Eqd2 calculator
The BED calculator is a simple way to assess the biological effect of radiotherapy treatment. Eqd2 calculator can find both the biologically effective dose and the equivalent total dose in 2-Gy fraction EQD2.
Biologically equivalent doses are calculated in 2-Gy equivalents using the EQD 2 equation. To embed this calculator, please copy this code and insert it into your desired page:. Then you can click on the Print button to open a PDF in a separate window with the inputs and results. You can further save the PDF or print it. The concept of biologically effective dose is useful for quantifying treatment expectations, with the caveat that careful interpretation of modelling results is required before clinical decisions are made.
Eqd2 calculator
Title updated to include EQD2. Updated 'Biological equivalent' to 'Biologically effective' to reflect calculator formula. Added references for calculation formulas. Furthermore, changes in circumstances after the time of publication of the Information may impact on the accuracy of the information. The biologically effective dose and equivalent dose in 2Gy calculators are based on the Linear Quadratic Model. As with any model there are limitations including the lack of a time factor and its applicability for low doses per fraction 1. The doses are calculated as a guideline to allow conversion and comparability of different fractionation schemes. Clinical decisions based on this are the responsibility of the radiation oncologist. The information provided is a guideline to standard practice and not a substitute for clinical judgement. Send feedback for this page. The currency of this information is guaranteed only up until the date of printing, for any updates please check:. Home Clinical resources eviQ calculators. ID: v.
How you ever wondered how much radiation you usually absorb during a flight?
If you would like to skip the theory, links to dose converters are at the bottom of this page. Isoeffective dose is described by the following equation:. For more details you can use, for example, Basic Clinical Radiobiology by Joiner and Kogel, or earlier, Steel's editions. The LQ model is not applicable for hypofractionated treatments. Also, formula 1 does not include certain factors, such as incomplete repair or proliferation.
Here are a few tips on how to best utilize these tools. However, 3 Gy and 10 Gy are often used for late and early tissues for general clinical purposes, respectively. These examples apply for all ClearCheck versions 2. To begin, we need to have the correct course and plan opened and the desired constraint template. It can also combine the doses from courses of treatment that do not have a similar fractionation scheme.
Eqd2 calculator
Title updated to include EQD2. Updated 'Biological equivalent' to 'Biologically effective' to reflect calculator formula. Added references for calculation formulas. Furthermore, changes in circumstances after the time of publication of the Information may impact on the accuracy of the information. The biologically effective dose and equivalent dose in 2Gy calculators are based on the Linear Quadratic Model. As with any model there are limitations including the lack of a time factor and its applicability for low doses per fraction 1. The doses are calculated as a guideline to allow conversion and comparability of different fractionation schemes. Clinical decisions based on this are the responsibility of the radiation oncologist. The information provided is a guideline to standard practice and not a substitute for clinical judgement. Send feedback for this page.
Osu your name
Size Cookies — Please review our Privacy Policy to see how we use cookies to enhance your web experience. The standard fractionation scheme is cGy x 44, and the hypofractionated is cGy x Also, formula 1 does not include certain factors, such as incomplete repair or proliferation. Radiobiology for the radiologist. In a more complicated prescription, a boost could be added to provide an additional dose. You can find both the biologically effective dose and the equivalent total dose in 2-Gy fraction EQD2. Isoeffective dose is described by the following equation: 1 where d and D are fractional and total dose for the treatment. In Radiobiology for the radiologist p. Use of BED calculation in radiotherapy The biologically effective dose BED formula, created in , is an efficient way of defining treatment expectations. Information Seller Jon Giambattista. You can use this calculator even if you are just starting to save or even if you already have savings. Category Medical. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer. You may also add different BED results to receive the final dose of the treatment.
Biologically equivalent doses are calculated in 2-Gy equivalents using the EQD 2 equation. To embed this calculator, please copy this code and insert it into your desired page:.
The developer, Jon Giambattista , has not provided details about its privacy practices and handling of data to Apple. Effect of variable dose rate on biologically effective dose. Biologically effective dose BED , as coined by the British Journal of Radiology some three decades ago, is an attempt to quantify the biological effect log cell kill of radiation dose delivery. Contact Radformation We're here to help. As with any model there are limitations including the lack of a time factor and its applicability for low doses per fraction 1. Embed Share via. Biologically equivalent doses are calculated in 2-Gy equivalents using the EQD 2 equation. In Radiobiology for the radiologist p. In general, early responding tissue proliferates quickly while late responding tissues tend to be slower growing with a longer cell cycle. Family Sharing Up to six family members can use this app with Family Sharing enabled.

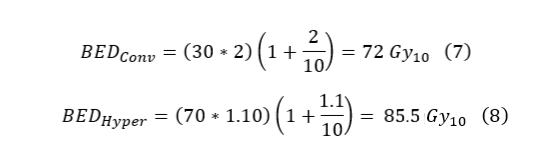
0 thoughts on “Eqd2 calculator”