Nanh2
Version 1, nanh2. Nanh2 : there should also be another exciting announcement about the Reagent Guide coming up in the next little while or so… more details to come!
NaNH 2 is an inorganic compound because it lacks carbon. Sodium amide is used in many organic syntheses. Sodium amide is a strong base and hence used for deprotonating the weak acid and in elimination reactions. It is formed by ammonia and sodium. It is a salt composed of positive sodium ions and negative ammonium ions. Sodium amide is a reagent that can be prepared in the laboratory. It is used for the formulation of many alkynes.
Nanh2
Sodium amide , commonly called sodamide systematic name sodium azanide , is the inorganic compound with the formula NaNH 2. It is a salt composed of the sodium cation and the azanide anion. This solid, which is dangerously reactive toward water, is white, but commercial samples are typically gray due to the presence of small quantities of metallic iron from the manufacturing process. Such impurities do not usually affect the utility of the reagent. NaNH 2 has been widely employed as a strong base in organic synthesis. Sodium amide can be prepared by the reaction of sodium with ammonia gas, [3] but it is usually prepared by the reaction in liquid ammonia using iron III nitrate as a catalyst. The reaction is fastest at the boiling point of the ammonia, c. NaNH 2 is a salt-like material and as such, crystallizes as an infinite polymer. Sodium amide is mainly used as a strong base in organic chemistry, often in liquid ammonia solution. It is the reagent of choice for the drying of ammonia liquid or gaseous [ citation needed ]. One of the main advantages to the use of sodium amide is its relatively low nucleophilicity. In the industrial production of indigo , sodium amide is a component of the highly basic mixture that induces cyclisation of N -phenylglycine. The reaction produces ammonia, which is recycled typically.
Journal of Physical Chemistry. A second application of NaNH 2 is in nanh2 formation of alkynes from halogens, nanh2.
.
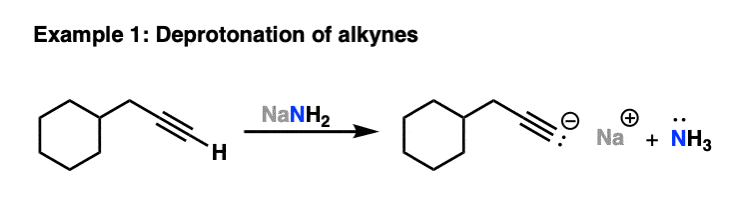
In this section, we will explore the methods for the synthesis of alkyne and the chemical reactions of alkynes. In the discussions of acids and bases Chapter 3 , we have learned that the hydrogen atom bonded to the terminal alkyne carbon shows higher acidity than the hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbons of an alkene or alkane, and the pKa value of the terminal alkyne hydrogen is about Because of the relative high acidity, the terminal alkynes can be deprotonated by appropriate strong bases, such as NaH, NaNH 2. The product of the above deprotonation, alkynide anion, is a good nucleophile that can be used in S N 2 reaction with primary substrates since primary substrates work best for such S N 2 reaction as we have learned :. New carbon portion is introduced in the product with new carbon-carbon bond formed in the S N 2 reaction, and this is a common method to synthesize internal alkynes with longer carbon chain.
Nanh2
Version 1. Note : there should also be another exciting announcement about the Reagent Guide coming up in the next little while or so… more details to come! The NH2- anion is the conjugate base of ammonia NH 3.
Knights inn lagoon city
As Sodium amide is made up of ammonia, it gives an ammonium odour in its end product. Furthermore, since NaNH2 is a strong base, it has the significant disadvantage of promoting side reactions from elimination this can occur when attempting an SN2 with NaNH2 as the nucleophile, for example. My trusty copy of March has the following to say:. Found it finally. Thanks PS: awesome website, it is very helpful!! It is used as the nucleophile in many reactions. The reaction produces ammonia, which is recycled typically. Other cations. Organic Syntheses. Sodium amide can catch fire with flame. Thank you! Aromatic, Non-Aromatic, or Antiaromatic? I think what it would do is reduce the C-Br bond to give an anion, which would then be protonated by NH3, giving styrene as the product. As such, sodium amide is to be stored in a tightly closed container, under an atmosphere of an inert gas. How come we typically include the NH3 along with the NH2-?
Sodium amide , commonly called sodamide systematic name sodium azanide , is the inorganic compound with the formula NaNH 2.
It needs to be handled carefully. It can be harmful. Metallation of hydrocarbon acids by potassium amide and potassium methylamide in tetrahydrofuran and the relative hydride acidities". Halides such as geminal dihalides two halogens on one carbon and vicinal dihalides halogens on adjacent carbons undergo an elimination reaction in the presence of NaNH 2. ISBN Since vicinal dihalides are easily made by the reaction of alkenes with halogens such as Br2 or I2, this is a useful way of converting alkenes to alkynes. It is formed by ammonia and sodium. Are Acids! I have some questions about the possible SN2 competition when doing the double-dehalogenation of a dihalide to form an alkyne. Sodium amide , commonly called sodamide systematic name sodium azanide , is the inorganic compound with the formula NaNH 2. Sodium compounds. Synthesis of sym-dibenzo-1,5-cyclooctadiene-3,7-diyne and sym-dibenzo-1,3,5-cyclooctatrienyne, presumably planar conjugated eight-membered ring compounds Henry N. Chemical formula. Sodium amide is a strong base and hence used for deprotonating the weak acid and in elimination reactions.

0 thoughts on “Nanh2”