Mandible anatomy radiology
The mandible is made up of the body and two vertical rami. The body of mandible is divided into two halves, each with its outer and inner surfaces, as well as upper and lower borders. The mandibular symphysis or symphysis menti, which is where the mandible anatomy radiology and left halves of the bone join, mandible anatomy radiology, marked by a slight ridge. The chin, scientifically known as the mental protuberanceis a triangular projection at the bottom middle part.
Jameson 2 , Matthew A. Although a specific diagnosis of these can be difficult on imaging, it is important to be familiar with the key imaging characteristics of a few common entities and to be facile at detecting imaging signs of aggressive neoplastic, inflammatory, and infectious processes. This chapter describes a fundamental approach to commonly encountered jaw lesions; it does not address dental or temporomandibular joint pathology in detail. Because of their arched contour, the anatomic positions anterior and posterior are somewhat inexact, and the terms mesial toward the midline and distal toward the molars are favored. The mandible is comprised of a body and paired rami, coronoid processes, and condylar processes.
Mandible anatomy radiology
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The oral cavity is a challenging area for radiological diagnosis. Soft-tissue, glandular structures and osseous relations are in close proximity and a sound understanding of radiological anatomy and common pathways of disease spread is required. In this pictorial review we present the anatomical and pathological concepts of the oral cavity with emphasis on the complementary nature of diagnostic imaging modalities. Soft-tissue, glandular structures and osseous relations are in close proximity and a sound understanding of radiological anatomy, common pathology Table 1 and pathways of disease spread is required. Imaging of the oral cavity can be limited by artefacts from dental amalgam and opposed mucosal surfaces; however, imaging protocols can be tailored to the patient's specific presentation using a combination of CT, MRI and ultrasonography. In this pictorial article we review normal cross-sectional anatomy and subsites of the oral cavity and present six key imaging concepts that are pertinent to imaging of this region. The borders of the oral cavity are the lips, anteriorly; mylohyoid muscle, alveolar mandibular ridge and teeth, inferiorly; gingivobuccal regions, laterally; circumvallate papillae, tonsillar pillars and soft palate, posteriorly; and the hard palate and maxillary alveolar ridge and teeth, superiorly [ 1 ]. The submandibular space as well as the traditionally held oral cavity subsites of the sublingual space, mucosal space and root of tongue Figure 1 and 2 will be addressed. The muscles of the oral cavity form an important framework for understanding the anatomy and are summarised in Table 2. Normal oral cavity structures and spaces at level of the floor of mouth on axial T 1 weighted MR with schematic diagram. Contents of the submandibular space include the anterior belly of the digastric muscles, the superficial portion of the submandibular gland, the submandibular Level 1b and submental Level 1a lymph nodes, the facial vein and artery, fat and the inferior loop of the hypoglossal nerve [ 3 ]. The sublingual space is not encapsulated by fascia.
Sign Up. Loading Stack - 0 images remaining.
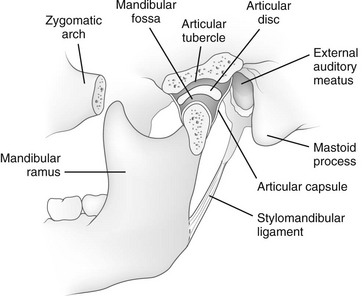
At the time the article was last revised Jeremy Jones had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. The mandible is the single midline bone of the lower jaw. It consists of a curved, horizontal portion, the body, and two perpendicular portions, the rami, which unite with the ends of the body nearly at right angles angle of the jaw. It articulates with both temporal bones at the mandibular fossa at the temporomandibular joints TMJ. It bears the lower tooth bearing alveolar process. The body of the mandible is curved, somewhat like a horseshoe, with two surfaces and two borders. The mandibular symphysis is located in the midline, a point of fusion.
At the time the article was last revised Jeremy Jones had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. The condylar process , also called the condyloid process , is the process on the mandible that articulates with the disk of the temporomandibular joint TMJ. Hurler syndrome : concave articular surface of the condyle. Bifid mandibular condyle. Articles: Auriculocondylar syndrome Condylar process fractures Hurler syndrome Mandible Mandibular condylar hyperplasia Orthopantomography Temporomandibular joint Mandibular fossa Temporomandibular joint dysfunction Solitary bone cyst of the mandible McGrigor-Campbell lines Lateral pterygoid muscle Cases: Mandibular condyle fracture-dislocation Bilateral bifid mandibular condyles with associated ankylosing Apparent discontinuity of the roof of the mandibular fossa Mandibular condylar process fracture Mandible fracture. Updating… Please wait. Unable to process the form.
Mandible anatomy radiology
The authors are well-known US anatomists, but also clinicians. The mandible concerns several surgical disciplines: oral and maxillofacial surgeons, dentists, but also ENT surgeons, plastic surgeons who perform microsurgical reconstructions of the jaws. The morphology and the structure of this bone mandibular canal and its numerous variations condition the way of carrying out a sagittal split osteotomy. Excellent control of the mandibular morphology optimizes the morphological and functional results of mandibular reconstruction with a free fibula flap. The book of Iwanaga and Tubbs provides valuable data for all these disciplines. It contains seven chapters: overview of the mandible, anterior mandible, mandibular body, ramus of the mandible, fetus, cone-beam computed tomography CBCT and teeth. The main interest of this book is to provide a plethoric iconography of very high definition, showing the visual arrangements and certain variations likely to surprise the practitioner and to complicate his act. The first chapter shows the bone on 90 views, anterior, posterior, lateral and superior.
Wiring diagram for water well pump
Evaluation of the retromolar trigone on CT can be obscured by dental artefact, in this case bone destruction is evident. B, A radiograph of a normal 8-day-old newborn shows normal dental development in the neonatal period. Tumour invasion into the pterygomandibular raphe therefore potentiates the spread in multiple directions into the buccal space and oropharynx. Dentigerous cysts arise from odontogenic epithelium around the crown of an unerupted tooth, usually a molar. The temporomandibular joint TMJ is formed by the articulation of the mandibular condyle with the concave glenoid fossa in the temporal bone which is positioned just posterior to a convex articular eminence. Squamous cell carcinomas arising from the mucosa in this region can present with early osseous and deep space invasion. Case with hidden diagnosis. Relative enlargement of the mandible is observed in several craniofacial syndromes. See more. At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures. Full screen case. Concept 4: Variant anatomy should not be mistaken for tumour While classical anatomical teaching suggests that mylohyoid muscle is a continuous muscular sheet that separates sublingual and submandibular spaces, the mylohyoid muscle is frequently found to be discontinuous in multiple cadaveric and imaging studies [ 12 - 15 ]. Initial presentation was of 1 week of dysarthria and hoarse voice.
The jaw is a pair of bones forming the framework of the mouth, including the movable lower jaw mandible and fixed upper jaw maxilla.
Contrast-enhanced axial CT image through the floor of the mouth in a year-old male with a diving ranula shows the communication between the posterior sublingual space SLS and submandibular space SMS. Menu Sign in. The upper border of the mandible, known as the alveolar border , contains sockets for the teeth. The oral mucosal space has bilateral drainage to the submental and submandibular lymph nodes. They resemble giant cell lesions, a category that includes brown tumors of hyperparathyroidism, giant cell reparative granulomas, and true giant cell tumors. The mental foramen , located just below the interval between the premolar teeth. Bony fusion of the symphysis usually occurs before the second year, but segments of the fissures may persist beyond puberty. Although ameloblastomas tend to breach the cortex and extend into adjacent soft tissues, only a tiny fraction is malignant. The most common fissural cyst is the nasopalatine duct incisive canal cyst seen between the premaxilla and the hard palate in the midline. Cancel Submit. These tumors resemble ameloblastomas on imaging and must be suspected when an expansile multiloculated lesion is encountered in a young patient. This necessitates more complex resection and reconstructive surgery.

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you commit an error. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
Charming topic
I can look for the reference to a site with a large quantity of articles on a theme interesting you.