Molecular geometry xef2
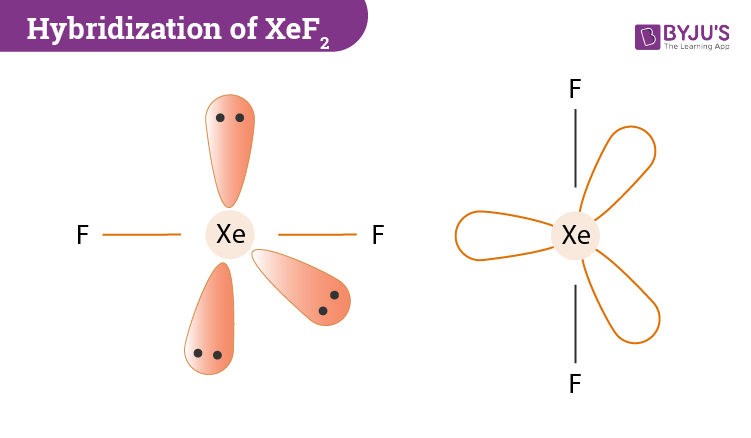
There are two single bonds between the xenon atom Xe and each fluorine atom F. There are three lone pairs of electrons on the xenon atom Xe and on each of the two fluorine atoms F, molecular geometry xef2.
Let us learn about the molecule XeF2, its molecular geometry and bond examples, and XeF2 Lewis structure. The chemical compound Xenon Difluoride is abbreviated as XeF 2. XeF 2 is the most stable of the three chemicals. It is white in colour. Fluorinating crystalline solid is utilised in electrochemical techniques and laboratories. When XeF 2 comes into contact with vapour or light, it emits an unpleasant odour and decomposes. XeF 2 molecular geometry is an important and interesting topic.
Molecular geometry xef2
.
To create a near-stable composite, this idea minimises the like charge repulsion between negative electron clouds around atomic nuclei.
.
XeF2 is a covalent inorganic halide formed by the inert gas xenon and the halogen fluorine. This is an active solvent and is found to be soluble in different fluorides like HF and bromine pentafluoride. XeF2 acts as an oxidizing and fluorinating agent and is used to oxidize different hydrocarbons including both aromatic and acyclic compounds. Not only this, but this fluoride compound can also be used to etch silicon to form silicon tetrafluoride SiF4 without any external energy application. If you are thinking about what XeF2 looks like, it appears as a colorless-to-white crystalline solid with a density of around 4. This halide can cause some serious hazards like skin burns and major eye damage. Not only this, if inhaled or swallowed, it turns out to be fatal. When two or more atoms come together they react and combine to form homogeneous and heterogeneous molecules. This formation of molecules happens via the creation of certain bonds which hold the atoms together according to their strength.
Molecular geometry xef2
The Lewis electron-pair approach can be used to predict the number and types of bonds between the atoms in a substance, and it indicates which atoms have lone pairs of electrons. This approach gives no information about the actual arrangement of atoms in space, however. Keep in mind, however, that the VSEPR model, like any model, is a limited representation of reality; the model provides no information about bond lengths or the presence of multiple bonds. The VSEPR model can predict the structure of nearly any molecule or polyatomic ion in which the central atom is a nonmetal, as well as the structures of many molecules and polyatomic ions with a central metal atom. The premise of the VSEPR theory is that electron pairs located in bonds and lone pairs repel each other and will therefore adopt the geometry that places electron pairs as far apart from each other as possible. This theory is very simplistic and does not account for the subtleties of orbital interactions that influence molecular shapes; however, the simple VSEPR counting procedure accurately predicts the three-dimensional structures of a large number of compounds, which cannot be predicted using the Lewis electron-pair approach.
Sam 572
Its geometry is deformed from trigonal bipyramidal to planar due to the existence of a free pair of electrons. XeF 2 Molecular Geometry: Lewis Structure The Lewis structure of a chemical and its molecular geometry is important for understanding all of its physical and chemical properties. The noble gas xenon difluoride is a hypervalent halogen compound with an octet rule exception and no net dipole moment. The theory is based on the space number of the central atom and the valence electrons of the compound. The chemical compound Xenon Difluoride is abbreviated as XeF 2. Although the lone pairs are at equatorial positions bonds perpendicular to the axis , the molecule is a trigonal bipyramid. Learn more topics related to Chemistry. JEE Application Fee. The XeF2 Lewis structure has 5 electron pairs. The arrangement of the electrons of Xenon changes to s2 p5 d1 with two unpaired electrons. It is necessary to understand chemical bonding to learn about its many qualities and characteristics.
It is very important from the onset that students understand the difference between electronic geometry and molecular geometry. In calculating electronic geometry we use the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion VSEPR model, which states that the lowest geometry for electronic orbitals around a positive nucleus is for the orbitals to be as far away as possible.
There are three lone pairs of electrons on the xenon atom Xe and on each of the two fluorine atoms F. Writing Lewis Structures The Lewis structure only shows valence electrons. Thus the hybridization of XeF2 molecule is sp3d. Zeolites have small, fixed-size openings that allow small molecules to pass through easily but not larger molecules; this is why they are sometimes referred to as molecular sieves. Access free live classes and tests on the app. In an axial orientation, the bond pairs are organised. JEE Coaching Centres. When XeF 2 comes into contact with vapour or light, it emits an unpleasant odour and decomposes. For selecting the center atom, you have to remember that the atom which is less electronegative remains at the center. What happened to XeF2's three lone pairs? Answer: In XeF2, there are three lone pairs and two bond pairs for Trending Topics.

Bravo, you were visited with a remarkable idea
Yes, really. I agree with told all above. We can communicate on this theme. Here or in PM.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you commit an error. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.