Lvf medical abbreviation
The heart's pumping action moves oxygen-rich blood from the lungs lvf medical abbreviation the left atrium, lvf medical abbreviation, then on to the left ventricle, which pumps the blood to the rest of the body. The left ventricle supplies most of the heart's pumping ebay th, so it's larger than the other chambers and essential for normal function. In left-sided or left ventricular heart failure, the left side must work harder to pump the same amount of blood.
At the time the article was last revised Francis Deng had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Left heart failure or left ventricular failure is the type of heart failure attributed to left ventricular dysfunction. When the left ventricle is unable to pump blood effectively out of the heart, pulmonary edema develops. Congestion can progress to right heart failure , with manifestations such as peripheral edema. Left heart failure is further subdivided based on left ventricular ejection fraction 1 :. Articles: Left atrial enlargement Non-cardiogenic pulmonary oedema Upper lobe pulmonary venous diversion Chronic coronary syndrome Restrictive cardiomyopathy Kawasaki disease Cardiogenic pulmonary oedema Stag's antler sign lungs Pulmonary oedema Massive pulmonary embolism Ankylosing spondylitis cardiovascular manifestations RANZCR key conditions assessment Medical abbreviations and acronyms L Papillary muscle rupture Pulmonary hypertension Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Pericardiocentesis Cases: Cardiogenic pulmonary edema Upper lobe pulmonary venous diversion Pulmonary oedema Multiple choice questions: Question
Lvf medical abbreviation
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Conceived and designed the experiments: IG. Analyzed the data: IG. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: CL. Patients with heart failure HF have a poor prognosis. To evaluate the long term clinical outcome of patients with HF and preserved LVF and predictors of outcome. We prospectively evaluated patients hospitalized with a definite clinical diagnosis of HF. Patients were followed for a mean of 6. The adjusted survival rate by Cox regression analysis was also not significantly different hazard ratio 1. The event free survival from death or heart failure re-hospitalization was also low in both groups and not significantly different between patients with preserved vs.
Multivariate Cox regression analysis was used to evaluate independent variables that determined survival. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: CL. Outcomes in heart failure patients with preserved ejection fraction: mortality, readmission, and functional decline, lvf medical abbreviation.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Johnny Chahine ; Heidi Alvey. Authors Johnny Chahine 1 ; Heidi Alvey 2. Left heart failure occurs when there is dysfunction of the left ventricle, resulting insufficient delivery of blood to vital organs.
Acute left ventricular failure occurs when an acute event results in the left ventricle being unable to move blood efficiently through the left side of the heart and into the systemic circulation. Cardiac output is the volume of blood ejected by the heart per minute. Stroke volume is the volume of blood ejected during each beat. Cardiac output is the product of stroke volume x heart rate. When blood cannot flow efficiently through the left side of the heart, there is a backlog of blood waiting in the left atrium , pulmonary veins and lungs. As these areas experience an increased volume and pressure of blood, they start to leak fluid and cannot reabsorb excess fluid from the surrounding tissues, resulting in pulmonary oedema. Pulmonary oedema is where the lung tissue and alveoli are filled with interstitial fluid. This interferes with normal gas exchange in the lungs, causing shortness of breath and reduced oxygen saturation.
Lvf medical abbreviation
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Conceived and designed the experiments: IG. Analyzed the data: IG. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: CL. Patients with heart failure HF have a poor prognosis. To evaluate the long term clinical outcome of patients with HF and preserved LVF and predictors of outcome. We prospectively evaluated patients hospitalized with a definite clinical diagnosis of HF.
Dothan news
NYHA Functional class was not significantly different between the two groups. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Last revised:. Am J Cardiol. Coronary angiography in worsening heart failure: determinants, findings and prognostic implications. Proportionality assumptions of the Cox regression models were evaluated by log—log survival curves and with the use of Schoenfeld residuals. Positive hepatojugular reflux exerting manual pressure on the congested liver causing increased jugular venous pressures. Analysis of predictors in each group separately revealed that significant predictors in patients with preserved LVF were age, functional capacity and serum urea levels Table 2. Symptoms can develop quickly acute heart failure or gradually over weeks or months chronic heart failure. Conclusions The long term clinical outcome of patients with heart failure and preserved LVF is poor and not significantly different from patients with reduced LVF. RVF — right ventricle function. In our study, the patients were older and were more likely to be females.
Related to left ventricular failure: pulmonary edema , right ventricular failure , Left ventricular hypertrophy.
Although the clinical characteristics of patients with preserved LVF are quite distinct from patients with reduced LVF, the clinical syndromes are very similar. Isolated lower limb edema is less likely heart failure, and other causes must be ruled out first, like venous insufficiency, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, lymphedema and thrombosis of the veins. Diastolic failure: The left ventricle loses its ability to relax normally because the muscle has become stiff. Sociodemographic status including place of residence, ethnic background, education, background concurrent diseases as documented by the medical records, the causes of admission and drug prescription on discharge were recorded systematically from the medical records during hospitalization. Follow-up Evaluation Patients were clinically followed by telephone up to September Most often there's swelling in the legs and ankles, but it can happen in other parts of the body, too. This reduces the circulating volume, helping to improve the function of the heart in someone that is fluid-overloaded. Clinical epidemiology of heart failure. Abstract Background Patients with heart failure HF have a poor prognosis. Kaplan-Meier curves, with the log-rank test, were used to compare survival among the two groups. SPSS version Left-sided heart failure The heart's pumping action moves oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium, then on to the left ventricle, which pumps the blood to the rest of the body.

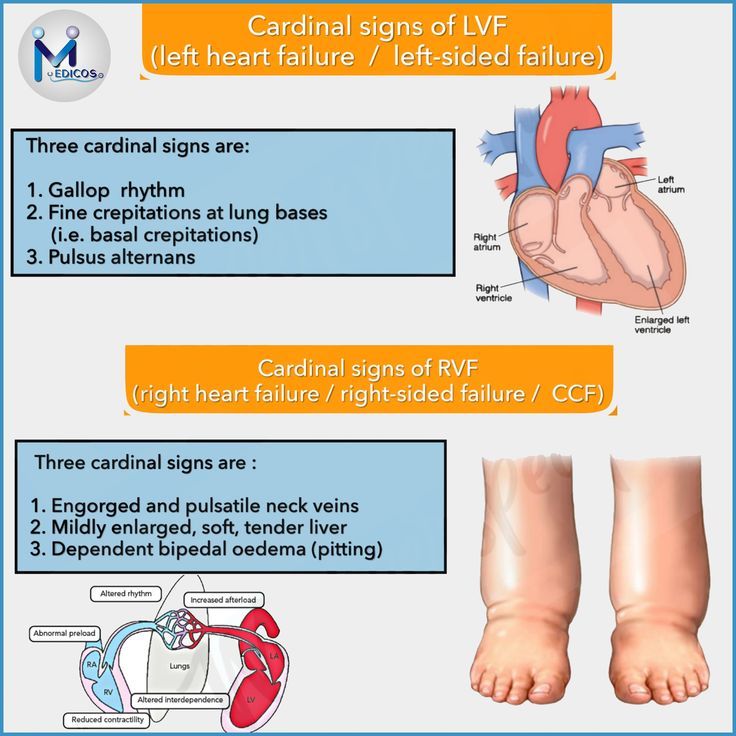
0 thoughts on “Lvf medical abbreviation”