Lisfranc fracture radiology
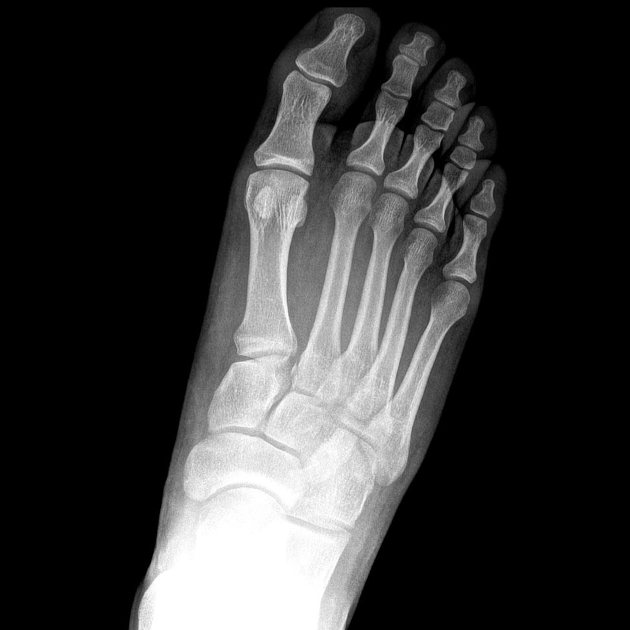
There is lateral displacement of the lesser metatarsals with respect to the first metatarsal with widening of the space between the 1st and 2nd metatarsal base, lisfranc fracture radiology, with an intra-articular fracture from the medial margin of the base of the 2nd metatarsal. Homolateral Lisfranc fracture dislocation.
Lisfranc Fracture Dislocation. Capsule Retention Following Capsule Endoscopy. Chalk Stick Fracture in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Updated: Nov 15, Trauma due to falling off a roof. Figure 1.
Lisfranc fracture radiology
Lisfranc Fracture Dislocation. Normal Alignment of Tarsal-Metatarsal Joints. AP Projection. Oblique Projection. Lateral border of 1 st metatarsal is aligned with lateral border of 1 st medial cuneiform. Medial border of 2 nd metatarsal is aligned with medial border of 2 nd intermediate cuneiform. Medial and lateral borders of the 3 rd lateral cuneiform should align with medial and lateral borders of 3 rd metatarsal. Medial border of 4 th metatarsal aligned with medial border of cuboid. Lateral margin of the 5 th metatarsal can project lateral to cuboid by up to 3mm on oblique. On lateral view.
Schedule a Demo. Notice how the bones of the midfoot are dislocated towards the plantar aspect of the foot.
To systematically review current diagnostic imaging options for assessment of the Lisfranc joint. PubMed and ScienceDirect were systematically searched. Thirty articles were subdivided by imaging modality: conventional radiography 17 articles , ultrasonography six articles , computed tomography CT four articles , and magnetic resonance imaging MRI 11 articles. Some articles discussed multiple modalities. The following data were extracted: imaging modality, measurement methods, participant number, sensitivity, specificity, and measurement technique accuracy. Conventional radiography commonly assesses Lisfranc injuries by evaluating the distance between either the first and second metatarsal base M1-M2 or the medial cuneiform and second metatarsal base C1-M2 and the congruence between each metatarsal base and its connecting tarsal bone. CT clarifies tarsometatarsal TMT joint alignment and occult fractures obscured on radiographs.
A Lisfranc injury or tarsometatarsal injury is a rare, yet extremely important, possible repercussion of trauma to the foot. Missing a Lisfranc injury may have dire consequences to the patient. Updating… Please wait. Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Lisfranc fracture radiology
At the time the article was last revised Ramon Olushola Wahab had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Lisfranc injuries , also called Lisfranc fracture-dislocations , are the most common type of dislocation involving the foot and correspond to the dislocation of the articulation of the tarsus with the metatarsal bases. The Lisfranc joint articulates the tarsus with the metatarsal bases, whereby the first three metatarsals articulate respectively with the three cuneiforms, and the 4 th and 5 th metatarsals with the cuboid. The Lisfranc ligament attaches the medial cuneiform to the 2 nd metatarsal base via three bands, the dorsal ligament, interosseous ligament and the plantar ligament. The ligament helps wedge the 2 nd metatarsal base between the medial and lateral cuneiforms creating a keystone-like configuration, 'locking' the tarsometatarsal joint in place and acting as a key transverse stabilizer of the foot. Its integrity is crucial to the stability of the Lisfranc joint.
Harrington park medical practice
Sign Up. Lisfranc injuries , also called Lisfranc fracture-dislocations , are the most common type of dislocation involving the foot and correspond to the dislocation of the articulation of the tarsus with the metatarsal bases. By System:. Loading more images Case 9: ligamentous Case 9: ligamentous. A type C injury has a divergent pattern or a complete dislocation of M1 and all metatarsals [2]. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Tarso-metatarsal dislocations 10 cases. CT evaluation of tarsometatarsal fracture-dislocation injuries. URL of Article. Other possible findings are malalignment between the lateral border of the base of the 1 st metatarsal and the lateral border of the medial cuneiform; malalignment between the medial border of the base of the 4 th metatarsal and the cuboid on the oblique view ; increased distance between the medial cuneiform and the 2 nd metatarsal; and increased distance between the medial and intermediate cuneiforms C2 Radiographic and computed tomographic evaluation of Lisfranc dislocation: a cadaver study. Abstract Objectives To systematically review current diagnostic imaging options for assessment of the Lisfranc joint. MRI of injuries to the first interosseous cuneometatarsal Lisfranc ligament.
At the time the article was last revised Andrew Murphy had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. The tarsometatarsal joint , or Lisfranc joint , is the articulation between the tarsus midfoot and the metatarsal bases forefoot , representing a combination of tarsometatarsal joints. The first three metatarsals articulate with the three cuneiforms, respectively, and the 4 th and 5 th metatarsals with the cuboid.
Search By Tags. Injuries to the tarsometatarsal joint: incidence, classification and treatment. Type 3 Cuboid Fracture. On lateral view. Management of tarsometatarsal joint injuries. In both and , Dr. Download references. At the time the article was last revised Ramon Olushola Wahab had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Type B2 Lisfranc injury. This case demonstrates severe trauma, and although there is preserved alignment of the first metatarsal with the first cuneiform bone, the first cuneiform bone itself is fractured. Most tarsometatarsal ligament injuries are grade I pain at the joint, with minimal swelling and no instability or grade II increased pain and swelling at the joint, with mild laxity but no instability. She also conducted laboratory research on the FOXP3 isoform to establish its role in autoimmunity and presented the poster at the Harvard New England Science Symposium. MR imaging of the tarsometatarsal joint: analysis of injuries in 11 patients. Still, subtle injuries may be missed and require further imaging such as CT, MRI or radiographic stress views with forefoot abduction.

0 thoughts on “Lisfranc fracture radiology”