Glass coma scale chart
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf.
The Glasgow Coma Scale GCS was first described in and has become an important clinical tool in the assessment of patients worldwide. It provides a consistent, reliable and easily communicated approach for assessing patients with head injury. Please visit the GCS website via the link below:. Close Menu Neurology in Glasgow and Clyde. Cognitive Disorders. General Neurology.
Glass coma scale chart
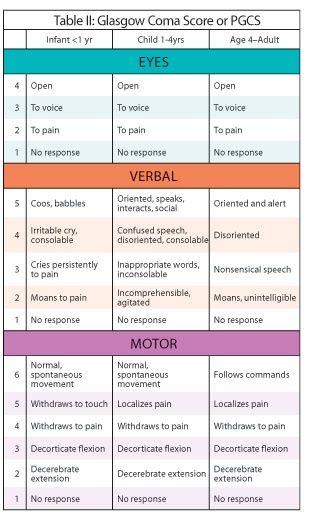
The Glasgow Coma Scale [1] GCS is a clinical scale used to reliably measure a person's level of consciousness after a brain injury. The GCS assesses a person based on their ability to perform eye movements, speak, and move their body. These three behaviours make up the three elements of the scale: eye, verbal, and motor. A person's GCS score can range from 3 completely unresponsive to 15 responsive. This score is used to guide immediate medical care after a brain injury such as a car accident and also to monitor hospitalised patients and track their level of consciousness. Lower GCS scores are correlated with higher risk of death. However, the GCS score alone should not be used on its own to predict the outcome for an individual person with brain injury. The Glasgow Coma Scale is used for people above the age of two and is composed of three tests: eye , verbal , and motor responses. The scores for each of these tests are indicated in the table below. The Glasgow Coma Scale is reported as the combined score which ranges from 3 to 15 and the score of each test E for eye, V for Verbal, and M for Motor. For each test, the value should be based on the best response that the person being examined can provide. For example, if a person obeys commands only on their right side, they get a 6 for motor.
The Glasgow Coma Scale was initially adopted by nursing staff in the Glasgow neurosurgical unit. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica. A systematic review has not been reported on comparisons between the reliability and prognostic yield of the Four Score and the GCS Score.
.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Shobhit Jain ; Lindsay M. Authors Shobhit Jain 1 ; Lindsay M. Iverson 2. The Glasgow Coma Scale GCS is used to objectively describe the extent of impaired consciousness in all types of acute medical and trauma patients.
Glass coma scale chart
The Glasgow Coma Scale GCS , designed in , is a tool that has the ability to communicate the level of consciousness of patients with acute or traumatic brain injury. Developed by Graham Teasdale and Bryan J. Jennett, professors of neurosurgery at the University of Glasgow's Institute of Neurological Sciences, this scale is the gold standard used for all acute medical and trauma patients. Used by trained medical professionals, the GCS is an objective and reliable tool that nurses and nursing students should become familiar with regardless of their place of employment. The Glasgow Coma Scale can identify changes to consciousness in traumatic brain injury patients but requires nurses to fully understand its purpose and how to use it. Identifying the patients that require scoring is the first step in properly using the scale. An initial GCS should be done at the time of admission and then every four hours unless otherwise indicated by the medical team.
Dogs licking teens
Adding up the Glasgow Coma Score. Predicting Mortality in Critically Ill Patients. Simplifying the use of prognostic information in traumatic brain injury. There are instances when the Glasgow Coma Scale is unobtainable despite efforts to overcome the issues listed above. The Glasgow Coma Scale has been taken into numerous guidelines and assessment scores. Abnormal flexion to painful stimuli decorticate response. These additional features have been found to have lesser relations to with outcome than the eye and motor scales. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal. Spinal decompression Discectomy Intervertebral disc annuloplasty Cordotomy Rhizotomy. In these circumstances, the score is given as 1 with a modifier attached e. ISBN In individual patients, the clinical findings in three components should, therefore, be reported separately.
Jump to navigation.
The Glasgow Coma Scale has been taken into numerous guidelines and assessment scores. Proceedings of the 6th European Congress of Neurosurgery. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology in French. Review Current reporting of responsiveness in acute cerebral disorders. Hemodynamics Hypotension Level of consciousness Acid—base imbalance Water-electrolyte imbalance. Turn recording back on. The Glasgow Coma Scale GCS is used to objectively describe the extent of impaired consciousness in all types of acute medical and trauma patients. The Glasgow Coma Scale can be used in children older than 5 years with no modification. PLoS Med. February This is because the prognostic implications of the score are influenced by several factors. The reliability of the GCS Scale has undergone extensive study. Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness. Authors Shobhit Jain 1 ; Lindsay M. Information Leaflets.

0 thoughts on “Glass coma scale chart”