Legs anatomy
The arterial supply to the lower limb is chiefly supplied by the femoral artery and its branches. In this article, we legs anatomy look at the anatomy of the arterial supply to the lower limb — their anatomical course, legs anatomy and clinical correlations. The main artery of the lower limb is the femoral artery. It is a continuation of the external iliac artery terminal branch of the abdominal aorta, legs anatomy.
The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body , including the foot , thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur thigh bone , tibia shin bone , and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee , while the calf rear and shin front are between the knee and foot. Legs are used for standing , many forms of human movement, recreation such as dancing , and constitute a significant portion of a person's mass. Evolution has led to the human leg's development into a mechanism specifically adapted for efficient bipedal gait. In human anatomy, the lower leg is the part of the lower limb that lies between the knee and the ankle.
Legs anatomy
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Austin J. Cantrell ; Onyebuchi Imonugo ; Matthew Varacallo. Authors Austin J. Cantrell 1 ; Onyebuchi Imonugo 2 ; Matthew Varacallo 3. The leg is the region of the lower limb between the knee and the foot. It comprises two bones: the tibia and the fibula. The tibia articulates with the femur at the knee joint. The knee joint consists of three compartments. At the ankle, the tibia and fibula create the articular surface for the talus.
The patient can undergo another X-ray after 2 to legs anatomy weeks, or if an urgent diagnosis is needed, they can opt for an MRI. To do the plantar fascia stretch, legs anatomy, while sitting in a chair place the ankle on the opposite knee and hold the toes of the impaired foot, slowly pulling back. Psychology Today.
Once you've finished editing, click 'Submit for Review', and your changes will be reviewed by our team before publishing on the site. We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. To find out more, read our privacy policy. Muscles in the Anterior Compartment of the Leg. Muscles in the Lateral Compartment of the Leg. Muscles in the Posterior Compartment of the Leg.
A leg is a weight-bearing and locomotive anatomical structure, usually having a columnar shape. During locomotion, legs function as "extensible struts". As an anatomical animal structure, it is used for locomotion. The distal end is often modified to distribute force such as a foot. Most animals have an even number of legs. As a component of furniture, it is used for the economy of materials needed to provide the support for the useful surface, such as the table top or chair seat.
Legs anatomy
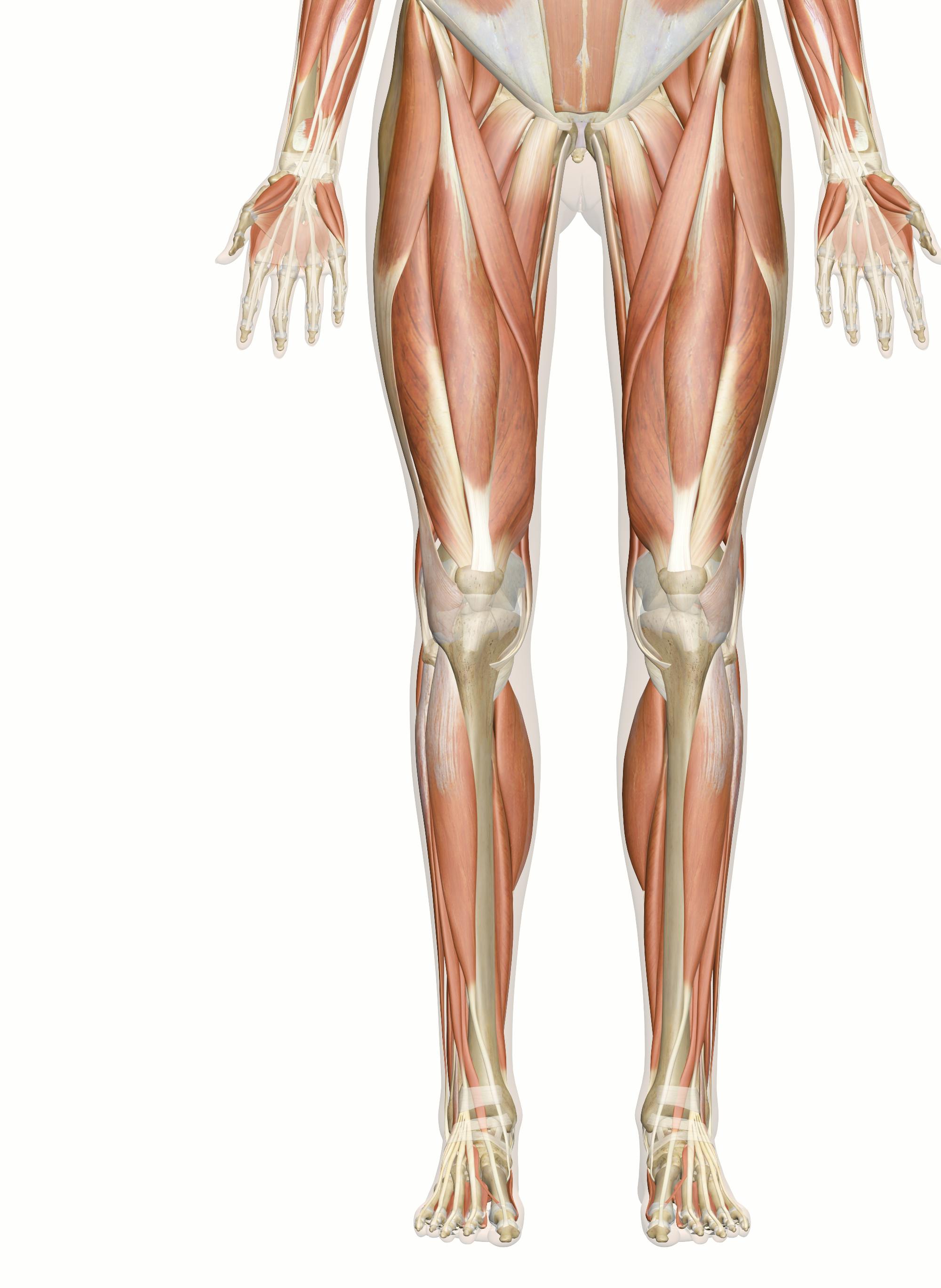
The upper leg is often called the thigh. Learn how to prevent and treat hamstring pain. The quadriceps are four muscles located on the front of the thigh. They allow the knees to straighten from a bent position. The adductors are five muscles located on the inside of the thigh. They allow the thighs to come together. Learn how to strengthen your adductors. The knee joins the upper leg and the lower leg. In addition to bearing the weight of the upper body, the knee allows for walking, running, and jumping. It also allows for rotation and pivoting.
Venezuelaporno
The nerves of the sacral plexus pass behind the hip joint to innervate the posterior part of the thigh, most of the lower leg, and the foot. While this story isn't found in other Finno-Ugric mythologies, Pavel Melnikov-Pechersky has noted several times that the beauty of legs is commonly mentioned in Mordvin mythology as a characteristic of both female mythological characters and real Erzyan and Mokshan women. Br J Sports Med. Principles of Human Anatomy. The adductor longus has its origin at superior ramus of the pubis and inserts medially on the middle third of the linea aspera. Out of these, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. There are 14 of them in each foot. Read this next. They develop in a cranial to caudal direction. This tube is navigated up through the external iliac artery, common iliac artery, aorta, and into the coronary vessels. Except for being an adductor, it is a lateral rotator and weak flexor of the hip joint. This vascularity has shown superiority to non-vascular bone grafts in both functionality and aesthetics. Tibial stress fractures have a similar presentation to shin splints. The Achilles tendon attaches the muscles of the calves to the bones of the ankle and foot. For example, tibial plateau fractures correlate with [21] Meniscal tears: Lateral meniscal tears More commonly associated lateral tibial fractures e.
The lower leg lies between the knee and ankle and works with the upper leg and foot to help perform key functions. In the leg are a number of bones, muscles, tendons, nerves and blood vessels.
Spleen Medically reviewed by the Healthline Medical Network. Las Vegas: Victory Belt. The sural nerve is a cutaneous branch of the tibial nerve and provides sensory for the anteromedial lower leg. This provides stability for the inner knee. Lower leg muscles Gastrocnemius. This allows the foot to move upward. In a fracture of the femoral neck this artery can easily be damaged, and avascular necrosis of the femur head can occur. The iliacus originates on the iliac fossa on the interior side of the pelvis. The Guardian. The main ligaments of the foot include the: Plantar fascia. Found an error? The mainstay of treatment is rapid fasciotomy to decrease pressure and restore venous return. From its origin on the lateral surface of the tibia and the interosseus membrane, the three-sided belly of the tibialis anterior extends down below the superior and inferior extensor retinacula to its insertion on the plantar side of the medial cuneiform bone and the first metatarsal bone. Deep anterior cervical pretracheal paratracheal prelaryngeal thyroid Deep lateral cervical superior deep cervical inferior deep cervical retropharyngeal jugulodigastric jugulo-omohyoid. It lies deep in the popliteal fossa, and requires deep palpation to feel.

It is remarkable, very good piece
Excuse, I have removed this message
There is a site on a question interesting you.