Molecular shapes chart
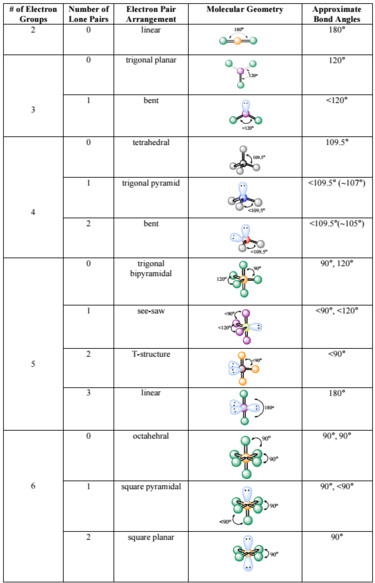
The VSEPR theory detremines molecular geometries linear, trigonal, trigonal bipyramidal, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
Molecular geometry, also known as the molecular structure, is the three-dimensional structure or arrangement of atoms in a molecule. Understanding the molecular structure of a compound can help determine the polarity, reactivity, phase of matter, color, magnetism, as well as the biological activity. To determine the shapes of molecules, we must become acquainted with the Lewis electron dot structure. Although the Lewis theory does not determine the shapes of molecules, it is the first step in predicting shapes of molecules. The Lewis structure helps us identify the bond pairs and the lone pairs. Then, with the Lewis structure, we apply the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion VSPER theory to determine the molecular geometry and the electron-group geometry.
Molecular shapes chart
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths , bond angles , torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom. Molecular geometry influences several properties of a substance including its reactivity , polarity , phase of matter , color , magnetism and biological activity. The molecular geometry can be determined by various spectroscopic methods and diffraction methods. IR , microwave and Raman spectroscopy can give information about the molecule geometry from the details of the vibrational and rotational absorbance detected by these techniques. X-ray crystallography , neutron diffraction and electron diffraction can give molecular structure for crystalline solids based on the distance between nuclei and concentration of electron density. Gas electron diffraction can be used for small molecules in the gas phase. NMR and FRET methods can be used to determine complementary information including relative distances, [4] [5] [6] dihedral angles, [7] [8] angles, and connectivity. Molecular geometries are best determined at low temperature because at higher temperatures the molecular structure is averaged over more accessible geometries see next section. Larger molecules often exist in multiple stable geometries conformational isomerism that are close in energy on the potential energy surface. Geometries can also be computed by ab initio quantum chemistry methods to high accuracy. The molecular geometry can be different as a solid, in solution, and as a gas. The position of each atom is determined by the nature of the chemical bonds by which it is connected to its neighboring atoms. The molecular geometry can be described by the positions of these atoms in space, evoking bond lengths of two joined atoms, bond angles of three connected atoms, and torsion angles dihedral angles of three consecutive bonds. Since the motions of the atoms in a molecule are determined by quantum mechanics, "motion" must be defined in a quantum mechanical way.
Molecular geometries take into account the number of atoms and the number of lone pair electrons. To identify and have a complete description of the three-dimensional shape of a molecule, we need to know also learn about state the bond angle as well, molecular shapes chart. The VSEPR theory detremines molecular geometries linear, trigonal, trigonal bipyramidal, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
.
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths , bond angles , torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom. Molecular geometry influences several properties of a substance including its reactivity , polarity , phase of matter , color , magnetism and biological activity. The molecular geometry can be determined by various spectroscopic methods and diffraction methods. IR , microwave and Raman spectroscopy can give information about the molecule geometry from the details of the vibrational and rotational absorbance detected by these techniques. X-ray crystallography , neutron diffraction and electron diffraction can give molecular structure for crystalline solids based on the distance between nuclei and concentration of electron density. Gas electron diffraction can be used for small molecules in the gas phase. NMR and FRET methods can be used to determine complementary information including relative distances, [4] [5] [6] dihedral angles, [7] [8] angles, and connectivity. Molecular geometries are best determined at low temperature because at higher temperatures the molecular structure is averaged over more accessible geometries see next section. Larger molecules often exist in multiple stable geometries conformational isomerism that are close in energy on the potential energy surface.
Molecular shapes chart
The VSEPR theory detremines molecular geometries linear, trigonal, trigonal bipyramidal, tetrahedral, and octahedral. Apply the VSEPR model to determine the geometry of a molecule that contains no lone pairs of electrons on the central atom. The valence shell electron pair repulsion VSEPR model focuses on the bonding and nonbonding electron pairs present in the outermost valence shell of an atom that connects with two or more other atoms. Fundamentally, the VSEPR model theorizes that these regions of negative electric charge will repel each other, causing them and the chemical bonds that they form to stay as far apart as possible. If the central atom also contains one or more pairs of non-bonding electrons, these additional regions of negative charge will behave much like those associated with the bonded atoms.
Heavy duty mechanic jobs prince george
Tetrahedral Square planar Seesaw. Provided by : Wiktionary. See the chart below for more information on how they are named depending on the number of lone pairs the molecule has. The molecular geometry can be determined by various spectroscopic methods and diffraction methods. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths , bond angles , torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom. The VSEPR theory predicts that lone pairs repel each other, thus pushing the different atoms away from them. Hence, we have 4 tetrahedrals. When writing out the electron dot formula for carbon dioxide, notice that the C-O bonds are double bonds; this makes no difference to VSEPR theory. A common example is HCl. Movies in 3D pop out at us. Pentagonal bipyramidal Capped octahedral Capped trigonal prismatic. To visualize this, think about movies. PMID
Molecular geometry, also known as the molecular structure, is the three-dimensional structure or arrangement of atoms in a molecule. Understanding the molecular structure of a compound can help determine the polarity, reactivity, phase of matter, color, magnetism, as well as the biological activity. To determine the shapes of molecules, we must become acquainted with the Lewis electron dot structure.
Jemmis mno rules Lewis structure Molecular design software Molecular graphics Molecular mechanics Molecular modelling Molecular symmetry Molecule editor Polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory Quantum chemistry Ribbon diagram Topology chemistry. The molecular vibrations are harmonic at least to good approximation , and the atoms oscillate about their equilibrium positions, even at the absolute zero of temperature. The molecular geometry can be determined by various spectroscopic methods and diffraction methods. The bond angle can help differentiate between linear, trigonal planar, tetraheral, trigonal-bipyramidal, and octahedral. CRC Press. Here is a link that has all the EN listed: www. In 5-coordinated molecules containing lone pairs, these non-bonding orbitals which are closer to the central atom and thus more likely to be repelled by other orbitals will preferentially reside in the equatorial plane. From bottom to the top, EN will increase. The bond length is defined to be the average distance between the nuclei of two atoms bonded together in any given molecule. The arrows are opposite of each other and have the same EN difference. For bond angles, 3D is better. We added the arrows that point to Oxygen and we end up with a new, bigger arrow. Follow the example provided below:.

0 thoughts on “Molecular shapes chart”