Heating of ferrous sulphate crystal
Thus, the crystals of ferrous sulphate on heating give ferric oxide, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide. Byju's Answer. Open in App. The reaction of ferrous sulphate upon heating: The water of crystallisation is present in ferrous sulphate crystals FeSO 4.
Find the answer to this question and access a vast question bank that is customized for the student. Explanation: —. FeSO 4. When ferrous sulphate is heated, it loses its water molecules and creates an anhydrous ferrous sulphate molecule, as well as changing the color of the ferrous sulphate molecule from green to white. Complete the following steps in order:. A decomposition reaction occurs when a chemical compound is broken down into two or more other compounds. The double decomposition reaction occurs when reactants exchange positive and negative ions, resulting in the synthesis of new molecules.
Heating of ferrous sulphate crystal
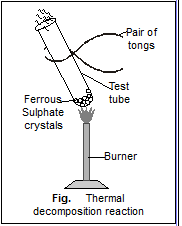
Viva Voce. Decomposition Reaction. Materials required: Procedure: Real Lab Procedure: Take about 2g of ferrous sulphate crystals in a dry boiling tube and note the colour of the crystals. Hold the boiling tube with a test tube holder and heat the boiling tube over the flame of a burner. Smell the gas being emitted. Observe the colour of the crystals after heating. To put copper carbonate into the test tube, drag the spatula over the test tube. To turn on the burner, click on the knob of the burner. To heat the contents of the test tube, drag the test tube over the burner. Wait for some time to complete the reaction. You can see the chemical equation of the corresponding reaction on the side menu. You can see the inference by clicking on the inference icon. Adjust the resistance of the rheostat using the slider. Use the slider to select the power of light from the source.
So, the gas emitted smells like burning sulphur.
.
Earlier, it was also known as the green vitriol of copperas. It was formerly used as a fixative for dyes in textile industries, blackening hide and as a component in ink. Approximately 7 centuries ago, the process of preparing sulfuric acid included the distillation of ferrous sulfate. Iron II sulfate is a bluish-green chemical that is employed in several applications like manufacturing ink, dye, and medicines. You should know about ferrous sulfate in detail because this chemical compound has a lot of importance in our day to day life. To know the concepts related to ferrous sulfate, you can simply give a read to this article. In this article, you will study the meaning of ferrous sulfate, its chemical name, its other names and how it is defined in chemistry.
Heating of ferrous sulphate crystal
The hydrated form is used medically to treat or prevent iron deficiency , and also for industrial applications. Known since ancient times as copperas and as green vitriol vitriol is an archaic name for sulfate , the blue-green heptahydrate hydrate with 7 molecules of water is the most common form of this material. The name copperas dates from times when the copper II sulfate was known as blue copperas, and perhaps in analogy, iron II and zinc sulfate were known respectively as green and white copperas. Industrially, ferrous sulfate is mainly used as a precursor to other iron compounds. It is a reducing agent , and as such is useful for the reduction of chromate in cement to less toxic Cr III compounds. Historically ferrous sulfate was used in the textile industry for centuries as a dye fixative.
Witch dress costume
Write chemical equations for each one of the above reactions. The reaction of ferrous sulphate upon heating: The water of crystallisation is present in ferrous sulphate crystals FeSO 4. You can see the inference by clicking on the inference icon. Open in App. Use the slider to select the power of light from the source. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this change? Observations: The ferrous sulphate crystals are light green in colour. Waft gases emitted from ferrous sulphate on heating gently towards your nose holding the test tube at a distance. How does this colour change after heating? The crystals of ferrous sulphate on heating gives:. Explanation: —. Thus, the crystals of ferrous sulphate on heating give ferric oxide, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide. The gas emitted has the characteristic odour of burning sulphur.
The positions of the hydrogen atoms were located based on DFT calculations.
Oxides of Nitrogen. So, the gas emitted smells like burning sulphur. You are given the following materials: i Iron nails ii Copper sulphate solution iii Barium chloride solution iv Copper powder v Ferrous sulphate crystals vi Quicklime Identify the type of chemical reaction taking place when: a Barium chloride solution is mixed with copper sulphate solution and a white precipitate is observed. On heating, the colour changes from light green to white. To put copper carbonate into the test tube, drag the spatula over the test tube. Adjust the resistance of the rheostat using the slider. The decomposition of calcium carbonate to calcium oxide and carbon dioxide is another example of a thermal decomposition reaction. When ferrous sulphate is heated further, it breaks down into ferric oxide, Sulphur trioxide, and Sulphur dioxide. The reaction of ferrous sulphate upon heating: The water of crystallisation is present in ferrous sulphate crystals FeSO 4. On heating, ferrous sulphate crystals lose water and anhydrous ferrous sulphate FeSO 4 is formed. Find the answer to this question and access a vast question bank that is customized for the student.

0 thoughts on “Heating of ferrous sulphate crystal”