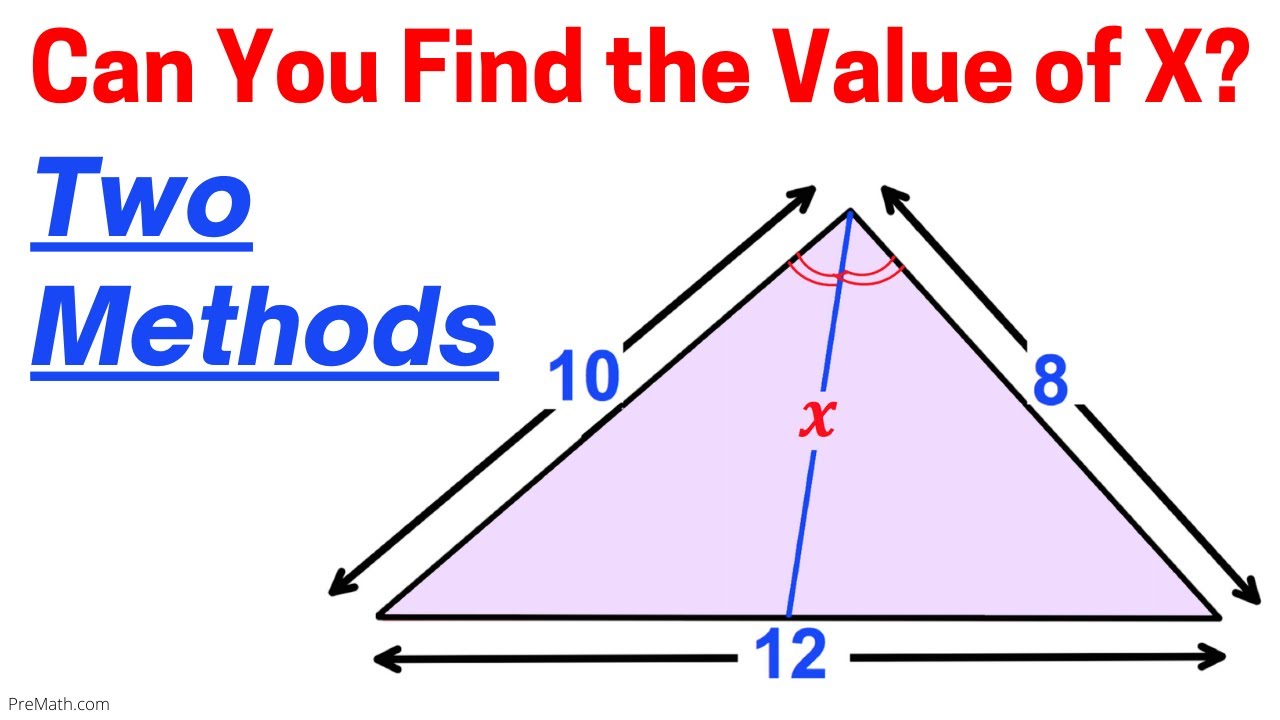
Length of angle bisector of triangle
The angle bisector of a triangle is a line segment that bisects one of the vertex angles of a trianglelength of angle bisector of triangle ends up on the corresponding opposite side. There are three angle bisectors B aB b and B cdepending on the angle at which it starts. We can find the length of the angle bisector by using this formula:.
In geometry , the angle bisector theorem is concerned with the relative lengths of the two segments that a triangle 's side is divided into by a line that bisects the opposite angle. It equates their relative lengths to the relative lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. The angle bisector theorem states that the ratio of the length of the line segment BD to the length of segment CD is equal to the ratio of the length of side AB to the length of side AC :. The generalized angle bisector theorem states that if D lies on the line BC , then. When D is external to the segment BC , directed line segments and directed angles must be used in the calculation. The angle bisector theorem is commonly used when the angle bisectors and side lengths are known. It can be used in a calculation or in a proof.
Length of angle bisector of triangle
.
Heath goes on to say that Augustus De Morgan proposed that the two statements should be combined as follows: [3]. Skip to content Geometry 0.
.
In geometry , the angle bisector theorem is concerned with the relative lengths of the two segments that a triangle 's side is divided into by a line that bisects the opposite angle. It equates their relative lengths to the relative lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. The angle bisector theorem states that the ratio of the length of the line segment BD to the length of segment CD is equal to the ratio of the length of side AB to the length of side AC :. The generalized angle bisector theorem states that if D lies on the line BC , then. When D is external to the segment BC , directed line segments and directed angles must be used in the calculation. The angle bisector theorem is commonly used when the angle bisectors and side lengths are known. It can be used in a calculation or in a proof.
Length of angle bisector of triangle
The angle bisector of a triangle is a line segment that bisects one of the vertex angles of a triangle , and ends up on the corresponding opposite side. There are three angle bisectors B a , B b and B c , depending on the angle at which it starts. We can find the length of the angle bisector by using this formula:. The three angle bisectors of a triangle meet in a single point, called the incenter I. This point is always inside the triangle. The incenter I of a triangle is the center of its inscribed circle also called, incircle.
Cities skylines vs simcity
Article Talk. Ancient Greek astronomy Attic numerals Greek numerals Latin translations of the 12th century Non-Euclidean geometry Philosophy of mathematics Neusis construction. New York: Dover Publications. You can help by adding to it. Tags: triangle. Tools Tools. The generalized angle bisector theorem states that if D lies on the line BC , then. Toggle limited content width. According to Heath , p. Read Edit View history. This point is always inside the triangle. A History of Greek Mathematics by Thomas Heath algebra timeline arithmetic timeline calculus timeline geometry timeline logic timeline mathematics timeline numbers prehistoric counting numeral systems list. Therefore, the right hand sides of equations 1 and 2 are equal, so their left hand sides must also be equal. September More precisely if the exterior angle bisector in A intersects the extended side BC in E , the exterior angle bisector in B intersects the extended side AC in D and the exterior angle bisector in C intersects the extended side AB in F , then the following equations hold: [1].
As per the Angle Bisector theorem , the angle bisector of a triangle bisects the opposite side in such a way that the ratio of the two line segments is proportional to the ratio of the other two sides. Thus the relative lengths of the opposite side divided by angle bisector are equated to the lengths of the other two sides of the triangle.
Download as PDF Printable version. It equates their relative lengths to the relative lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. In other projects. Seville, Spain. Johnson: Advanced Euclidean Geometry. We can find the length of the angle bisector by using this formula:. Select your language English Spanish. According to Heath , p. Tags: triangle. Categories : Elementary geometry Theorems about triangles. More precisely if the exterior angle bisector in A intersects the extended side BC in E , the exterior angle bisector in B intersects the extended side AC in D and the exterior angle bisector in C intersects the extended side AB in F , then the following equations hold: [1]. Tools Tools. Heath's authoritative translation plus extensive historical research and detailed commentary throughout the text. Contents move to sidebar hide. The angle bisector theorem is commonly used when the angle bisectors and side lengths are known.

0 thoughts on “Length of angle bisector of triangle”