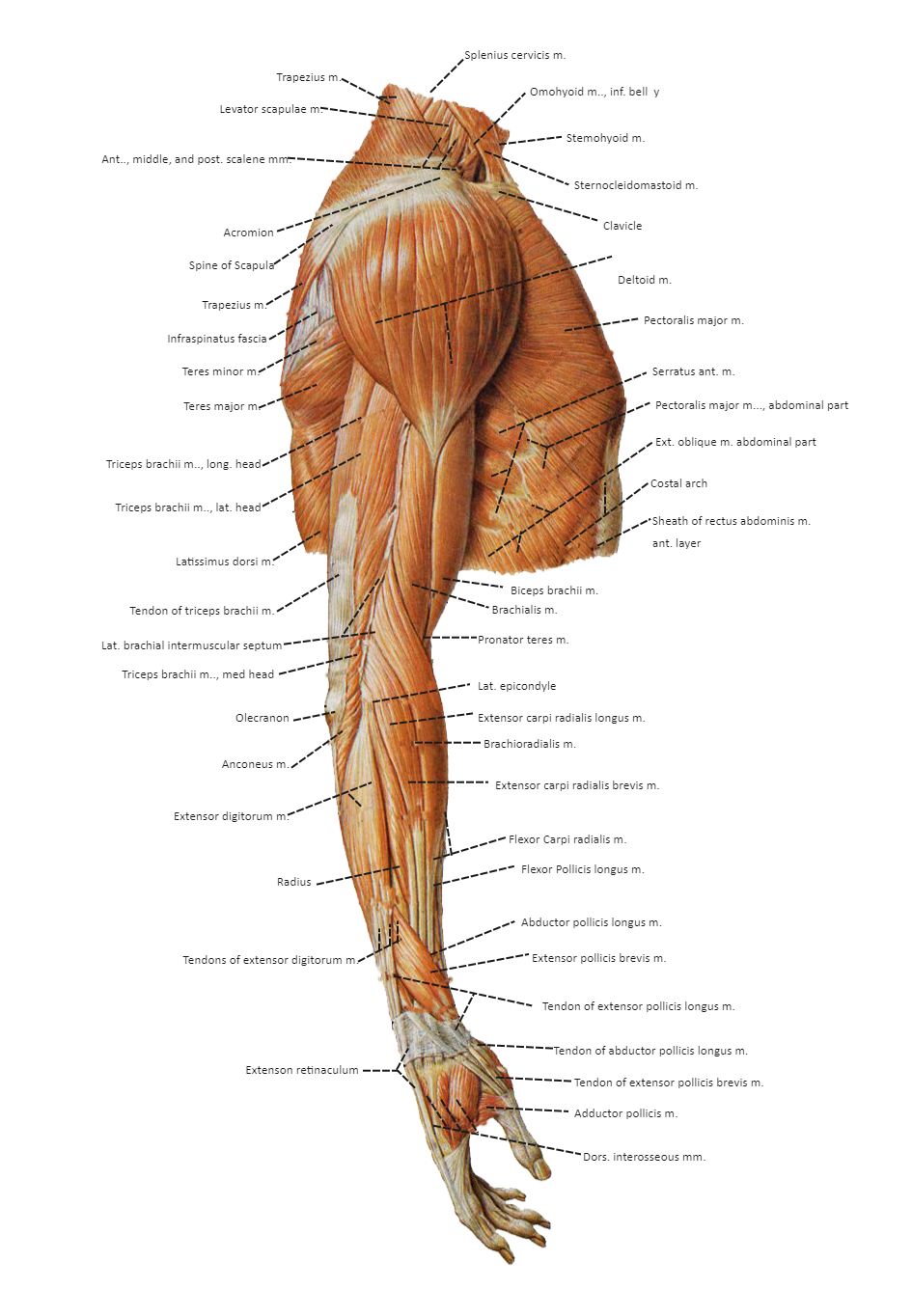
Muscles in the arm diagram
Search by image. We have more than , assets on Shutterstock. Our Brands.
Human arms anatomy diagram, showing bones and muscles while flexing. Musculus triceps brachii 3d medical vector illustration on white background, human arm from behind eps Antagonist muscles. The biceps is the chief flexors of the forearm. The triceps is an extensor muscle of the elbow joint. Muscles of shoulder and arm 3d medical vector illustration on white background eps Biceps muscle with anatomical skeletal medical arm structure outline diagram.
Muscles in the arm diagram
The upper arm is located between the shoulder joint and elbow joint. It contains four muscles — three in the anterior compartment biceps brachii, brachialis, coracobrachialis , and one in the posterior compartment triceps brachii. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the muscles of the upper arm — their attachments, innervation and actions. There are three muscles located in the anterior compartment of the upper arm — biceps brachii, coracobrachialis and brachialis. They are all innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve. A good memory aid for this is BBC — b iceps, b rachialis, c oracobrachialis. Arterial supply to the anterior compartment of the upper arm is via muscular branches of the brachial artery. The biceps brachii is a two-headed muscle. Although the majority of the muscle mass is located anteriorly to the humerus , it has no attachment to the bone itself. As the tendon of biceps brachii enters the forearm, a connective tissue sheet is given off — the bicipital aponeurosis. This forms the roof of the cubital fossa and blends with the deep fascia of the anterior forearm. The brachialis muscle lies deep to the biceps brachii, and is found more distally than the other muscles of the arm. It forms the floor of the cubital fossa. Fig 1 — The coracobrachialis, biceps brachii and brachialis muscles of the anterior upper arm.
This muscleusually referred to as your triceps, runs along your humerus and allows for the flexion and extension of your forearm.
Your arms contain many muscles that work together to allow you to perform all sorts of motions and tasks. Each of your arms is composed of your upper arm and forearm. Your upper arm extends from your shoulder to your elbow. Your forearm runs from your elbow to your wrist. Your upper arm contains two compartments, known as the anterior compartment and the posterior compartment. Your forearm contains more muscles than your upper arm does.
The arm extends from the shoulder to the wrist, including the upper arm and forearm. Different muscles may work together in intricate ways to help the arm, wrists, fingers, and hands function. Knowing about the form and function of each muscle and how they interact can help a person understand how muscles in the arm work. Keeping the arm muscles healthy and limber may help prevent issues from injury or overworking. This article discusses the function and anatomy of muscles in the arms, conditions that may affect the arms, and tips for arm muscle health. All the muscles in the body have different functions. So, when a person wants to move their arm or do something else, one or more of the muscles engage to perform the action. Muscles usually work in pairs and move in various ways: The basic functional movements include:. The upper arm is the area between the shoulder and elbow joints. There are two major compartments in the upper arm, each containing muscles.
Muscles in the arm diagram
The upper arm is located between the shoulder joint and elbow joint. It contains four muscles — three in the anterior compartment biceps brachii, brachialis, coracobrachialis , and one in the posterior compartment triceps brachii. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the muscles of the upper arm — their attachments, innervation and actions.
Globe prepaid internet promo 2019
Geography and Landscapes. Labeled educational scheme with long, medial and lateral head muscular system vector illustration. Labeled educational arm bone muscular inner parts detailed description with sarcomere magnification vector illustration. Sport injury - shoulder impingement , rotator cuff problems. Motor neuron controls muscle movement. The biceps brachii is a two-headed muscle. The palmaris brevis muscle lies just underneath the skin. Function: Extension of the arm at the elbow. Labeled inner skeleton and muscle structure scheme. A Text book of Naked Eye Anatomy.
The muscles of the arms attach to the shoulder blade, upper arm bone humerus , forearm bones radius and ulna , wrist, fingers, and thumbs. These muscles control movement at the elbow, forearm, wrist, and fingers.
This muscle allows your forearm to rotate outward so your palm faces up. Symbol of strength. The quadratus plantae is a muscle in the foot that extends from the anterior front of the calcaneus heel bone to the tendons of the digitorum…. Sport woman doing exercise with jumping jack pose for cardiovascular health and boosting your metabolism. Isolated vector illustration signs set. Arterial supply to the posterior compartment of the upper arm is via the profunda brachii artery. The triceps is an extensor muscle of the elbow joint. Necessary Necessary. Labeled educational medical movement of hand, arm and leg as extension, flexion, abduction and adduction vector illustration. Vector illustration. Structure of muscle with isolated myosin and actin closeup outline diagram. Structure of skeletal muscle fibers. It allows adduction of your upper arm and flexion of your shoulder.

You commit an error. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
There is a site, with an information large quantity on a theme interesting you.