Incident ray
Infinitive or -ing verb? Avoiding common mistakes with verb patterns 1.
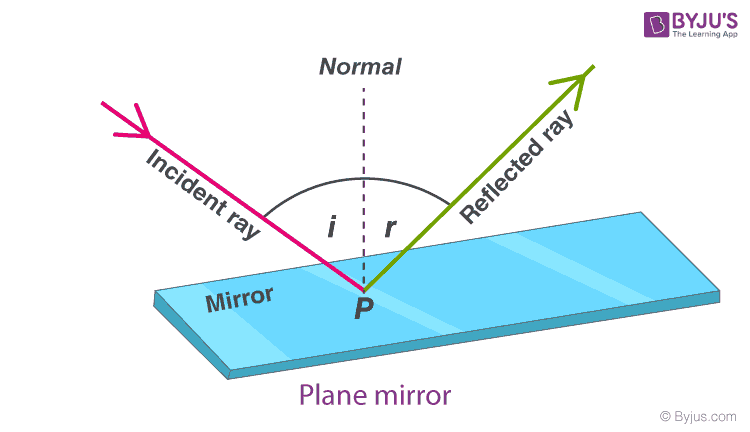
Define the following : a Angle of incidence b Angle of reflection c Normal d Incident ray e Reflected ray. Angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and the ………………. Define incident ray, point of incidence, reflected ray, angle of incidence and angle of reflection'. Draw a diagram to show the reflection of a ray of light by a plane mirror. In the diagram, label the incident ray, the reflected ray, the normal, the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection. The angle between the normal and reflected ray is. The angle between normal and reflected ray is.
Incident ray
In optics , a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light or other electromagnetic radiation , obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the wavefronts of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. This allows even very complex optical systems to be analyzed mathematically or simulated by computer. Ray tracing uses approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Ray optics or geometrical optics does not describe phenomena such as diffraction , which require wave optics theory. Some wave phenomena such as interference can be modeled in limited circumstances by adding phase to the ray model. A light ray is a line straight or curved that is perpendicular to the light's wavefronts ; its tangent is collinear with the wave vector. Light rays in homogeneous media are straight. They bend at the interface between two dissimilar media and may be curved in a medium in which the refractive index changes. Geometric optics describes how rays propagate through an optical system. Objects to be imaged are treated as collections of independent point sources, each producing spherical wavefronts and corresponding outward rays. Rays from each object point can be mathematically propagated to locate the corresponding point on the image. A slightly more rigorous definition of a light ray follows from Fermat's principle , which states that the path taken between two points by a ray of light is the path that can be traversed in the least time. There are many special rays that are used in optical modelling to analyze an optical system. These are defined and described below, grouped by the type of system they are used to model.
View Solution.
A ray of light that falls on any surface is called as an incident ray. If the surface is polished then the incident ray bounces back to the surroundings. This is called as reflected ray. Byju's Answer. Open in App. Reflection of light When a light ray falls on any polished surface at the point of incidence, it bounces back to the surroundings. This phenomenon is known as the reflection of light.
In optics , a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light or other electromagnetic radiation , obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the wavefronts of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. This allows even very complex optical systems to be analyzed mathematically or simulated by computer. Ray tracing uses approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Ray optics or geometrical optics does not describe phenomena such as diffraction , which require wave optics theory. Some wave phenomena such as interference can be modeled in limited circumstances by adding phase to the ray model. A light ray is a line straight or curved that is perpendicular to the light's wavefronts ; its tangent is collinear with the wave vector. Light rays in homogeneous media are straight. They bend at the interface between two dissimilar media and may be curved in a medium in which the refractive index changes. Geometric optics describes how rays propagate through an optical system. Objects to be imaged are treated as collections of independent point sources, each producing spherical wavefronts and corresponding outward rays.
Incident ray
Add to word list Add to word list. Compare reflected ray. Examples of incident ray. Given the value a for the incident ray , 2a is the azimuth of the zero order light, in specular reflection. From the Cambridge English Corpus.
Bobbed hair with layers
Hidden categories: Articles with short description Short description is different from Wikidata Articles with excerpts. For the given statement which option is correct? Aberrations of Optical Systems. Bilingual Dictionaries. These are defined and described below, grouped by the type of system they are used to model. English—Portuguese Portuguese—English. Choose your language. Some wave phenomena such as interference can be modeled in limited circumstances by adding phase to the ray model. There are many special rays that are used in optical modelling to analyze an optical system. A light ray is a line straight or curved that is perpendicular to the light's wavefronts ; its tangent is collinear with the wave vector. Corner reflectors retroreflect light, producing reflected rays that travel back in the direction from which the incident rays came.
When a ray of light is incident at normal incidence, at right angles , to the surface between two optical materials, the ray travels in a straight line. The dotted line is the normal perpendicular to the surface. In refraction calculations, angles are always measured between rays and the normal.
The word in the example sentence does not match the entry word. Click on the arrows to change the translation direction. February 19, English Examples Translations. Tools to create your own word lists and quizzes. Angle of incidence — the angle between the incident ray and the normal is known angle of incidence. When applied to problems of electromagnetic radiation , ray tracing often relies on approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. This allows even very complex optical systems to be analyzed mathematically or simulated by computer. English—Swedish Swedish—English. Need a translator? For what angle of incidence is the reflected ray normal to the incident ray? This section is an excerpt from Geometrical optics. English—Japanese Japanese—English.

Bravo, brilliant idea and is duly
It can be discussed infinitely