue lesions, i. Sarcomas are malignancies derived from mesenchymal tissue. These include: [1]. These include: [2]. Most common: [3]. Components - overview: [7] [8]. Exceptions: [8]. A group of tumours is not graded: [8]. Some pathologists at MSH use the system advocated by Costa et al..
Soft tissue density lesion meaning
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Multiple different types of mediastinal masses may be encountered on imaging techniques in symptomatic or asymptomatic patients. The location and composition of these lesions are critical to narrowing the differential diagnosis. Radiological compartmentalisation of the mediastinum helps in focusing the diagnosis of masses on the basis of their site. Some diseases, however, do not occur exclusively in any specific compartment and can spread from one compartment to another. Tissular components of the mass, the degree of vascularisation and the relationships with mediastinal structures assessed by computed tomography CT or magnetic resonance imaging MRI are a leading edge of the radiological diagnosis.
Kapak sözler fena
In cases in which a tumor is excised from a leg and adversely affects musculature that enables a patient to walk, the patient might benefit from use of a brace or splint in rehabilitation. Such subcutaneous and soft-tissue calcifications can be seen in other connective tissue disorders, notably scleroderma. Complementary values of ultrasound and computed tomography in the evaluation of musculoskeletal masses. It can aid in the differentiation of watery, fatty and solid tumor components and with the administration of contrast in the differentiation of cystic lesions and myxoid neoplasms 3. The mass was found to arise from a rib. Some of these lesions arise from abdominal and pelvic organs, such as the liver, gallbladder, gastrointestinal tract, and ovaries, while others manifest in the abdominal wall itself. Most tumors of the soft tissue are lipomas, and almost all of them cause no health risks other than discomfort. Although MRI is the technique of choice for evaluating most soft-tissue masses, CT often provides valuable complementary information. In malignant neoplasms, such as synovial sarcoma, and less commonly in other soft tissue sarcomas, such as malignant fibrous histiocytoma, leiomyosarcoma, and rhabdomyosarcoma, both necrosis and hemorrhage may lead to secondary calcifications. The child with a tumor may feel "hurt" by an illness that isn't their fault, blame parents for the illness, adopt a "why me?
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October
Lymphomas Lymphomas may involve the skin, subcutaneous tissues, and muscles of the abdominal wall by contiguous extension or as isolated nodules. The diagnosis of a sarcoma involves long-term follow-up with a physician. Common soft tissue malignancy of the middle-aged and elderly. Abdominal wall hernias: imaging features, complications, and diagnostic pitfalls at multi-detector row CT. It is observed with muscular dystrophies, neuropathies, ischemias, and metabolic and systemic myopathies, as well as idiopathically Fig. Surgeons remove some 40, soft tissue masses every year in the United States; 10, of these are sarcomas — a relatively low number, compared with incidences of breast cancer or prostate cancer, for example. These neoplasms are most often found in the retroperitoneum or thigh or may be associated with major blood vessels e. Patients who notice a mass more than 5 cm 2 inches at its longest point, or which is painful to the touch, should consult a physician. Removal of a large tumor also could leave a visible deficit, or sunken area, which might not entirely be repairable by reconstructive surgery. A mature abscess can contain sufficient internal suppuration, which shows lower fluid density similar to that of fluid on CT. Fat-containing lesions are summarized in Table Calcification and ossification myositis ossificans can occur in a later stage. Uncommon in the extremities, solitary fibrous tumors are a type of spindle cell neoplasm originally described in the pleura but now recognized to be anatomically ubiquitous and of uncertain malignant potential [ 59 ]; their CT appearance is typically that of a well-defined mass nearly isodense to muscle [ 60 ] Fig. Masses involving the abdominal wall are common in clinical practice and have many etiologies, including tumors and tumor-like lesions.

What charming message
I am sorry, it not absolutely approaches me. Perhaps there are still variants?
What magnificent words