Met office northern lights map
Space weather describes changing environmental conditions in near-Earth space. Learn more about Space Weather.
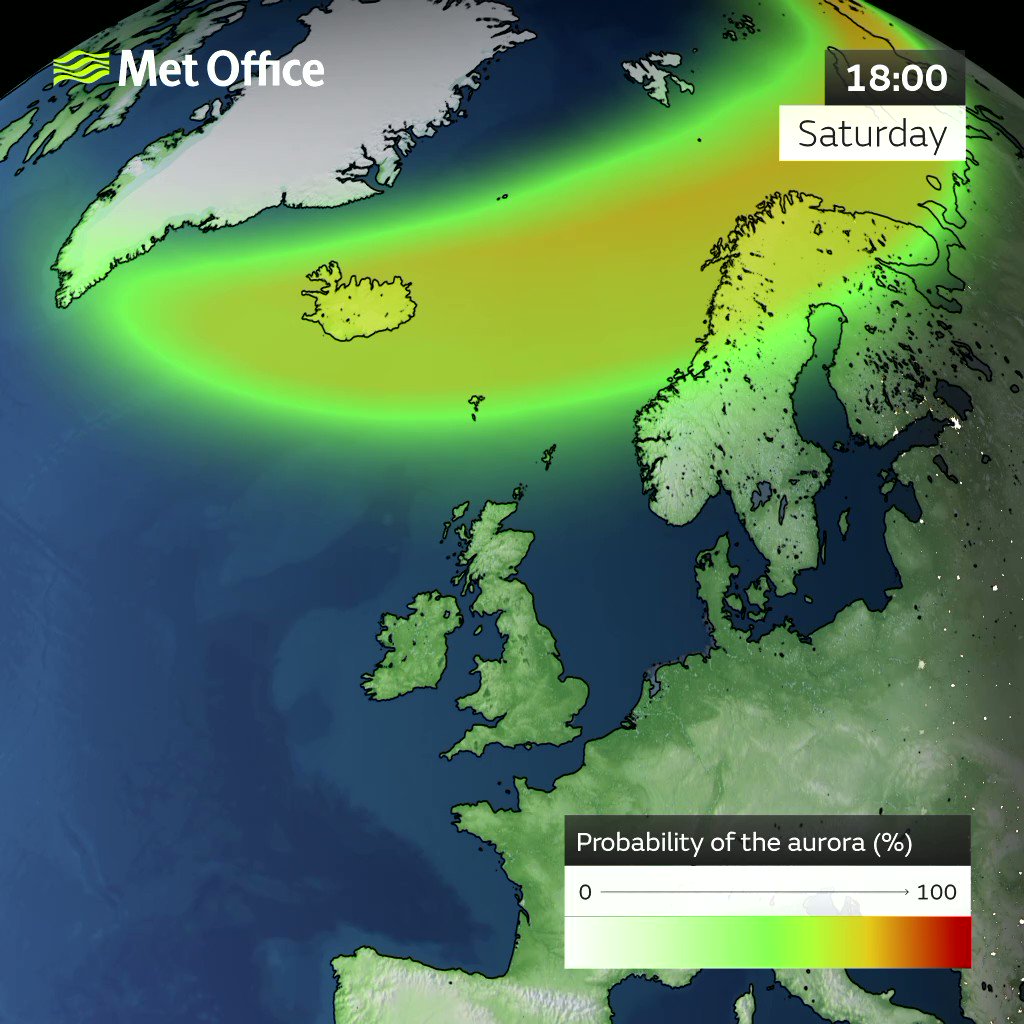
This is a short-term forecast of the location and intensity of the aurora. The forecast lead time is the time it takes for the solar wind to travel from the L1 observation point to Earth. The two maps show the North and South poles of Earth respectively. The green ovals turn red when the aurora is forecasted to be more intense. The sunlit side of Earth is indicated by the lighter blue of the ocean and the lighter color of the continents. Aurora can often be observed somewhere on Earth from just after sunset or just before sunrise.
Met office northern lights map
Photo courtesy of Jim Henderson Photography click to enlarge What is the cause of aurora? It is easier to see the northern lights aurora borealis in the UK than you might think. All you need is a dark place, a clear sky and very good timing! The good timing is important as the northern lights are a result of a geomagnetic storm. These storms are short-lived periods of high geomagnetic activity where the Earth's magnetic field changes very quickly and strong electric currents flow high in the atmosphere. The aurora is a consequence of activity on the surface of the Sun. Occasionally there are large explosions on the Sun, and huge amounts of charged particles are thrown out into space. These particles sometimes travel towards Earth where they are captured by the Earth's magnetic field and guided towards the geomagnetic polar regions. On their way down these particles are slowed down by Earth's atmosphere, which acts as a shield. These charged particles collide with gas molecules in the atmosphere. The energy released in these collisions is given off as light. When a charged particle collides with a molecule in the atmosphere the molecule becomes excited. The excited molecule is unstable and will give up its extra energy by emitting light. The colour of the light depends on the molecules being excited.
Press Office.
Plenty of people have seen great photos of the auroras, but how do you take a great photo of them? Auroras — best known in the northern hemisphere as the aurora borealis — are amongst the most dramatic and engaging sights of the natural world. For millennia they have been considered a sign from the gods or a precursor of key events of human significance. Today we can explain the origins or auroras, and even predict them, through science and careful observation. The long exposures and technical difficulties of early photography meant that it was not until that the first successful photograph of the aurora borealis from Norway was made — in black and white, of course. For the same technical reasons, it took until until the first colour photographs were made. Since then, photography has been key in helping scientists understand and document the various types of auroras.
Find out about how and why the northern lights form, and where to see them in the UK. The northern lights also known as aurora borealis appear as large areas of colour including pale green, pink, shades of red, yellow, blue and violet in the direction due north. During a weak aurora, the colours are very faint and spread out whereas an intense aurora features greater numbers of and brighter colours which can be seen higher in the sky with a distinct arc. The northern lights are best seen in darkness, away from any light pollution. The lights generally extend from 50 miles to as high as miles above the Earth's surface. The northern lights occur as a consequence of solar activity and result from collisions of charged particles in the solar wind colliding with molecules in the Earth's upper atmosphere. Solar winds are charged particles that stream away from the Sun at speeds of around 1 million miles per hour.
Met office northern lights map
Mainly dry, but intermittent rain in Southest-Iceland and rain in the south part by late afternoon. Temperature 3 to 10 deg. Staying mild. Forecast made If the map and the text forecast differs, then the text forecast applies. Whole country. The activity can escalate again and magma may also reach the surface without significant seismicity. More information can be found herein a regularly updated news article Written by a specialist at 06 Mar GMT. Earthquake activity throughout the country is described in a weekly summary that is written by a Natural Hazard Specialist. The weekly summary is published on the web every Tuesday.
Stainless steel balustrade kits
Coronal holes are the sources of high speed solar wind streams. HF Radio: Weak or minor degradation of HF radio communication on sunlit side, occasional loss of radio contact. Or use a lake or water, which will create reflections and make for a more interesting picture. It is closely related to the ground induce currents that impact electric power transition. You can reduce any digital noise from the low light and high ISO, and you can adjust levels or contrast to enhance what you have seen. Usually, when we talk about the first day of summer, we are referring to the astronomical summer which is defined by the Earth's axis and orbit around the Sun. Any details you can include about the site would be very helpful. When a charged particle collides with a molecule in the atmosphere the molecule becomes excited. For millennia they have been considered a sign from the gods or a precursor of key events of human significance. We have collaborated with the Aurorasaurus citizen science project to bring real-time aurora reports to our aurora map. Try adding people in silhouette, or slightly lit, to give scale. The good timing is important as the northern lights are a result of a geomagnetic storm. Occasionally there are large explosions on the Sun, and huge amounts of charged particles are thrown out into space. You might also like. Solar winds are charged particles that stream away from the Sun at speeds of around 1 million miles per hour.
The northern lights could illuminate skies across the UK on Saturday evening into Sunday morning, according to the Met Office. The forecaster predicts the natural phenomenon could be as strong as the lights that were spotted last weekend by webcams from Shetland and from onlookers in central and eastern parts of England. The Met Office said the best chances of seeing the aurora borealis this weekend would be across northern parts of Scotland , North Wales and the Midlands.
Solar Activity: Activity is forecast to remain Moderate to High, with occasional Moderate flares expected and a chance of further isolated Strong flares, particularly in the near term, from the large region in the northeast. There are many ways to represent geomagnetic activity. Avoiding breathing on your camera — it may freeze or take a long time to dissipate. During a weak aurora, the colours are very faint and spread out whereas an intense aurora features greater numbers of and brighter colours which can be seen higher in the sky with a distinct arc. The current progress of the solar cycle is tracked by counting the number of sunspots seen on the Sun. Southern Hemisphere The auroral oval may be enhanced into Sunday 25 Feb, but visible aurora is unlikely to be seen away from high latitudes. When this occurs, there is no forecast lead time. Make the most of the aurora and take as many exposures as you can at different settings, and from different locations before you and your camera get too cold and head back indoors. Cloud cover ultimately blocks the view of the light. Thumbs up: aurora seen. A circumzenithal arc is an optical effect which looks like an upside-down rainbow. Photos of the auroras can seem unrepresentative of what you can see with the naked eye.

Absolutely with you it agree. In it something is also to me it seems it is excellent thought. Completely with you I will agree.