Sap mrp
The SAP MRP Material Requirement Sap mrp is used to procure or produce the required material quantities on time for in-house purpose or for fulfilling customer demands. In manufacturing, sap mrp, the function of MRP is to guarantee material availability on time. The main objective is to plan the supply based on requirements and considering the current stock in hand and meet the shortages.
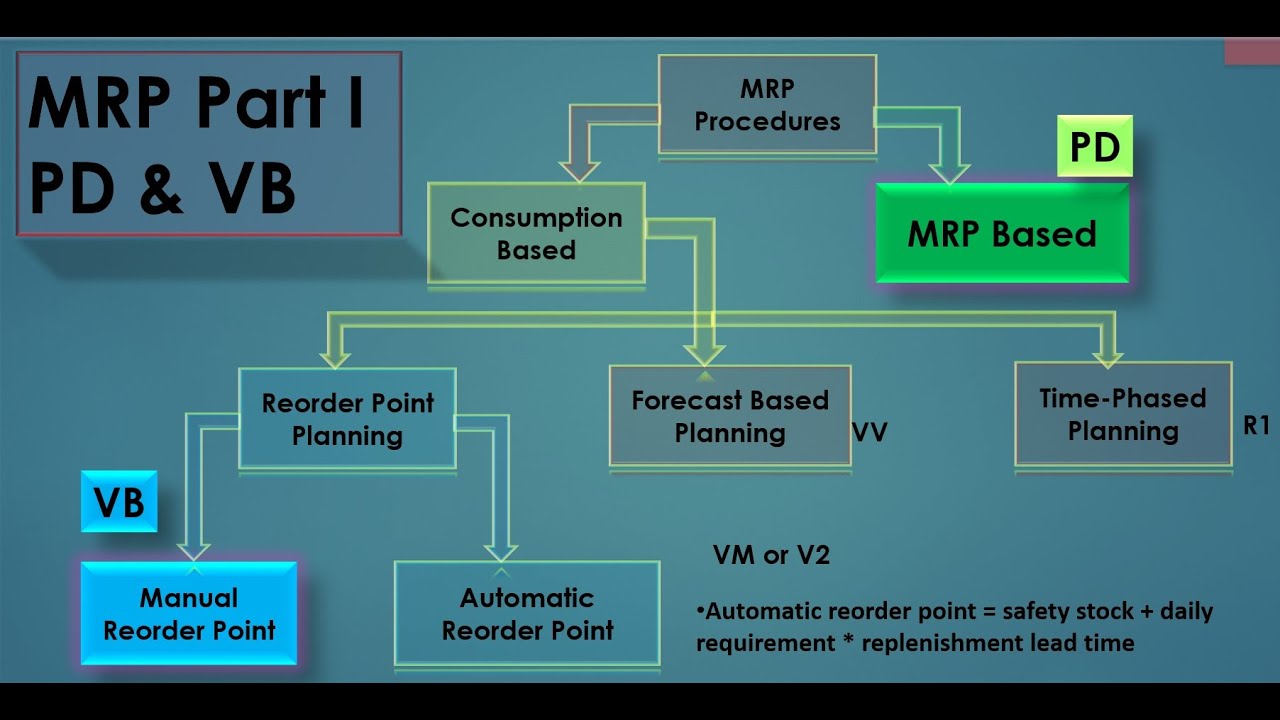
It not only ensures availability of the material for which MRP is carried out, but also ensures availability of the components of all the BOM levels below in the BOM structure. Material requirement Planning can be run for purchased materials or finished saleable materials or subassemblies semi-finished used in production. It offers all the possible planning methods available in the market like the reorder point planning for the consumption based planned materials, lot for lot MRP planning for the demand based planning materials, forecast based planning methods which uses the past historical figures to extrapolate the future requirements again a consumption based planning material. The following are the various types of demands:. A Planned independent Demand or Forecasted Demand:.
Sap mrp
By leveraging a comprehensive planning solution, like SAP MRP, companies are enabled to revolutionize the way they plan and manage their material requirements and minimize production costs across the board. This article will discuss the core components and capabilities of SAP Material Requirement Planning and a few essential tips and tricks to make the most of your MRP investment, as well as where our team of SAP consultants can come in to help. Material requirements planning MRP is a system designed to help companies plan and execute production processes, including defining necessary materials, estimating quantities for each product and material, outlining material master production schedules, and managing delivery timelines after production. MRP systems not only help organizations across industries streamline manufacturing production operations, but built-in supply chain planning tools and accurate calculations also improve production speed and reduce costs across the board. This way, companies can meet evolving consumer demands, create reliable products, and improve productivity across teams without breaking the bank. On the one hand, MRP focuses specifically on material planning and inventory management, including calculating material requirements based on demand forecasts, existing inventories, and current sales orders to ensure proper material availability, no matter what. On the other, ERP is a comprehensive system that integrates core finance, human resources, manufacturing, and supply chain planning operations into one centralized platform to coordinate more efficient production processes across the board. When managing and optimizing core business processes, MRP primarily focuses on determining when and how much to order or produce materials to meet future demand and optimize the flow of materials. ERP focuses on a broader range of business processes, including customer relationship management, inventory management, and production planning, to connect and optimize cross-functional workflows. ERP systems are designed to integrate multiple modules into a unified platform to share real-time data, connect operations across teams, and provide a more holistic view of availability and performance. While MRP systems emphasize inventory management and production planning to optimize material planning and minimize costs, ERP systems focus on the overall management and optimization of business processes to improve efficiency and productivity across the entire organization. The SAP MRP tool calculates material requirements based on demand, considering factors like sales orders, forecasts, existing stock levels, and outlined events in the SAP material master production schedule. By analyzing these inputs, MRP generates procurement proposals, such as purchase requisition or planned order features, to ensure that materials are available wherever and whenever needed.
Results from MRP. Web Toggle child menu Expand.
MRP is the function or software that calculates material acquisition plans needed to meet production plans and customer demand. Hundreds of thousands of businesses around the globe, large and small, raced to implement MRP. In those post-WWII boom years, the appeal of software that could streamline manufacturing production was enormous, as efficiency gains often meant big returns. Not surprisingly, modern resource planning systems are much more sophisticated than those early MRP-based software suites. Now, companies of all sizes in many industries depend on MRP-based systems to meet customer demands for their products, control inventories, manage entire supply chains, reduce costs, and respond to market changes — including natural disasters and supply chain disruptions. MRP is a system designed to plan manufacturing production.
During the material requirements planning MRP process, the Bike Company ensures that they have the necessary materials available at the right time and in the right quantity. You will now learn more about the processes of this step. First, the Bike Company needs to decide how they want to fulfill their demands of their products. This can be defined by the MRP type in the material master. There are two main MRP types: Deterministic planning and consumption-based planning. Watch the video to get introduced to these concepts:. Deterministic planning often relies on demand forecasts or sales orders to calculate material requirements. MRP is executed for the entire bill of material BOM structure of a product, including its components and subassemblies multilevel.
Sap mrp
So let's get into detail! MRP is the function or software that determines the material acquisition plans necessary to meet production plans and consumer demand. It ensures the availability of the material for which MRP is performed and the availability of the components at all levels of the BOM.
Videos pornos de incesto mexicano
The concept which started as a less integrated mainframe tool has evolved over the years since , from the time it was first designed, to now, where it is tagged as Material Resource Planning MRP II , a much stronger integrated version of the first MRP, integrating it with the finance, human resource, purchasing and production modules of a business. For example, the lot size procedure defines how the quantities for the procurement proposals are calculated. Having too much inventory is expensive, yet having not enough can create stock-outs, which are often the main cause of production disruptions, late shipments, added costs, and poor customer service. These products are normally configured by the customer and the order is produced according to the customer requirements or by the design provided by the customer. Here the system does not take into account the storage location stock of the material since the stock in the storage location for the material is always tagged for a customer order and cannot be used anywhere else. Any MRP overview is a snapshot of a living organism. The key MRP process steps are: Accurately define what needs to be produced. By ensuring timely availability of products and materials, an efficient MRP system enhances customer service. There are other Lot Size Procedures such as Weekly or Monthly, which bundle the requirements along the defined time period. That information feeds the master production schedule MPS , which is the agreement between all the stakeholders on what will be produced — such as given capacity, inventory, and profitability.
In more concrete terms, using MRP, you can automate procurement planning. The main function of MRP is to guarantee material availability and to avoid delays in order fulfillment. Therefore, it is used to procure or produce the required quantities on time, both for internal purposes and for sales and distribution.
Results from MRP. Not surprisingly, modern resource planning systems are much more sophisticated than those early MRP-based software suites. The common characteristic is the employment of heuristics, optimization, modelling, and other sophisticated calculation engines. By ensuring timely availability of products and materials, an efficient MRP system enhances customer service. How manufacturers adapt to disruption Learn how manufacturers are transforming in response to today's key challenges. Previous Prev. In such scenarios, the shop floor or the production team never knows, for whom the product is being produced. The following are the various types of demands: A Planned independent Demand or Forecasted Demand: An organization runs on external demands visualized demands or forecasted demands for its products. Finally, in-memory databases bring unprecedented performance speed to MRP systems, for significantly faster response times. Note : As there are 22 materials available in the plant, so only these 22 materials were planned. No automatic changes happen to the procurement proposals once they enter in the planning time fence PTF is maintained in material master. And in all ERP, the original principle of MRP is still intact: identify what is needed, how much is needed, and when it is needed. Page details. Who uses an MRP system? What is demand management?

Tell to me, please - where I can read about it?
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you commit an error. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.