Sb peritonitis
Federal government websites often end in.
There is also the possibility of accepting book reviews of recent publications related to General and Digestive Surgery. The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years. SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact. SNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
Sb peritonitis
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Ascitic paracentesis remains the chief diagnostic procedure. Automated cell counters have the same diagnostic accuracy as the manual measurement of white cells. Lately, the use of leucocyte reagent strips dipsticks has emerged as a useful alternative. Examination of the fluid is not complete unless the sample is inoculated in blood culture bottles. Following a single episode of SBP patients should have long term antibiotic prophylaxis. They suggest the performance of paracentesis in all cirrhotic patients with ascites on hospital admission and also in all patients who develop other signs suggestive of peritoneal infection—namely encephalopathy, renal impairment and peripheral blood leucocytosis without a precipitating factor. Therefore, it seems reasonable to refer patients after their first episode of SBP for liver transplant assessment. However, signs of sepsis in patients with SBP may be masked because patients with cirrhosis have characteristics which make recognition of sepsis difficult 8 —namely, reduced polymorphonuclear leucocyte PMNL count due to hypersplenism, elevated baseline heart rate due to the hyperdynamic circulation, baseline hyperventilation due to hepatic encephalopathy, and blunted elevation of body temperature. Recent published articles have reduced these ungrounded fears and established the safety profile of abdominal paracentesis.
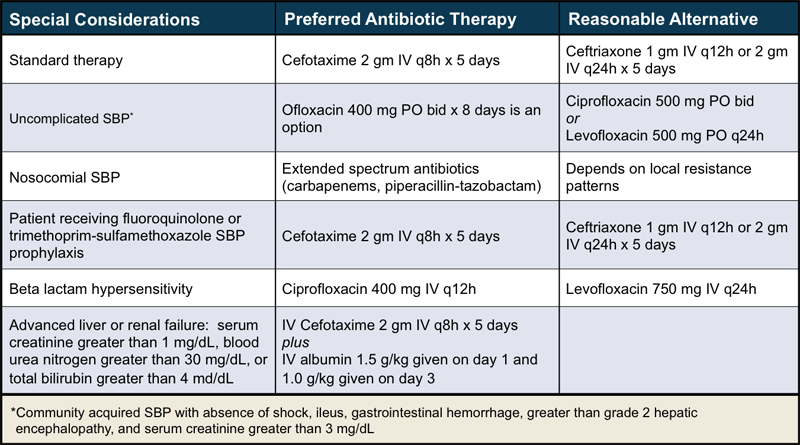
A randomized controlled trial found that intravenous albumin on the day of admission and on hospital day 3 can reduce sb peritonitis impairment. This section was adapted from content using the following evidence based resources in combination with expert consensus, sb peritonitis. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
You can direct patients to the following: Paracentesis. Lab tests. This section was adapted from content using the following evidence based resources in combination with expert consensus. Authors: Dr. Lynora Saxinger, Dr.
You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis SBP is the most frequent and life-threatening infection in patients with liver cirrhosis requiring prompt recognition and treatment. First, diagnostic criteria and tools available for rapid and accurate diagnosis are reviewed. Second, since prophylaxis is of crucial relevance when trying to improve survival, we discuss who should be treated, when, how and for how long to prevent episodes of SBP. Identification of risk factors and individualisation of timing and selection of prophylactic measures are the key to success without major development of resistant bacteria. Finally, effective therapy is essential since treatment failure is associated with poor outcome. Since the emergence and spread of drug-resistant bacteria has accelerated, criteria for the choice of antibiotic regimen in the individual patient are pivotal for optimising therapy. Provenance and peer review Commissioned; externally peer reviewed. Skip to main content. Log in via OpenAthens.
Sb peritonitis
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis SBP is infection of ascitic fluid without an apparent source. Manifestations may include fever, malaise, and symptoms of ascites and worsening hepatic failure. Diagnosis is by examination of ascitic fluid. Treatment is with cefotaxime or another antibiotic.
Real estate rural properties victoria
Issue 4. Review Emergency medicine updates: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. The site is secure. Hepatology 40 — Ann Intern Med — This has been shown to reduce both in-hospital mortality and renal damage compared to the use of antibiotic therapy alone. Am J Gastroenterol 96 — Review Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. A spontaneous fungal infection can often follow a spontaneous bacterial infection that has been treated with antibiotics. Bacterial translocation and its consequences in patients with cirrhosis. Incidence of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with ascites. Would love your thoughts, please comment. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 17 — This is important, as lack of improvement after 48 hours of therapy may indicate an underlying perforation or abscess formation, such as secondary bacterial peritonitis, that may require surgery.
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis SBP is the development of a bacterial infection in the peritoneum , despite the absence of an obvious source for the infection. The diagnosis of SBP requires paracentesis , a sampling of the peritoneal fluid taken from the peritoneal cavity.
Ramos, P. Download as PDF Printable version. Treatment with octreotide or midodrine is helpful if renal failure develops. I found what I was looking for on the page. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis SBP is an acute infection of the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the abdomen ascites without an identifiable source of infection. Spontaneous vs. Moreover, liver transplantation should be considered for the survivors of SBP, who are otherwise good transplantation candidates. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, eds. Postgrad Med J. Gut 53 — SBP can occur in adults and children. Clinical Features of Refractory Ascites in Outpatients.

I think, that you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.