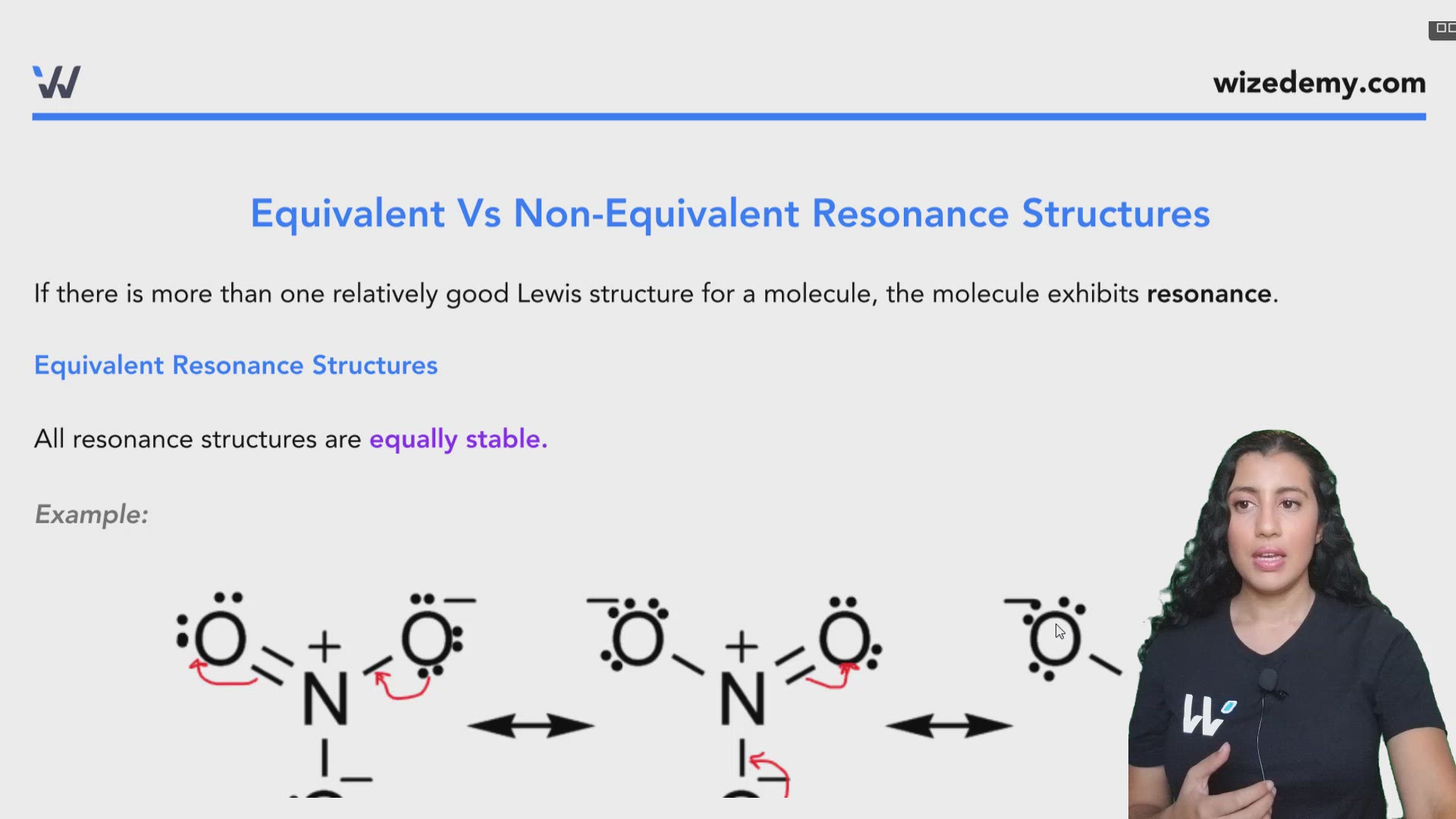
Equivalent resonance structures
In cases in which more than one reasonable plausible Lewis structure can be drawn for a species, these structures are called resonance structures or resonance contributors. Resonance structures can be either equivalent or non-equivalent. However, they are not really identical or the sameequivalent resonance structures, equivalent resonance structures are just equivalent. Each structure is called a resonance structure, and they can be connected by the double-headed resonance arrow.
Lewis formulas are misleading in the sense that atoms and electrons are shown as being static. By being essentially two-dimensional representations they also fail to give an accurate idea of the three-dimensional features of the molecule, such as actual bond angles and topography of the molecular frame. Furthermore, a given compound can have several valid Lewis formulas. For example CH 3 CNO can be represented by at least three different but valid Lewis structures called resonance forms, or resonance structures , shown below. However, a stable compound such as the above does not exist in multiple states represented by structures I, or II, or III. The compound exists in a single state called a hybrid of all three structures.
Equivalent resonance structures
Revolutionized is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commision. Learn more here. Chemists must know about equivalent resonance structures in their work. What are they, and why does it matter? Before getting into equivalent resonance structures, people must understand Lewis structures. They also indicate the bonds between atoms. Lewis structures can tell people important things, but only if they follow the correct steps when making them. Equivalent resonance structures have more than one Lewis structure representing them. They are chemical or molecular compounds with different electron and atom arrangements. Although each Lewis structure differs, these structures have the same stability and energy. North Carolina State University offers a free and interactive Lewis structure builder. Chemists also learn about non-equivalent resonance structures when training to enter the field.
Introduction There are some basic principle on the resonance theory. The reader must know the flow of the electrons. In the resonance forms shown above the atoms remain in one place.
A resonance form is another way of drawing a Lewis dot structure for a given compound. Equivalent Lewis structures are called resonance forms. They are used when there is more than one way to place double bonds and lone pairs on atoms. Resonance structures arise when there are more than one way to draw a Lewis dot diagram that satisfies the octet rule. Remember the octet rule is where the atom gains, loses, or shares electrons so that the outer electron shell has eight electrons. We draw them when one structure does not accurately show the real structure.
Lewis formulas are misleading in the sense that atoms and electrons are shown as being static. By being essentially two-dimensional representations they also fail to give an accurate idea of the three-dimensional features of the molecule, such as actual bond angles and topography of the molecular frame. Furthermore, a given compound can have several valid Lewis formulas. For example CH 3 CNO can be represented by at least three different but valid Lewis structures called resonance forms, or resonance structures , shown below. However, a stable compound such as the above does not exist in multiple states represented by structures I, or II, or III.
Equivalent resonance structures
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Resonance structures. About About this video Transcript. Introduction to resonance structures, when they are used, and how they are drawn. Created by Jay.
Union salon pasadena ca
Charge delocalization helps stabilize the whole species. Draw all of the resonance structures for azide anion, N 3 — , and indicate the most stable o ne. Always check the net charge after each structure. References McMurry, John M. The structure shown below is structurally different from the ones shown above. There is a third resonance form that can be drawn for the acetate ion hybrid. The main difference between these and equivalent resonance structures is that the former has different atom arrangements, and often, different atomic structures. For non-equivalent resonance structures, the bonding and charge distributions are different, so they are in different energy levels. Search site Search Search. The total number of valence electrons being shared for all atoms is 4 from carbon and 3 from the three hydrogens, for a total of 7. Before getting into equivalent resonance structures, people must understand Lewis structures. Avoid having unpaired electrons single electrons with no partners unless the total number of valence electrons for all elements is an odd number. Make sure the arrows are clear including the single and half headed arrow.
In cases in which more than one reasonable plausible Lewis structure can be drawn for a species, these structures are called resonance structures or resonance contributors.
This is why formal charges are very important. From the examples given so far it can be seen that some resonance forms are structurally equivalent and others are not. The actual structure can not be shown with a conventional Lewis structure because the regular Lewis structures do not include partial charges, and there are two-thirds of a full negative charge on each oxygen atom in CO When she isn't working, Emily enjoys playing video games or curling up with a good book. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commision. The sp 2 hybridized atom is either a double-bonded carbon, or a carbon with a positive charge, or it is an unpaired electron. The better ones have minimal formal charges, negative formal charges are the most electronegative atoms, and bond is maximized in the structure. First resonance structures are not real, they just show possible structures for a compound. Draw all of the resonance structures for azide anion, N 3 — , and indicate the most stable o ne. Less electronegative atoms are more comfortable with positive charges. Finally, after drawing the resonance form make sure all the atoms have eight electrons in the outer shell.

Magnificent phrase
Now all became clear to me, I thank for the necessary information.