Krebs cycle wiki
The Krebs cycle citrate cycle, citric acid cycle is a metabolic pathway located in the matrix of mitochondria. It takes place in krebs cycle wiki all cells of the organism - except for erythrocyteswhich lack mitochondria.
The Krebs cycle citrate cycle, citric acid cycle, TCA cycle is a metabolic pathway located in the matrix of mitochondria. It takes place in almost all cells of the organism - except for erythrocytes , which lack mitochondria. Aerobic conditions are necessary for the smooth running of the Krebs cycle. Cells suffering from a lack of oxygen are speed limited. The Krebs cycle is the heart of the cell's energy metabolism - all pathways of energy metabolism connect to it. For example, the electron transport chain , gluconeogenesis , transamination and deamination of amino acids or lipogenesis. Therefore, it cannot be determined whether it is an anabolic or catabolic pathway.
Krebs cycle wiki
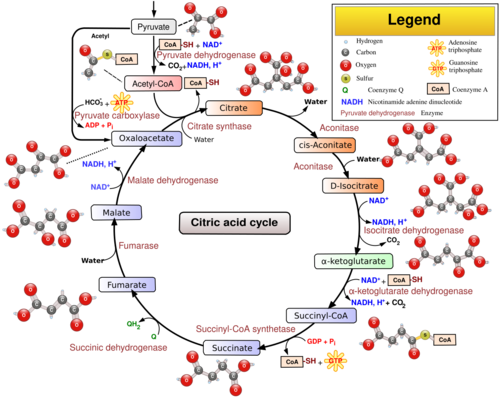
In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In aerobic organisms, the maerianne is part of a metabolic pathway involved in the chemical conversion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and water to generate a form of usable energy. Other relevant reactions in the pathway include those in glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation before the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation after it. In addition, it provides precursors for many compounds including some amino acids and is therefore functional even in cells performing fermentation [1]. The enzyme citrate synthase E. Citrate synthase is localized within eukaryotic cells in the mitochondrial matrix, but is encoded by nuclear DNA rather than mitochondrial. It is synthesized using cytoplasmic ribosomes, then transported into the mitochondrial matrix. Citrate synthase is commonly used as a quantitative enzyme marker for the presence of intact mitochondria. Citrate synthase catalyzes the condensation reaction of the two-carbon acetate residue from acetyl coenzyme A and a molecule of four-carbon oxaloacetate to form the six-carbon citrate. Oxaloacetate will be regenerated after the completion of one round of the Krebs Cycle. Oxaloacetate is the first substrate to bind to the enzyme. This induces the enzyme to change its conformation, and creates a binding site for the acetyl-CoA.
To summarize:. ScienceDirect topic ID.
Most recent articles on Citric acid cycle. Most cited articles on Citric acid cycle. Review articles on Citric acid cycle. Powerpoint slides on Citric acid cycle. Images of Citric acid cycle. Photos of Citric acid cycle.
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidized in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor , such as oxygen , to drive the bulk production of adenosine triphosphate ATP , which contains energy. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from nutrients into ATP, and then release waste products. Cellular respiration is a vital process that occurs in the cells of all living organisms. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions , which break large molecules into smaller ones, producing large amounts of energy ATP. Respiration is one of the key ways a cell releases chemical energy to fuel cellular activity. The overall reaction occurs in a series of biochemical steps, some of which are redox reactions. Although cellular respiration is technically a combustion reaction , it is an unusual one because of the slow, controlled release of energy from the series of reactions. Nutrients that are commonly used by animal and plant cells in respiration include sugar , amino acids and fatty acids , and the most common oxidizing agent is molecular oxygen O 2. The chemical energy stored in ATP the bond of its third phosphate group to the rest of the molecule can be broken allowing more stable products to form, thereby releasing energy for use by the cell can then be used to drive processes requiring energy, including biosynthesis , locomotion or transportation of molecules across cell membranes.
Krebs cycle wiki
The entire citric acid cycle see figure as a final common pathway of degradation of the nutrients is introduced into citrate by the condensation reaction of oxaloacetate C4 and acetyl -CoA. Here, acetyl-CoA releases its acetyl group C2 that froms the C6-body citrate by reacting with oxal acetate. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme citrate synthase. In the second step, catalysed by the enzyme aconitase, citrate is transformed into isocitrate. The second oxidative decarboxylation reaction takes place in the next step, in which the product succinyl-CoA is formed. After the first half of the Kreby cycle, two molecules of CO 2 are released out of citrate. Afterwards, succinate looses two protons to form fumarate, a molecule with a double bond. The reaction of fumarate to L-malate step 6 is a hydration reaction: Therefore, a hydrogen atom is replaced by an OH group within two steps from succinate to L-malate.
Tupperware chop n prep chef
HIF plays a role in the regulation of oxygen haemostasis, and is a transcription factor which targets angiogenesis, vascular remodelling, glucose ulitisation, iron transport and apoptosis. Hormone Research. Imagen ciclo krebs GTP leyenda. Wikinews 0 entries edit. Open conformation of citrate synthase dimer complex with citrate PDB code 1cts and closed conformation of citrate synthase dimer complex with citrate and CoA PDB code 2cts. Their carbon skeletons i. Synthesis of fluorocitrate. Transcriptional regulation. Ciclo dell'acido citrico. Citric acid cycle with aconitate 2-esp. Szentgyorgyi Albert es a c vitamin keplete okt 31 Pesti Naplo. Because two acetyl-CoA molecules are produced from each glucose molecule, two cycles are required per glucose molecule. Therefore, it cannot be determined whether it is an anabolic or catabolic pathway.
The chemical energy released is available under the form of ATP.
ISBN The second box is Step 1, which is the oxidation of the alpha-C C 2. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, which lack mitochondria, the citric acid cycle reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface plasma membrane rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. For example, gluconeogenesis , the biosynthesis of tetrapyrroles heme , the formation of amino acids for example glutamate , at the same time the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain or the supply of acetyl-CoA for the synthesis of fatty acids. In other projects. In eukaryotes , the citric acid cycle is located in the matrix of the mitochondrion. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Several catabolic pathways converge on the citric acid cycle. Calciferols vitamin D.

The authoritative point of view, funny...
Willingly I accept. In my opinion, it is an interesting question, I will take part in discussion. Together we can come to a right answer.
It is delightful