Macroeconomics unit 1 study guide basic economic concepts
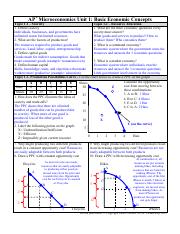
Capital - all manufactured aids to production tools, machinery, equipment, and factory, storage, transportation, and distribution facilities used in producing goods and services. Labor - physical and mental talents of individuals available and usable in producing goods and services. Entrepreneurial ability - the entrepreneur 1 takes the initiative in combining the other resources to produce a good or service. Production Possibilities Curve.
Scarcity is the basic problem in economics in which society does not have enough resources to produce whatever everyone needs and wants. Basically, it is unlimited wants and needs vs. Scarcity is faced by all societies and economic systems. Since we are faced with scarcity , we must make choices about how to allocate and use scarce resources. Economics is the study of how individuals, firms, and governments deal with scarcity.
Macroeconomics unit 1 study guide basic economic concepts
.
C money spent on books and supplies. The curve bows outwards because of the Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost, which states that the amount of a good which has to be sacrificed for each additional unit of another good is more than was sacrificed for the previous unit.
.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Donate Log in Sign up Search for courses, skills, and videos. Unit 1. Unit 2.
Macroeconomics unit 1 study guide basic economic concepts
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Donate Log in Sign up Search for courses, skills, and videos. Unit 1. Unit 2. Unit 3. Unit 4. Unit 5.
Draco malfoy aesthetic
Trade-offs — each of the alternative choices that you gave up when making a decision. This is done by dividing your marginal utility MU by the price of the product. Macroeconomics Microeconomics is the study of how individuals, households, and firms make decisions and allocate resources. How will goods and services be produced? Land - all natural resources usable in the production process Capital - all manufactured aids to production tools, machinery, equipment, and factory, storage, transportation, and distribution facilities used in producing goods and services Labor - physical and mental talents of individuals available and usable in producing goods and services Entrepreneurial ability - the entrepreneur 1 takes the initiative in combining the other resources to produce a good or service. B wages the student gave up to attend college. There are several factors that can cause the production possibilities curve to shift. This question is answered after the production of goods and services, as it is decided who should be allowed to consume the goods and services that have been produced. Capital - all manufactured aids to production tools, machinery, equipment, and factory, storage, transportation, and distribution facilities used in producing goods and services. The curve bows outwards because of the Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost, which states that the amount of a good which has to be sacrificed for each additional unit of another good is more than was sacrificed for the previous unit.
Advanced Placement AP. Want to know how to study for AP Macroeconomics? All the study tools we provide below are designed to walk you through how to study for the AP Macroeconomics exam!
The advantage of this type of economic system is that it is easier to produce goods and make sure everyone is receiving the basic necessities. Since 2 is less than 4, Canada has comparative advantage in coal. Terms of Trade — the rate at which one good can be exchanged for another. Change in the quantity or quality of resources. If you are given total utility TU , you must first calculate marginal utility MU. Economic freedom - businesses, workers, consumers have a high degree of freedom in economic activities 6. Comparative Advantage — the ability to produce a good at the lowest opportunity cost. Scarcity is faced by all societies and economic systems. Output problems focus on data associated with what each party can produce with a given set of resources and who should specialize in each good. E money spent on clothing expenses. Another advantage is that it rewards the most efficient producers with the highest profit, as well as encouraging innovation in an effort to meet customer needs.

0 thoughts on “Macroeconomics unit 1 study guide basic economic concepts”