Kuffer cells
Kuffer cells Kupffer cells KCs are the liver-resident macrophages and play a leading role in the regulation of liver homeostasis in physiological conditions and in pathology, kuffer cells. The study aims to investigate the anti-echinococcosis effect of KCs and the effects of hepatic stellate cells HSCs activation in the progression of liver fibrosis in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis hepatic AE.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are resident liver macrophages and play a critical role in maintaining liver functions. Under physiological conditions, they are the first innate immune cells and protect the liver from bacterial infections. Under pathological conditions, they are activated by different components and can differentiate into M1-like classical or M2-like alternative macrophages.
Kuffer cells
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Although macrophages contribute to cancer cell dissemination, immune evasion, and metastatic outgrowth, they have also been reported to coordinate tumor-specific immune responses. We therefore hypothesized that macrophage polarization could be modulated therapeutically to prevent metastasis. These findings demonstrate the significance of macrophage function in metastasis and identify Kupffer cells as a potential therapeutic target against pancreatic cancer metastasis to the liver. Marcelo M. Metastasis is among the leading causes of cancer-associated deaths 1. Metastatic lesions form from tumor cells that disseminate from a primary tumor and seed a distant tissue, such as the liver 2. During this process, disseminated tumor cells DTCs must evade elimination by local immune cells and adapt to a new microenvironment. Once acclimated, the DTC proliferates to establish a metastatic colony which ultimately manifests as an expanding metastatic lesion 2. In PDAC, the most common site of metastasis is the liver, with the lung and peritoneum being slightly less common 5. Thus, treatments to successfully intervene on the metastatic cascade in PDAC are a clinical unmet need 3.
Paracrine and cell autonomous signalling in pancreatic cancer progression and metastasis.
AoH publishes editorials, opinions, concise reviews, original articles, brief reports, letters to the editor, news from affiliated associations, clinical practice guidelines and summaries of congresses in the field of Hepatology. Our journal seeks to publish articles on basic clinical care and translational research focused on preventing rather than treating the complications of end-stage liver disease. The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years. SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Liver macrophages comprise Kupffer cells — which are self-maintaining, non-migratory tissue-resident phagocytes that originate from yolk sac-derived precursors during embryogenesis — and monocyte-derived macrophages. Kupffer cells are essential for hepatic and systemic homeostasis, as they contribute to metabolism, scavenge bacteria and cellular debris, and induce immunological tolerance. Following their activation by danger signals, Kupffer cells modulate inflammation and recruit immune cells — including large numbers of monocytes — to the liver. Kupffer cells and monocyte-derived macrophages rapidly adapt their phenotypes in response to local signals, which determine their ability to aggravate or cease liver injury. Liver macrophages are crucial in the pathogenesis of acute and chronic liver diseases, in which they orchestrate inflammation, fibrosis, angiogenesis and tumour progression, as well as tissue repair and tumour surveillance.
Kuffer cells
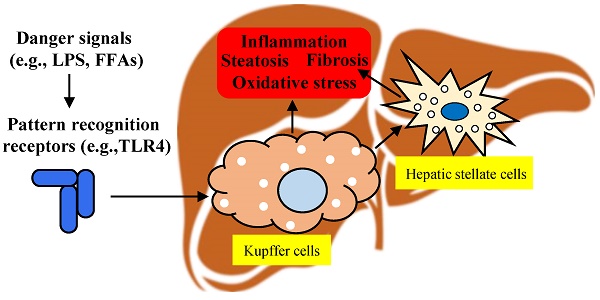
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Chronic alcohol consumption is linked to the development of alcohol-associated liver disease ALD. This disease is characterized by a clinical spectrum ranging from steatosis to hepatocellular carcinoma. Several cell types are involved in ALD progression, including hepatic macrophages. Kupffer cells KCs are the resident macrophages of the liver involved in the progression of ALD by activating pathways that lead to the production of cytokines and chemokines. In addition, KCs are involved in the production of reactive oxygen species. Reactive oxygen species are linked to the induction of oxidative stress and inflammation in the liver.
Moving truck rentals cheapest
Gastroenterology, , pp. Seki E, Brenner DA. Chem Res Toxicol. Ischemia-reperfusion: mechanisms of microvascular dysfunction and the influence of risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Nat Genet. Subsets of mouse Kupffer cells KCs are derived from monocytes and differentiate into liver resident macrophages. For experiments assessing tumor burden, mice were euthanized and then the portal vein and inferior vena cava were severed to drain the blood from the liver and lungs. The role of Kupffer cells in hepatitis B and hepatitis C virus infections. The multifaceted role of the microenvironment in liver metastasis: biology and clinical implications. Inhibition by prostaglandin E 2 of anaphylatoxin C5a- but not zymosan-induced prostanoid release from rat Kupffer cells.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS.
Mechanisms of macrophage activation in obesity-induced insulin resistance. In , Bucala and colleagues [ ] discovered the role of bone marrow-derived fibrocytes in fibrosis. These tumor-associated macrophages, while predominantly expressing M2 phenotype, have a distinct transcriptional profile that can contribute to enhanced tumor angiogenesis, due to increased expression of VEGF, which stimulates angiogenesis, and matrix metalloproteases, that facilitate angiogenic remodeling 68 , HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma. Therefore, timely administration of anti-fibrosis therapy is an important measure to hinder the progress of the disease. Ann Med. All animal studies were conducted in accordance with guidelines from the Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Pennsylvania. Liver X receptors bridge hepatic lipid metabolism and inflammation. Confocal microscopy picture showing the steady-state location and interactions between Kupffer cells Red , hepatic stellate cells green and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells blue. Hybrid inhibitor of peripheral cannabinoid-1 receptors and inducible nitric oxide synthase mitigates liver fibrosis. MJLR Medline. Special functions and metabolism of Kupffer cells suggest that they are an attractive target for therapy of liver inflammation and related diseases, including cancer and infectious diseases. Based on these few reports, there is a clear need at this time to expand our paradigm for PRRs in progression of liver injury beyond a specific interaction with TLR4 and incorporate the likely complex interactions between Kupffer cells and multiple PAMPs and DAMPs in the progression of chronic liver injury.

In my opinion you commit an error. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I am assured. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.