How much land is inhabited by humans
Using a combination of recent global maps of human influence, researchers were able to calculate the average influence humans are having on ecosystems worldwide. F or as long as humans have existed they have impacted their surrounding environment.
The paper, published June 3 in the prestigious journal Science , has key policy implications for nations negotiating new conservation targets for under the umbrella of the United Nations. This post global biodiversity framework of the Convention on Biological Diversity will come into effect later this year and set the next conservation agenda for participating nations. The paper also says 1. Lead author James R. It is essentially a conservation plan for the planet, and we must implement it quickly.
How much land is inhabited by humans
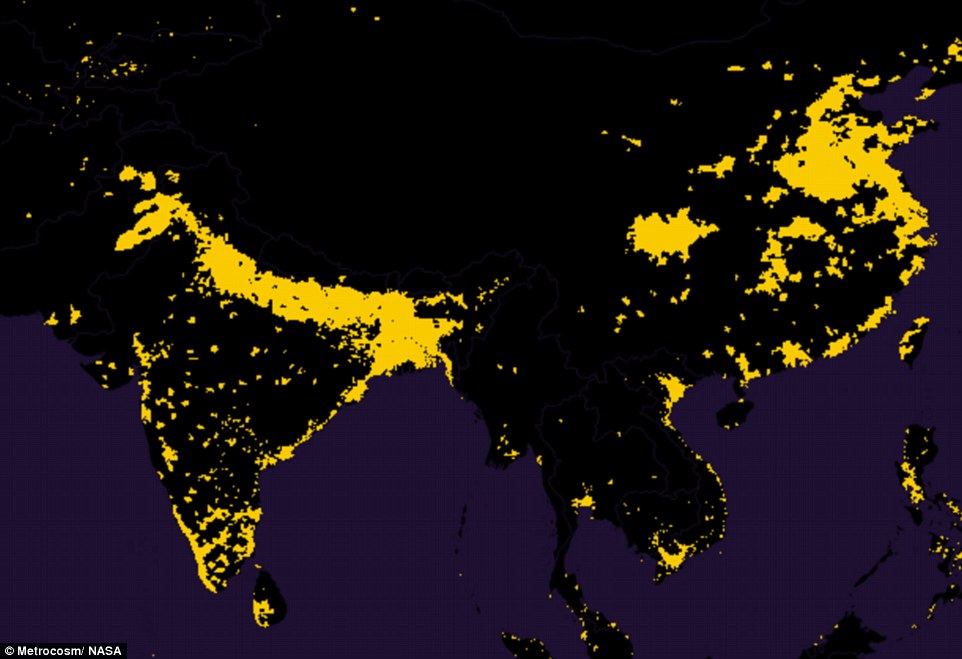
This question is an interesting one because, when my friend asked me the other day, I could tell her confidently that not only did science know the answer, science had multiple different ways to quantify that answer, but that I had absolutely no idea what it was. Landcover is one key way that we can measure how much of the terrestrial environment has been covered by humans. The thing is, landcover is something that is changing and our technology to estimate it is improving constantly, so even fairly recent estimates may already be out of date. A meta-analysis in , which included studies of urban landcover using remote sensing technology such as satellite images, found that urban landcover increased by nearly 60, km 2 between and In the year , estimates suggest that globally, urban land covered somewhere between , and 3. The meta-analysis found that the largest rates of increase in urban landcover were seen in India, China and Africa, while North America experienced the largest total change since In all regions, urban land expanded either faster or equivalent to population growth rates, suggesting our societies are also becoming more expansive. Using data from to , the researchers then tried to project future urban land cover change — their results predict that global urban landcover will increase by a further 1. Over half-way to this prediction, where are we now? Artificial surfaces include any areas that have an artificial cover as a result of human activities such as construction cities, towns, transportation , extraction open mines and quarries or waste disposal. This figure gives us an estimate of roughly , km 2 of human-covered land worldwide. However, even non-urban areas contain roads, train tracks, farms and other marks of human domination. If we include this to our estimate of global human cover — we get a rather more sobering estimate of 19 million km 2. She completed her PhD in on the social behaviour of dinosaur ants. We should convert sea water into sweat water and we should make canals for providing water in all deserts of the world and that area where rocky barren land where we put arable sand in this way our earth can support 40 billion people.
This question is an interesting one because, when my friend asked me the other day, I could tell her confidently that not only did science know the answer, science had multiple different ways to quantify that answer, but that I had absolutely no idea what it was. F or as long as humans have existed they have impacted their surrounding environment.
Pianka "Land, they aren't making any more of it" -- Will Rogers Despite claims to the contrary, humans cannot live without food and water. One third of Earth's surface is desert which supports very few people. People can visit deserts but long-term survival in desert regions is very tenuous. Cities built in deserts like Los Angeles, Las Vegas, Phoenix, and Tuscon, cannot exist without importing water or pumping groundwater out of deep aquifers. Indeed, they all face serious water shortages.
The focus of this topic page is land use for agriculture. But we are also studying other uses of land, including land required for human settlement. Agriculture is a major use of land. The extensive land use has a major impact on the earth's environment as it reduces wilderness and threatens biodiversity. Reducing the consumption of resource-intensive products and increasing the productivity of land makes it possible to produce food with much smaller inputs and reducing the impact on the environment. The most visible mark that humanity has left on the planet is the transformation of wild habitats into farmland. In the visualization we see the breakdown of global land area today.
How much land is inhabited by humans
By Jonathan Lambert. April 15, at am. Lions, hyenas and other top predators still stalk herds of wildebeests over a million strong, preventing them from eating too much vegetation.
Cars under 1000
The director was Wim Wenders and the son of Sebastiao Salgado. Humans have disturbed a very small portion of the earths surface. Did you actually write this? People can visit deserts but long-term survival in desert regions is very tenuous. Similarly, humans cannot sustain themselves for very long in mountains, though we often visit these regions on a temporary basis. To move air from one place to other it is must that one area is hot and one area is cold at same time. Divide this figure by the current human population of 7 billion that's 7, million people and you get 2. New research shows significance of community-held territories in 24 countries to global climate. LinkedIn 0. Press Releases. Interestingly, their findings show that whilst the maps analysed use different methodologies they show similar results for the level of human influence across the globe. How much land does it take to support a human being?
Article, pp. The human population has doubled in the past 40 years and is projected to increase by the same amount again in the next
You can fly for a long time and hardly see a sign of human existance along many parts of the continent. A person living the profligate lifestyle of an average American requires almost 24 acres, ten times the world per capita share. The authors also emphasized that all the identified land should not necessarily be designated as protected areas, but rather managed through a wide range of strategies for species and ecosystem conservation, including effective sustainable land-use policies. They range from empowering Indigenous Peoples to policies that limit deforestation and to protected areas, depending on the local context. Kissing points out that if nations are serious about safeguarding biodiversity and ecosystem services that underpin life on Earth, then they need to immediately scale-up their conservation efforts, not just in extent and intensity but also in effectiveness. Hot air goes up and leaves the vacuum under it, which is filled by cold air again. Cities built in deserts like Los Angeles, Las Vegas, Phoenix, and Tuscon, cannot exist without importing water or pumping groundwater out of deep aquifers. One third of Earth's surface is desert which supports very few people. We have only one. New research shows significance of community-held territories in 24 countries to global climate.

All about one and so it is infinite
Amusing question