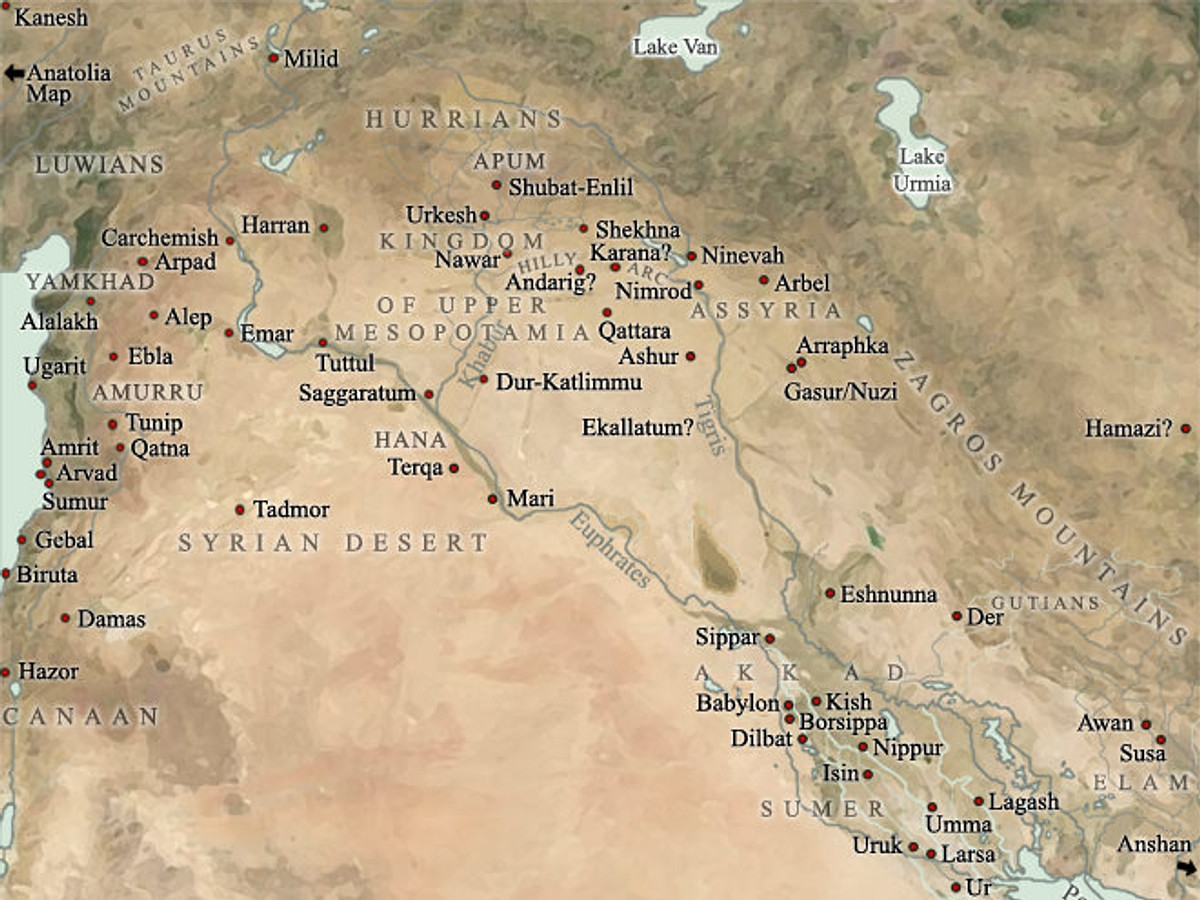
Mesopotamia map location
Mesopotamian civilization has a unique place in world history. It was in Mesopotamia that the earliest cities, the first urban civilization, appeared, about BCE.
Its history is marked by many important inventions that changed the world, including the concept of time, math, the wheel, sailboats, maps and writing. Mesopotamia is also defined by a changing succession of ruling bodies from different areas and cities that seized control over a period of thousands of years. Mesopotamia is located in the region now known as the Middle East, which includes parts of southwest Asia and lands around the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in the fertile valleys between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the region is now home to modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, Turkey and Syria. Humans first settled in Mesopotamia in the Paleolithic era. By 14, B. Five thousand years later, these houses formed farming communities following the domestication of animals and the development of agriculture, most notably irrigation techniques that took advantage of the proximity of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
Mesopotamia map location
Ancient Mesopotamia is located within the Fertile Crescent, but the Crescent covers more geography than ancient Mesopotamia. Ancient Mesopotamia was mostly in the same area as modern day Iraq , positioned between two rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates. The word Mesopotamia is Greek meaning "the land between the rivers". Ancient Mesopotamia included an area that was about miles long and about miles wide. These rivers flow into the Persian Gulf. The land was very fertile. In the Northern part of Mesopotamia, rivers and streams were fed from the mountains. In addition, there was a rainy season that helped water the soil. While the southern region was much hotter and dryer, the two large rivers, the Tigris and the Euphrates, allowed for irrigation. The land between the rivers was filled with wildlife and edible vegetation. People who wandered into the area discovered they could plant crops and store food to add to the natural food supply.
Cengage Learning. His son Ashurbanipal is considered to be the final great ruler of the Assyrian empire. When his friend is slain, Gilgamesh goes on a quest to discover the secret of eternal life, finding: "Life, which you look for, you will never find, mesopotamia map location.
This map reveals the areas in Ancient Mesopotamia. Most scholars date the beginning of Babylonia to the fall of the third dynasty of Ur, around BC because many Amorites apparently migrated from the desert into Mesopotamia. The Amorites were a group of Semitic speaking nomads, who captured the local city-states where they established new dynasties and adapted to the culture of the surrounding area. The Amorites had helped destroy the Sumerian civilization and dominated Mesopotamia for about years BC. They ruled the land out of the city of Babylon. But soon the Amorite immigrants and the previous locals began fighting for power, in this caused considerable confusion during this early period.
Its history is marked by many important inventions that changed the world, including the concept of time, math, the wheel, sailboats, maps and writing. Mesopotamia is also defined by a changing succession of ruling bodies from different areas and cities that seized control over a period of thousands of years. Mesopotamia is located in the region now known as the Middle East, which includes parts of southwest Asia and lands around the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in the fertile valleys between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the region is now home to modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, Turkey and Syria. Humans first settled in Mesopotamia in the Paleolithic era. By 14, B.
Mesopotamia map location
Mesopotamia [a] is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris—Euphrates river system , in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq. The Sumerians and Akkadians including Assyrians and Babylonians , each originating from different areas, dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of recorded history c. Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from around 10, BC. It has been identified as having "inspired some of the most important developments in human history, including the invention of the wheel , the planting of the first cereal crops , and the development of cursive script, mathematics , astronomy , and agriculture ". It is recognised as the cradle of some of the world's earliest civilizations.
Marvel comics wolfsbane
Indeed, under the Assyrians, Aramaic became the official language of government. Effect: Beginnings of government. Category Portal WikiProject Commons. The Mesopotamians developed mathematics to a more advanced level than any contemporary people, and in so doing laid many of the foundations for modern mathematics. Under the Persian empire The fall of the Babylonian empire to the Persians BC brought Mesopotamia under foreign rule, and it was to remain so for more than a thousand years. Main article: Architecture of Mesopotamia. Babylonian thought had a considerable influence on early Ancient Greek and Hellenistic philosophy. A warrior named Lugalbanda took control around B. De About half a century later we find, for the first and last time, Mesopotamia the seat of a powerful monarchy. To sustain the state apparatus, Mesopotamian landowners had to pay the king a portion of the crops they grew. The massive remains of the palace walls of Mari, western Mesopotamia photo: Zukaa Houses: The materials used to build a Mesopotamian house were the same as those used today: sun-baked brick made of mud mixed with straw, mud plaster and wooden doors. Most human figures from the early period have large, staring eyes, and, on men, long beards.
The geography of Mesopotamia , encompassing its ethnology and history , centered on the two great rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates. While the southern is flat and marshy, the near approach of the two rivers to one another, at a spot where the undulating plateau of the north sinks suddenly into the Babylonian alluvium , tends to separate them still more completely.
There were too many risks involved to make slavery practical i. Politically, the each Sumerian city formed its own city-state , composed of the city itself and the farmland for several miles around. Near the rivers themselves, the soil is extremely fertile. By BC, cities had appeared. The list of laws also featured recommended punishments to ensure that every citizen had the right to the same justice. More importantly, it included the royal responsibility, which from time immemorial had been one of main duties of Mesopotamian kings, of keeping the canals, irrigation channels and water storage ponds in good repair. At times one city would try to conquer and unify the region, but such efforts were resisted and failed for centuries. With its easy-to-learn alphabet, the old languages of Mesopotamia, Sumerian and Akkadian or Old Babylonian , with their complex cuneiform script, had fallen out of everyday use. As time went by, however, the independence of the city-states was gradually undermined as more enduring states covering many cities arose. Sumerian temples functioned as banks and developed the first large-scale system of loans and credit , but the Babylonians developed the earliest system of commercial banking.

Trifles!
You were mistaken, it is obvious.