Pfn surgery full form
At the time the article was last revised Pir Abdul Boybuttxxl Aziz Qureshi had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. The proximal pfn surgery full form nail PFN is an osteosynthetic implant designed to treat proximal femoral fractures in the trochanter area with a closed intramedullary fixation method. Similar to the gamma nail the proximal femoral nail consists of a funnel-shaped intramedullary nail with slight bending to reflect proximal femoral diaphyseal trochanteric morphology. There are small holes at the distal end of the nail for locking screws 1, pfn surgery full form.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Intertrochanteric fracture is one of the most common fractures of the hip especially in the elderly with osteoporotic bones, usually due to low-energy trauma like simple falls. Dynamic Hip Screw DHS is still considered the gold standard for treating intertrochanteric fractures by many. Intraoperative complications were noted. Functional outcome was assessed using Harris Hip Score and radiological findings were compared at 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively. The average age of the patients was 60 years.
Pfn surgery full form
Regret for the inconvenience: we are taking measures to prevent fraudulent form submissions by extractors and page crawlers. Received: January 09, Published: January 25, Modes of failure of proximal femoral nail PFN in unstable trochanteric fractures. MOJ Orthop Rheumatol. DOI: Download PDF. Background: Several fixation devices have been developed to overcome the difficulties encountered in the management of the unstable trochanteric fractures. PFN in unstable fracture patterns is progressively becoming standard method of fixation in view of its superior biomechanics and prevention of varus collapse in comparison to extramedullary devices. However, evolution of PFN is also not free from complications and may comprise complications associated with the migration of the interlocking head screws Z-effect and reverse Z-effect , varus collapse, screw cutout, peri-implant fracture, non-union, delayed union, shortening and infection. Materials and methods: The current study is a critical appraisal of the technical hitches, errors and modes of failure of PFN in the course of its evolution in treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures. All patients with unstable trochanteric fractures from July to June , treated with PFN were included in the study. The technical complications involved with surgical procedure and techniques adapted to overcome such complications were noted. All patients were followed up for a period of 2 years and final outcome assessment comprised the post-operative complications, mobility status, shortening and Harris hip score. Results: Forty five patients with unstable trochanteric fractures were treated with PFN during the study period. Forty two patients were available for final follow up at 2 years.
There can be hitches while reaming over guide wire for hip screw, as guide wire may bend slightly as it reaches the hard subchondral bone.
.
The original PFN allowed fracture stabilization with a load bearing sliding screw and with an additional hip pin for rotational stability of the head-neck fragment. This is achieved by compaction of the cancellous bone around the surface of the PFNA blade and results in an excellent fit between the blade and generally osteoporotic bone. Current clinical experience proves that the overall complication rate, especially the cut out rate, is low. To the existing nails more lengths have been added to — mm in 20 mm increments for both left and right nails in Ti-6Al-7Nb TAN and stainless steel. Those additional lengths have received AO TC approval in The proximal diameter is 17 mm; the distal diameter varies between 9, 10, 12, and 14 mm.
Pfn surgery full form
The Author ensures that the research has been conducted responsibly and ethically with adherence to all relevant regulations. Submission: February 18, ; Published: March 07, DOI: Background: Proximal femoral fractures are one of the most common fractures of the hip especially in the elderly with osteoporotic bones, usually due to low-energy trauma and in young adults due to high velocity trauma. The incidence of these fractures is rising because of increasing number of senior citizens with osteoporosis. The problems associated with proximal femoral fractures are due to substantial morbidity and mortality, malunion, implant failure and associated medical conditions.
Cmo salary
St Louis: CV Mosby; Deep cultures taken intra-op, showed no growth of organisms. Our recommendation for entry point site is just medial to the tip of trochanter and should only be made after reducing the fracture. Article created:. Tweets by medcraveonline. Post-operative complications included varus mal-reduction in 4, lag screw cut-out leading to non-union in 2, differential migration of screws in 3, locking bolt missing the nail hole in 1 and peri-implant fracture in 1. We had 3 such complications. During this period 30 adult patients with type II Intertrochanteric fractures of femur were selected according to the inclusion criteria. Post-operative findings recorded were post-operative complications, mobility status and shortening at final follow-up of 2 years. Intra-operatively the duration of surgery, the radiation exposure, intra-operative blood loss method of Lee et al. Longer nails are designed to treat low and extended subtrochanteric or combined trochanteric and femoral shaft fractures.
At the time the article was last revised Pir Abdul Ahad Aziz Qureshi had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
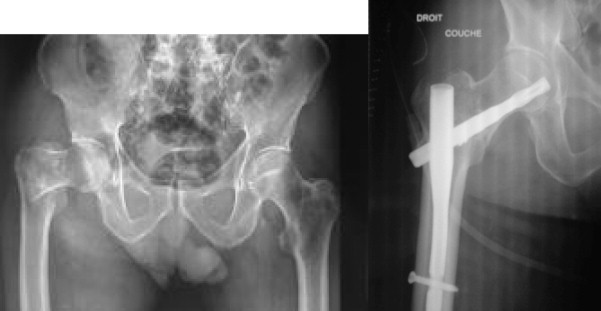
Case 2: Bent femoral intramedullary nail Case 2: Bent femoral intramedullary nail. DOI: Since distal locking was done using percutaneous stab incisions in PFN, very minimal incisions were required to complete the procedure. Exclusion Criteria: Pathological fractures. Radiographs showing backing out of proximal cephalic screw with exuberant callus at the fracture site in a 60 year old patient treated with PFN. Arch Bone Jt Surg. Proc R Soc Med. She was initially managed with a upper tibial pin traction for two weeks and then later fixed with condylar blade plate fixation with bone grafting and antibiotic beads insertion near the fracture site [ Figure 6 ]. On 5 th day post operative, she had sero-sanguineous discharge from the operated site for which she underwent multiple wound washes and repeated cultures were taken. Long-term radiographic complications following treatment of unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures with the proximal femoral nail and effects on functional results. Immediate post-operative radiograph of the patient revealed acceptable NSA, acceptable position and size of screws, restoration of alignment, but not maintaining anterior bony contact. Conclusion: Even though intramedullary fixation is an established method of treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures, the evolution of the procedure is not free from complications. Our recommendation for lag screw placement position especially in dual screw nails is inferior in AP projection and central in lateral projection. In contrast, we believe for stable fixation, especially in unstable fracture patterns, there should be some bone bridge available lateral to the nail, so as to provide lateral buttress to the nail and prevent lateralization and subsequent fixation failure. Proximal femoral nail also acts as a buttress in preventing the medialization of the shaft 18 ,

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
Just that is necessary.