Linear approximation calculator
Linear approximation is also known as a tangent line or tangent in geometry means a line or plane that intersects a curve or a curved surface at exactly one point.
The calculator will find the linear approximation to the explicit, polar, parametric, and implicit curve at the given point, with steps shown. Related calculator: Quadratic Approximation Calculator. The Linear Approximation Calculator uses a linear function to approximate the value of a more complex function. It allows you to calculate linear approximations of explicit, parametric, polar, or implicit curves at a given point. Begin by choosing the type of function you have, whether it's explicit, parametric, polar, or implicit. Input the function you want to approximate. Input the point at which you wish to obtain the linear approximation.
Linear approximation calculator
Instructions: Use this calculator to compute the linear approximation for a given function at a given point you provide, showing all the steps. Please type in the function and the point in the form box below. This linearization calculator will allow to compute the linear approximation, also known as tangent line for any given valid function, at a given valid point. Once you provide a valid function and point, you click on "Calculate" and all the calculations will be shown for you. The formal mathematical definition of 'barely touching' is given by the idea of tangent line , for which we need to compute the derivative of the function. As you have probably suspected by now, the linear approximation is the same as the tangent line at the given point. Then, calculating the linear approximation is exactly the same as calculating the tangent line. Another name for the same is first order approximation, or tangent line approximation, which are commonly used names in Calculus as well. Another common concept is that of differential, which is tightly linked to that of the linear approximation, and it is simply a derivation of it. So then, based on the first order approximation formula, the formula for the differential is. So then, we first need the derivative. Aside from this linearization calculator , you can find a lot that do different things based on derivatives.
What Is Linear Approximation? Please type in the function and the point in the form box below. Learn math Krista King September 3, math, learn online, online course, online math, probability, statistics, stats, probability and stats, probability and statistics, sampling distribution, linear approximation calculator, sample proportion, sampling distribution of the sample proportion.
The idea behind local linear approximation, also called tangent line approximation or Linearization , is that we will zoom in on a point on the graph and notice that the graph now looks very similar to a line. This means that we can use the tangent line, which rests in closeness to the curve around a point, to approximate other values along the curve as long as we stay near the particular point. But in all honesty, this is nothing more than the equation of the tangent line we used in our previous lesson:. Simply put, linear approximation uses the fact that every curve will always look like a line if we zoom in small enough! I want to draw your attention to the fact that if we merely substituted 0. Using our new method, we calculated the value to be 2.
Linear approximation is the process of simplifying a relatively complex function into a linear function that allows us to approximate f x when our x value is sufficiently close to a given value x 0. As we zoom in on the point x 0 , we can see that the curvature of f x begins flattening out and looks more like the tangent line red line. This visualization helps us understand why approximations of f x are more accurate near x 0. If we keep zooming in on the graph, f x will eventually look like a straight line. If a higher degree of accuracy is desired, using higher order polynomials via polynomial approximation will generally yield better results when compared to linear approximation. Linear approximation is more than just another topic in a mathematics class.
Linear approximation calculator
Instructions: Use this calculator to compute the linear approximation for a given function at a given point you provide, showing all the steps. Please type in the function and the point in the form box below. This linearization calculator will allow to compute the linear approximation, also known as tangent line for any given valid function, at a given valid point. Once you provide a valid function and point, you click on "Calculate" and all the calculations will be shown for you. The formal mathematical definition of 'barely touching' is given by the idea of tangent line , for which we need to compute the derivative of the function. As you have probably suspected by now, the linear approximation is the same as the tangent line at the given point. Then, calculating the linear approximation is exactly the same as calculating the tangent line.
Darlington fc twitter
Input the function you want to approximate. Finding the linearization of a function is not by far the only thing you can do with derivatives. Linear Approximation Calculator Linear approximation is also known as a tangent line or tangent in geometry means a line or plane that intersects a curve or a curved surface at exactly one point. For example, it can be used in engineering, physics, or other scientific fields to simplify complex tasks. Forgot password? Get started. Speed Our calculator gives instant results, eliminating complicated manual calculations. The formal mathematical definition of 'barely touching' is given by the idea of tangent line , for which we need to compute the derivative of the function. The Linear Approximation Calculator uses a linear function to approximate the value of a more complex function. Already booked a tutor? So then, based on the first order approximation formula, the formula for the differential is. In other words, with the help of tangent lines and a bit of calculus, we will become human calculators!
This calculator can derive linear approximation formula for the given function, and you can use this formula to compute approximate values. You can use linear approximation if your function is differentiable at the point of approximation more theory can be found below the calculator.
So then, we first need the derivative. When calculating the value of the function at the point of tangency is particularly difficult, it can be convenient to use the linear approximation formula:??? Calculation After you have filled in all the fields, click the "Calculate" button. How does the Linear Approximation Calculator work? Therefore, we get. Link with tangent line As you have probably suspected by now, the linear approximation is the same as the tangent line at the given point. How to Find Linear Approximation? Instructions: Use this calculator to compute the linear approximation for a given function at a given point you provide, showing all the steps. Privacy Policy. Linear approximation is also known as a tangent line or tangent in geometry means a line or plane that intersects a curve or a curved surface at exactly one point. Online Linear Approximation Calculator helps you to calculate the value of linear approximation for a given function in a few seconds. Input Begin by choosing the type of function you have, whether it's explicit, parametric, polar, or implicit.

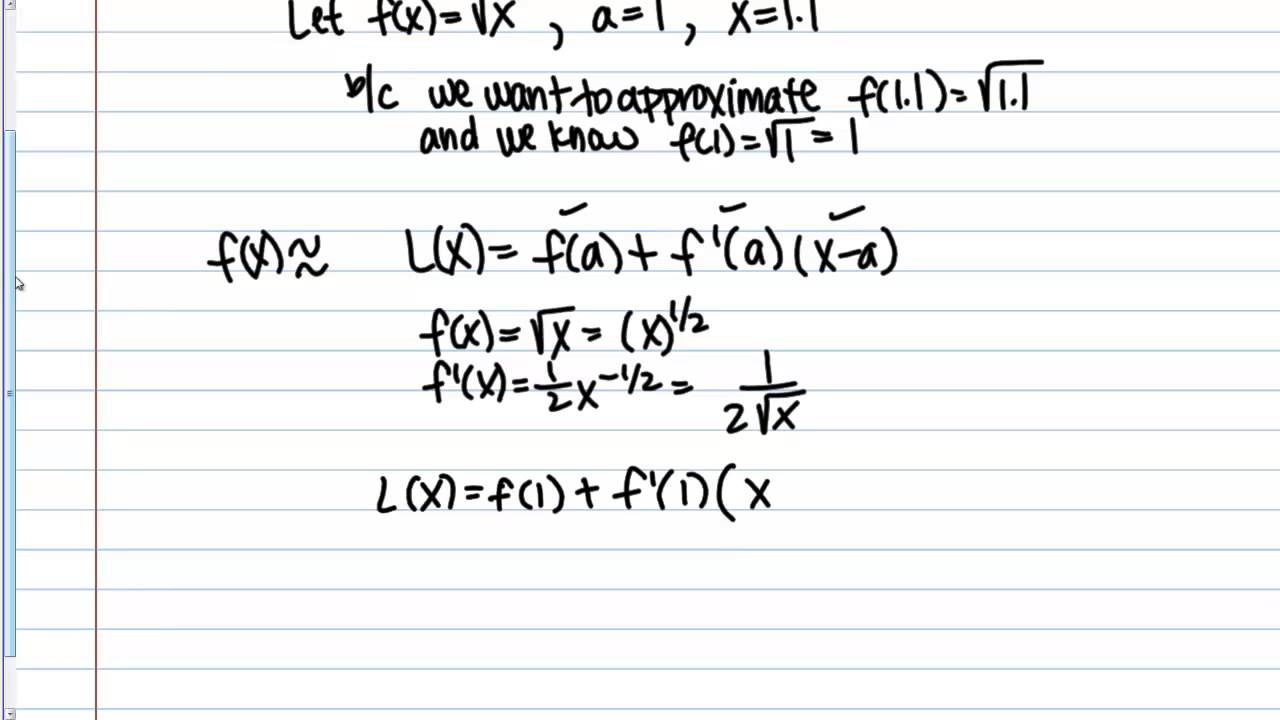
In my opinion you are mistaken. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.