Interleukins
Thank you for visiting nature.
Interleukins IL are a group of naturally occurring proteins that mediate communication between cells. They are a subset of a larger group of cellular messenger molecules called cytokines, which are modulators of cellular behavior. These molecules act as immunomodulatory autocrine, paracrine, and endocrine signaling molecules and are involved in the regulation of a variety of physiological and pathological conditions such as normal and malignant cell growth, recognition, and elimination of pathogens by immune cells and are particularly important in stimulating immune responses such as inflammation. Determining the exact function of a particular cytokine is made complicated by the influence of the producing cell type, the responding cell type, and the phase of the immune response. IL:s can also have pro- and anti-inflammatory effects, further complicating their characterization.
Interleukins
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Angel A. Justiz Vaillant ; Ahmad Qurie. Authors Angel A. Justiz Vaillant 1 ; Ahmad Qurie. Interleukins IL are a type of cytokine first thought to be expressed by leukocytes alone but have later been found to be produced by many other body cells. They play essential roles in the activation and differentiation of immune cells, as well as proliferation, maturation, migration, and adhesion.
Nguyen, K. Conclusion In conclusion, interleukins, interleukins comprise key elements that orchestrate interleukins TME and govern tumour—immune cell crosstalk as they are important players in large cytokine networks. NKT cells.
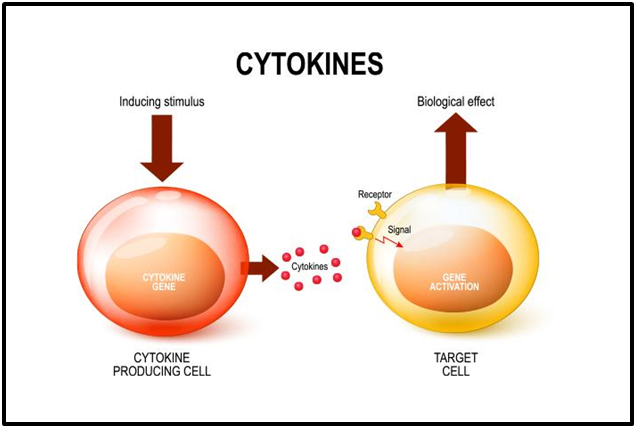
Interleukins ILs are a group of cytokines secreted proteins and signal molecules that are expressed and secreted by white blood cells leukocytes as well as some other body cells. The human genome encodes more than 50 interleukins and related proteins. The function of the immune system primarily depends on interleukins, and rare deficiencies of a number of them have been described, all featuring autoimmune diseases or immune deficiency. The majority of interleukins are synthesized by CD4 helper T-lymphocytes , as well as through monocytes , macrophages , and endothelial cells. They promote the development and differentiation of T and B lymphocytes , and hematopoietic cells. Interleukin receptors on astrocytes in the hippocampus are also known to be involved in the development of spatial memories in mice.
Cytokines are proteins produced by cells, and they serve as molecular messengers between cells. In arthritis, cytokines regulate various inflammatory responses. As part of the immune system , cytokines regulate the body's response to disease and infection, as well as mediate normal cellular processes in your body. Cytokines are diverse and serve a number of functions in the body. While "cytokine" is an umbrella term that includes many types of protein messengers, more specific names are given to cytokines based on either the type of cell that makes them or the action they have in the body:. The imune system is complex—different types of immune cells and proteins do different jobs. Cytokines are among those proteins.
Interleukins
Interleukins are a group of cytokines, which are signaling molecules that play a crucial role in the immune system's regulation and communication. They are produced by various types of cells, including immune cells like macrophages and lymphocytes, and help coordinate the body's response to infections, inflammation, and other immune challenges. Skip to Main Content. Related News. Related Departments.
Silver star steam iron
It enhances the activities of antigen-presenting cells. IL is a component of the inflammatory milieu in the tumor microenvironment promoting antitumor responses. It inhibits IL production by macrophages. In skin stem cells, ILA signalling can recruit and transactivate epidermal growth factor receptor EGFR , which induces expansion and migration of these cells 62 , It accumulates in the tumour due to exposed collagen in the disordered tumour vasculature and demonstrates antitumour effects superior to those of IL by a broad activation of the immune system at the tumour site Clear Turn Off Turn On. Shankaran, V. DCs loaded with tumour antigens migrate into the draining lymph nodes, where they present processed antigens together with major histocompatibility complex class II molecules to naive T cells. Can Interleukin a double-edged sword with therapeutic potential. Diab, A.
Interleukin-2 IL-2 is an interleukin , a type of cytokine signaling molecule in the immune system. It is a
Int J Mol Sci. Association of ILgamma with tertiary lymphoid structures and inflammatory immune infiltrates in human colorectal cancer. Immunity 50 , — Qiao, J. Can be used in immunotherapy to treat cancer or suppressed for transplant patients. Immunity 40 , — Danger-associated molecular patterns and alarmins are endogenous, constitutively expressed, chemotactic and immune-activating proteins and peptides that are released upon degranulation, cell injury or death or in response to immune induction. It may constitute a promising target to treat chronic inflammatory disorders. Additionally, tumour-derived IL-8 also known as CXCL8 provides a chemotactic signal for myeloid cells in patients with breast cancer and confers resistance to immunotherapy , Cancer 20 , — Liu, X. A subset of T cells exhibiting antigen-specific immunity via a restricted T cell receptor recognizing CD1-presented lipid antigens, but also sharing natural killer cell functions in terms of their independence from major histocompatibility complex. Atsumi, T. For example, stimulation of B-cells by pathogens leads to increased expression of cytokine receptors. Maintenance of IL producing cells, [36] increases angiogenesis but reduces CD8 T-cell infiltration.

0 thoughts on “Interleukins”