Sigma bond and pi bond examples
Sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds that differ in the overlapping of atomic orbitals.
When you hear the words sigma and pi bond, you might think of Greek life in college. But actually, sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds. Covalent bonds happen when atoms share electrons. They are found in single, double, and triple bonds. They only exist in double and triple bonds.
Sigma bond and pi bond examples
Forgot password? New user? Sign up. Existing user? Log in. Already have an account? Log in here. Sigma and pi bonds are chemical covalent bonds. Sigma and pi bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals. Sigma bonds are formed by end-to-end overlapping and Pi bonds are when the lobe of one atomic orbital overlaps another.
Reactions of Esters. They only exist in double and triple bonds. Aromatic Chemistry.
Our minds can handle two electrons interacting with one another in a sphere of space. But then we start putting in double bonds and triple bonds. So we need a more complex picture that works for all these electrons. The hybridization model helps explain molecules with double or triple bonds see figure below. The entire molecule is planar. As can be seen in the figure below, the electron domain geometry around each carbon independently is trigonal planar.
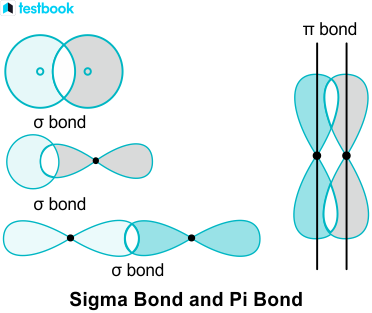
Sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds that differ in the overlapping of atomic orbitals. Covalent bonds are formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals. Sigma bonds are a result of the head-to-head overlapping of atomic orbitals whereas pi bonds are formed by the lateral overlap of two atomic orbitals. Various bond parameters such as bond length, bond angle, and bond enthalpy depend on the way the overlapping of atomic orbital takes place. This overlap occurs in two major ways, giving rise to two primary types of covalent bonds , i. This type of covalent bond is formed by head-on positive same phase overlap of atomic orbitals along the internuclear axis. Sigma bonds are the strongest covalent bonds, owing to the direct overlapping of the participating orbitals. Generally, all single bonds are sigma bonds.
Sigma bond and pi bond examples
A description of the double bond is the sigma-pi model shown in Figure 1. In this case only two of the p orbitals on each C atom are involved in the formation of hybrids. Two of these hybrids from each C atom overlap with H 1 s orbitals, while the third overlaps with an sp 2 hybrid on the other C atom.
Horario desayuno ihop
Acid-Base Indicators. To count sigma and pi bonds, draw the Lewis dot structure and count the single, double and triple bonds present. Plaster Of Paris Chemical Formula. What Is Waste. Multiple bonds are also useful for deciphering spectra obtained via nuclear magnetic resonance NMR. Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Reaction Mechanism. A Cl 2 molecule features a p-p overlap of the 3p z orbitals of two chlorine atoms. In a molecule of O2, there are two sigma bonds and two pi bonds. Sigma and Pi Bonds. AI-powered learning tools.
We mentioned in the previous post that covalent bonds are formed as a result of sharing two valence electrons in overlapping orbitals of two atoms. For example , the following Lewis structures represent covalent bonds together with some lone pairs of electrons:.
Sign up Sign up to read all wikis and quizzes in math, science, and engineering topics. Further Reading The Antibonding Effect. Hire With Us. Sigma and pi bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals. Licenses and Attributions. As they move closer and closer together, orbital overlap begins to occur, and a bond begins to form. Lewis Dot Diagrams. In this condition, one half-filled p orbital from each participating atom undergoes head-on overlapping along the internuclear axis. In addition, because of the greater number of bonds between the atoms, the strength should also be greater as bond order increases. Pi bonds restrict rotation around the bond axis to a certain extent because the electron density is above and below the internuclear axis. Skip to content. A double bond contains one sigma and one pi bond. For the H 2 molecule, the distance is 74 pm picometers, 10 meters. Every covalent bond in a given molecule has a characteristic length and strength. A single covalent bond consists of one sigma bond, and there are no pi bonds in a single bond.

0 thoughts on “Sigma bond and pi bond examples”