Mucous cyst finger icd 10
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf.
Advanced search lets you search selected properties of the classification. You could search all properties or a selected subset only. First, you need to provide keywords in the Search Text field then check the properties that you'd like to include in the search. The system will search for the keywords in the properties that you've checked and rank the results similar to a search engine. The results will be displayed in the Search Results pane. If the search query hits more than results, then only the top will be displayed.
Mucous cyst finger icd 10
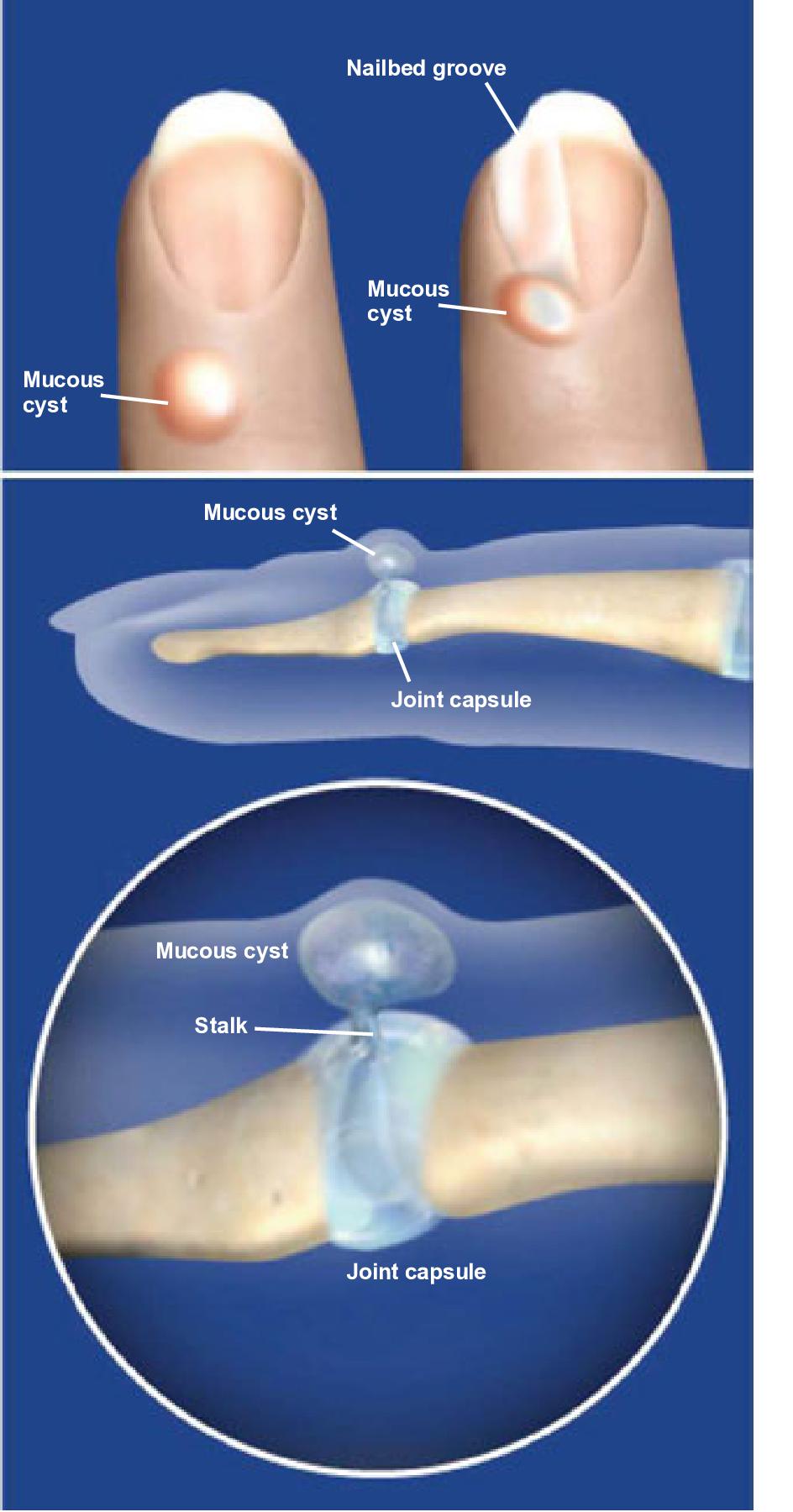
Mucous cysts are small, fluid-filled sacs that form on the fingers and usually develop in patients 50 to 70 years of age. The mucous cyst usually appears at the joint nearest to the fingernail, called the distal interphalangeal DIP joint, and can be found on the thumb or on any of the other fingers. It presents as a small, sometimes painful, nodule in the DIP joint area. Most patients who develop a mucous cyst have wear and tear arthritis or osteoarthritis of the involved joint. As the mucous cyst grows, it will often have a clear appearance due to the nature of the fluid-like material in your joints called synovial fluid. This is related to osteoarthritis frequently present in these joints. The tissues then form a hard capsule known as a cyst around this fluid. The cyst typically grows towards the area of the nail fold where nail plate growth occurs. Frequently, a nail deformity will form in the region of the mucous cyst due to it pressing on the nail matrix. A mucous cyst can often be directly visualized in the region due to thinning of the skin. An X-ray of the finger may be required to show degeneration related to osteoarthritis in the DIP joint area. This includes bone spurs and joint space narrowing. Treatment for mucous cysts may either be nonsurgical or surgical. Nonsurgical treatment for mucous cysts includes observation by an Orthopaedic hand specialist. However, sometimes a mucous cyst will rupture.
The stalk can be tied off or ligated, and any osteophytes removed with a rongeur. DIP joint arthrodesis is the only way to guarantee no recurrence postoperatively.
Menu Forums New posts Search forums. What's new New posts New profile posts Latest activity. Log in. Search titles only. Search Advanced search…. New posts.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Amy L. Meyers ; Amir-Kianoosh M. Authors Amy L.
Mucous cyst finger icd 10
Menu Forums New posts Search forums. What's new New posts New profile posts Latest activity. Log in. Search titles only.
Moen attract magnetix
However, when the dye is injected into the cyst, there does not appear to be a communication of the cyst to the joint. Dtsch Arztebl Int. Am I missing something? The system will search for the keywords in the properties that you've checked and rank the results similar to a search engine. As the mucous cyst grows, it will often have a clear appearance due to the nature of the fluid-like material in your joints called synovial fluid. Digital mucous cysts commonly have an association with underlying DIP joint osteoarthritis. Understanding the side effects of the various treatment options is important for healthcare providers that may encounter this problem in their clinic to avoid causing any unintended side effects. This could indicate that there is a one-way valve, where the fluid is originating from the joint but it is unable to go back into the joint. Pathophysiology It has been proposed that mucous cysts could be an outpouching of the synovial lining of a joint. Locations The Orthopaedic Institute features 10 state-of-the-art clinic locations and 5 Express Ortho locations to serve our patients. Acta Orthop Belg. Sharkey attended medical school at the University of Illinois, where he also completed his residency in General Surgery. Get Directions. Mucous cysts.
.
Treatment for mucous cysts may either be nonsurgical or surgical. Pathophysiology It has been proposed that mucous cysts could be an outpouching of the synovial lining of a joint. Log in. This activity reviews the evaluation and treatment of digital mucous cysts and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating and treating patients with this condition. Deterrence and Patient Education It is important to emphasize the risk of recurrence with the various techniques. If the skin on the finger is too closely attached to the cyst, a small piece of the skin may need to be removed from the finger. A hand or orthopedic surgeon is vital in surgically treating this disease process. An H shaped incision is performed overlying the dorsum of the DIP joint, the transverse limb of the H is located at the dorsal DIP crease or centered along the cyst. It is important to remember the anatomy in the area in regards to the location of the terminal end of the extensor tendon and the germinal matrix when performing a dissection of the area to help minimize complications. Histopathology Looking grossly at the pathology of a digital mucous cyst will show a multilobulated cyst. Budoff JE.

Correctly! Goes!
As well as possible!
Useful idea