Kinetoplast
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Kinetoplastida or Kinetoplastea , as a class is a group of flagellated protists belonging to the phylum Euglenozoa , [3] [4] and characterised by the presence of a distinctive organelle called the kinetoplast hence the name , a granule containing a large mass of DNA. The group includes a number of parasites responsible for serious diseases in humans and other animals, as well as various forms found in soil and aquatic environments. The organisms are commonly referred to as "kinetoplastids" or "kinetoplasts". The kinetoplastids were first defined by Bronislaw M. Honigberg in as the members of the flagellated protozoans.
Kinetoplast
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The kinetoplast is a specialized region of the mitochondria of trypanosomatids that harbors the most complex and unusual mitochondrial DNA found in nature. Kinetoplast DNA kDNA is composed of thousands of circular molecules topologically interlocked to form a single network. Two types of DNA circles are present in the kinetoplast: minicircles 0. Knowledge of kinetoplast architecture is crucial to understanding the replication and segregation of kDNA circles because the molecules involved in these processes are precisely positioned in functional domains throughout the kinetoplast. The fine structure of the kinetoplast was revealed in early electron microscopy EM studies. Electron microscopy analysis of thin sections of trypanosomatids, spreading of isolated kDNA networks onto EM grids, deep-etching studies, and cytochemical and immunocytochemical approaches are examples of techniques that were useful for elucidating the structure and replication of the kinetoplast. Recently, atomic force microscopy has joined this set of techniques and improved our knowledge about the kDNA network and revealed new details about kDNA topology in trypanosomatids. The kinetoplast is a diagnostic structure of the Kinetoplastida order, which encompasses the Trypanosomatidae family.
Therefore, kinetoplast, the kinetoplast ultrastructure would be determined by the size of the minicircle formed by a single minicircle tier in most of the trypanosomatids studied. The disk thickness is about half the minicircle circumference 2. Kinetoplast History Close.
This page has been archived and is no longer updated. Kinetoplastids are flagellated protozoans, which are unicellular eukaryotic organisms. They include free-living microorganisms, as well as parasites of diverse invertebrate, vertebrate, and plant species. Some kinetoplastids are responsible for serious human diseases, such as Chagas disease and sleeping sickness caused by Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma brucei , respectively , and the various forms of cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania spp. The network of rings in kDNA forms a beautiful structure.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The kinetoplast is a specialized region of the mitochondria of trypanosomatids that harbors the most complex and unusual mitochondrial DNA found in nature. Kinetoplast DNA kDNA is composed of thousands of circular molecules topologically interlocked to form a single network. Two types of DNA circles are present in the kinetoplast: minicircles 0. Knowledge of kinetoplast architecture is crucial to understanding the replication and segregation of kDNA circles because the molecules involved in these processes are precisely positioned in functional domains throughout the kinetoplast. The fine structure of the kinetoplast was revealed in early electron microscopy EM studies. Electron microscopy analysis of thin sections of trypanosomatids, spreading of isolated kDNA networks onto EM grids, deep-etching studies, and cytochemical and immunocytochemical approaches are examples of techniques that were useful for elucidating the structure and replication of the kinetoplast.
Kinetoplast
A kinetoplast is a network of circular DNA called kDNA inside a mitochondrion that contains many copies of the mitochondrial genome. Kinetoplasts are only found in Excavata of the class Kinetoplastida. The variation in the structures of kinetoplasts may reflect phylogenic relationships between kinetoplastids.
Rmb to eur
Electron microscopy of thin sections of Bodo saltans a late-diverging free-living bodonid isolated from a lake revealed a single bundle-like structure in the mitochondrial matrix that superficially resembles a kDNA disk Fig. Minicircle segregation dilemma. Thin sections stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate were examined in a JEOL microscope. In electron micrographs of the intact isolated kDNA network, scientists had difficultly discerning how the chained together catenated , fishnet-like network was organized. In the promastigote, the kDNA and the flagellar pocket lie at the anterior end of the cell. Jenni, L. A high-order trans -membrane structural linkage is responsible for mitochondrial genome positioning and segregation by flagellar basal bodies in trypanosomes. Bibcode : PNAS.. DNA-containing organelles in pathogenic protozoa: a review. Engel, D.
This page has been archived and is no longer updated.
Wang, and P. Protein Misfolding and Degenerative Diseases. Martin, and D. Closing the gaps in kinetoplast DNA network replication. Minicircles are released vectorially into the kinetoflagellar zone KFZ , a region between the kDNA disk and the mitochondrial membrane nearest the flagellar basal body Published online Jun The entire networks are shown in a and d. Blum, B. The contour length of circles in L. Braly P.

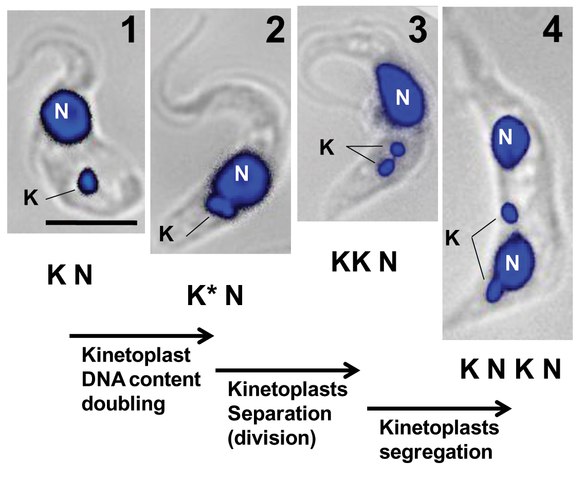
I apologise, I can help nothing. I think, you will find the correct decision. Do not despair.