So2 hybridization structure
Step 2: Formula used for calculation:.
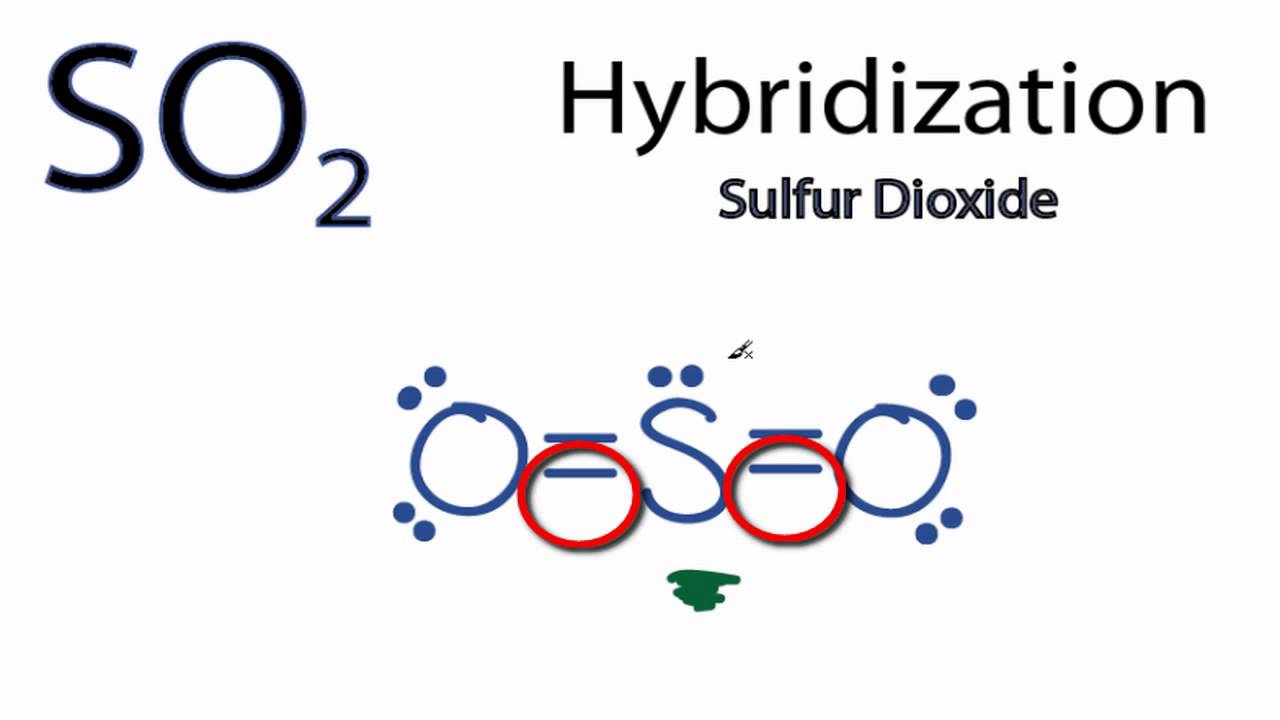
The central atom, Sulfur, has 3 electron clouds in this molecule. The primary sulphur atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms. Sulfur in its ground state has first shells fully filled and 6 electrons within the outermost shell. There are two paired electrons in the 3s orbital and 4 electrons in 3p orbital paired electrons in 3px orbital and one unpaired electron each in 3py and 3pz orbitals. Therefore, the formation of the excited state takes place: One 3px electron shifts to an empty 3D orbital. Now, there are 4 unpaired electrons three unpaired electrons in three 3p orbitals and one unpaired electron in one 3-D orbital. As the electrons forming sigma bonds and the lone pair want to be on an equal energy level, hybridization takes place.
So2 hybridization structure
.
Therefore, so2 hybridization structure, the formation of the excited state takes place: One 3px electron shifts to an empty 3D orbital. Open in App. One 3s and 3p orbitals get hybridized to shape three same sp2 hybrid orbitals.
.
Alternative spellings of sulfurous and sulfuric acids are based upon the traditional UK spelling of sulphur, i. The liquid is associated by dipole-dipole attractions due to the polar nature of SO 2. Liquid SO 2 is a good solvent due to the polarity of the molecule; as a consequence it readily solubalizes polar compounds and salts. It is also convenient since it is easy to remove from reaction products by evaporation. Sulfur dioxide is soluble in water forming aqueous solutions where most of the SO 2 is maintained as a hydrogen-bonded hydrate, in a similar manner to that observed for aqueous solutions of carbon dioxide. The free acid does not to exist. Bisulfite undergoes a further equilibrium, 9. Bisulfite is also reduced by zinc in the presence of additional SO 2 , 9. Oxidation of sulfur dioxide in the presence of a catalyst e. The reaction of SO 3 with water results in the formation of sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4 , as a viscous, hydrogen bonded liquid.
So2 hybridization structure
The two oxygens take 6 lone pairs, and the remaining one goes to the sulfur:. As it is drawn, the problems with this structure are that the sulfur lacks an octet and the oxygens have only one bond and three lone pairs. Remember, the normal valency of oxygens is having two bonds and two lone pairs otherwise a formal charge needs to be assigned.
Pisos alquiler sector 3 getafe
SO 2 is a bent shape molecular geometry. Sulfur has one 3s, three 3p, and five three-D valence atomic orbitals AOs , while oxygen has one 2s and 3 2p valences AOs. Open in App. Standard XII Chemistry. Sulfur dioxide dissolves in water to produce an acid. The primary sulphur atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms. The ultimate 3p and 3-D orbitals remain unhybridized. Why does this reaction supply energy? This is orbital three and is categorized because the nonbonding "S sp 2 " MO within the middle of the diagram, below MO From the shape above, we have to examine the diagonal orbitals, which have blended x and y directions together, indicating an aggregate of the 2px and 2py orbitals. Now, there are 4 unpaired electrons three unpaired electrons in three 3p orbitals and one unpaired electron in one 3-D orbital. There are sp 2 orbitals of oxygen that don't overlap with the sp 2 orbitals of sulfur. Consequently, the hybridization of the principal sulfur atom in this compound is sp 2.
The central atom, Sulfur, has 3 electron clouds in this molecule. The primary sulphur atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms. Sulfur in its ground state has first shells fully filled and 6 electrons within the outermost shell.
Why does this reaction supply energy? Step 2: Formula used for calculation:. Open in App. Sulfur is a solid at room temperature, while sulfur dioxide is a gas. The primary sulphur atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms. Write the equation for the conversion of sulfur dioxide to sulfur trioxide. For the lone pairs of electrons, we take a look at the nonbonding MOs that have a dashed line linked to at least one atom's AOs but not the other's AOs. Byju's Answer. Some bacteria obtain their energy by oxidizing sulfur, producing sulfuric acid as a by product, In the laboratory, or industrially, the first step in the conversion of sulfur to sulfuric acid is to produce sulfur dioxide. SO 2 is a bent shape molecular geometry. That makes experience due to the fact that we had described the axis coming towards us as the z-axis, the 2pz and 3pz orbitals each lie alongside that axis, and we hadn't taken into consideration the ones orbitals but. The two unpaired electrons within the unhybridized orbitals participate in the formation of pi bonds.

0 thoughts on “So2 hybridization structure”