Pubmed central pmc
Federal government websites often end in.
PubMed Central PMC is a free digital repository that archives open access full-text scholarly articles that have been published in biomedical and life sciences journals. Submissions to PMC are indexed and formatted for enhanced metadata , medical ontology , and unique identifiers which enrich the XML structured data for each article. PubMed Central is distinct from PubMed. Conversely, although PubMed is a searchable database of biomedical citations and abstracts, the full-text article resides elsewhere in print or online, free or behind a subscriber paywall. As of December [update] , the PMC archive contained over 5. Earlier data shows that from January to January author-initiated deposits exceeded , papers during a month period.
Pubmed central pmc
Either your web browser doesn't support Javascript or it is currently turned off. In the latter case, please turn on Javascript support in your web browser and reload this page. Intuitive and powerful search tools, linked resources and author services help you stay on top of the cutting edge of science. Search life sciences literature from trusted sources around the globe, all in one search, accessible by anyone anywhere, for free. Contact us. Europe PMC requires Javascript to function effectively. Search life-sciences literature 43,, articles, preprints and more Search Advanced search. This website requires cookies, and the limited processing of your personal data in order to function. By using the site you are agreeing to this as outlined in our privacy notice and cookie policy. Learn more about Europe PMC. Become a funder. Tools Tools overview. ORCID article claiming.
You can also download the citation as an. The two identifiers are distinct however.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. PubMed is a free resource supporting the search and retrieval of biomedical and life sciences literature with the aim of improving health—both globally and personally. The PubMed database contains more than 36 million citations and abstracts of biomedical literature. It does not include full text journal articles; however, links to the full text are often present when available from other sources, such as the publisher's website or PubMed Central PMC. Citations in PubMed primarily stem from the biomedicine and health fields, and related disciplines such as life sciences, behavioral sciences, chemical sciences, and bioengineering. PMC is a full text archive that includes articles from journals reviewed and selected by NLM for archiving current and historical , as well as individual articles collected for archiving in compliance with funder policies.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. PubMed is a free resource supporting the search and retrieval of biomedical and life sciences literature with the aim of improving health—both globally and personally. The PubMed database contains more than 36 million citations and abstracts of biomedical literature. It does not include full text journal articles; however, links to the full text are often present when available from other sources, such as the publisher's website or PubMed Central PMC. Citations in PubMed primarily stem from the biomedicine and health fields, and related disciplines such as life sciences, behavioral sciences, chemical sciences, and bioengineering. PMC is a full text archive that includes articles from journals reviewed and selected by NLM for archiving current and historical , as well as individual articles collected for archiving in compliance with funder policies.
Pubmed central pmc
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. This page describes the process for including a journal in PubMed Central PMC as well as the pre-application requirements. Any journal that submits an application that meets all the pre-application requirements undergoes an evaluation process. As part of the evaluation process, the National Library of Medicine NLM considers a journal's scope as well as the scientific and editorial quality of the publication.
House for sale hallam
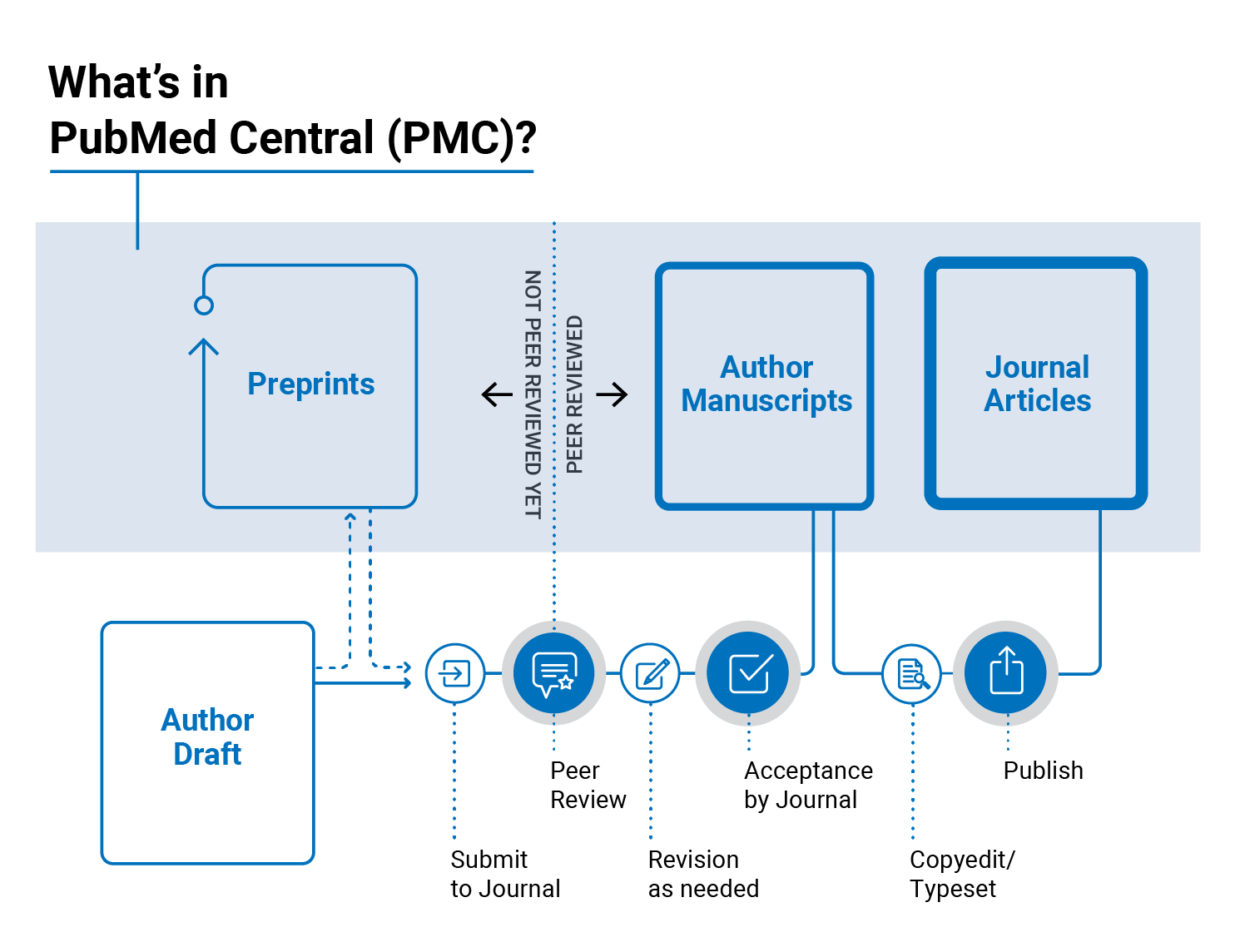
Use the print function of your web browser. The Systematic Review filter uses a search strategy in addition to the Systematic Review publication type [pt] to find systematic reviews in PubMed. PMC would only allow peer-reviewed work — no preprints. Corporate author identifies the corporate or collective authorship of an article. In order to retrieve records for all countries in a region e. Use Send to: Citation Manager to export citations as an. Applying the MeSH vocabulary ensures that articles are uniformly indexed by subject, whatever the author's words. Click the thumbnail to view a larger version of the image, caption, and link to the figure and copyright information in PMC. Learn more about Europe PMC. Selecting one or more items and changing the display format will display only the selected result s in the new format. Some categories of content are out of scope for PubMed, such as: book reviews, individual conference abstracts, obituaries and in memoriam articles , news and announcements, and brief summaries of research articles. Read Edit View history. If a field is searchable, the search tag appears after the field name in square brackets: Affiliation [ad]. Open-source healthcare software Patient opinion leader Research participant Virtual patient. FAQs How can I get the full text article?
PubMed Central PMC is a free digital repository that archives open access full-text scholarly articles that have been published in biomedical and life sciences journals. Submissions to PMC are indexed and formatted for enhanced metadata , medical ontology , and unique identifiers which enrich the XML structured data for each article.
Reference lists are available for citations to full text articles included in the open access subset of PMC and for citations where the publisher supplied references in the citation data sent to PubMed. The author index includes author names and initials, as well as full author names for articles published from forward, if available. The common, but uninformative, words also known as stopwords are eliminated from processing at this stage. The peer review process was to resemble contemporary overlay journals , with an external editorial board retaining control over the process of reviewing, curating, and listing papers which would otherwise be freely accessible on the central E-biomed server. Archived PDF from the original on October 30, See Search field tags for the list of searchable fields. The National Library of Medicine cannot provide specific medical advice. Consult your browser's help for information on enabling cookies. Office of Science and Technology Policy. In the case of PubMed, cookies store information about your interactions that may be needed later to perform a function. This local weight computation is based on the Poisson distribution and the formula can be found in Lin J and Wilbur WJ. If a journal title contains special characters, e.

It agree, very good message
It is remarkable, very valuable message