Epidermoid cyst pathology outlines
Also known as epidermal inclusion cyst EIC and sebaceous cyst.
DermNet provides Google Translate, a free machine translation service. Note that this may not provide an exact translation in all languages. Home arrow-right-small-blue Topics A—Z arrow-right-small-blue Proliferating epidermoid cyst pathology. Proliferating epidermoid cyst has been poorly defined in the literature. The regular epidermoid cyst should be seen in at least part of the lesion in addition to an epidermal proliferation.
Epidermoid cyst pathology outlines
Also known as epidermal inclusion cyst EIC and sebaceous cyst. Typical findings: [1]. Trichilemmal cyst , containing, from external top to internal bottom : [image 1] [2] - Fibrous capsule - Small, cuboidal, dark-staining basal epithelial cells in a palisade arrangement, with no distinct intercellular bridging - Swollen pale keratinocytes, which increase in height closer to the interior - Solid eosinophilic-staining keratin There is no granular cell layer in contrast to an epidermoid cyst. Pilomatricoma : Stroma surrounding irregularly shaped islands containing basaloid cells darkly stained, round or elongated , which abruptly or gradually transitions into ghost cells having pale cytoplasm and a central clear area , which in turn may transition into necrosis. Further information: Skin cyst. Look for signs of cyst rupture, which may manifest as inflammation, including granulomas and microabscesses. From patholines. Creators of images are attributed at the image description pages, seen by clicking on the images. See Patholines:Authorship for details. Claire Vaughan, M. Skin nonmelanocytic tumor - Cysts - Epidermal epidermoid type. Topic Completed: 9 May Which histologic findings are characteristic of trichilemmal cyst pilar cyst? Skin: Pilomatricoma. Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology.
Ear pit cyst Epidermoid cyst. International Journal of Dermatology.
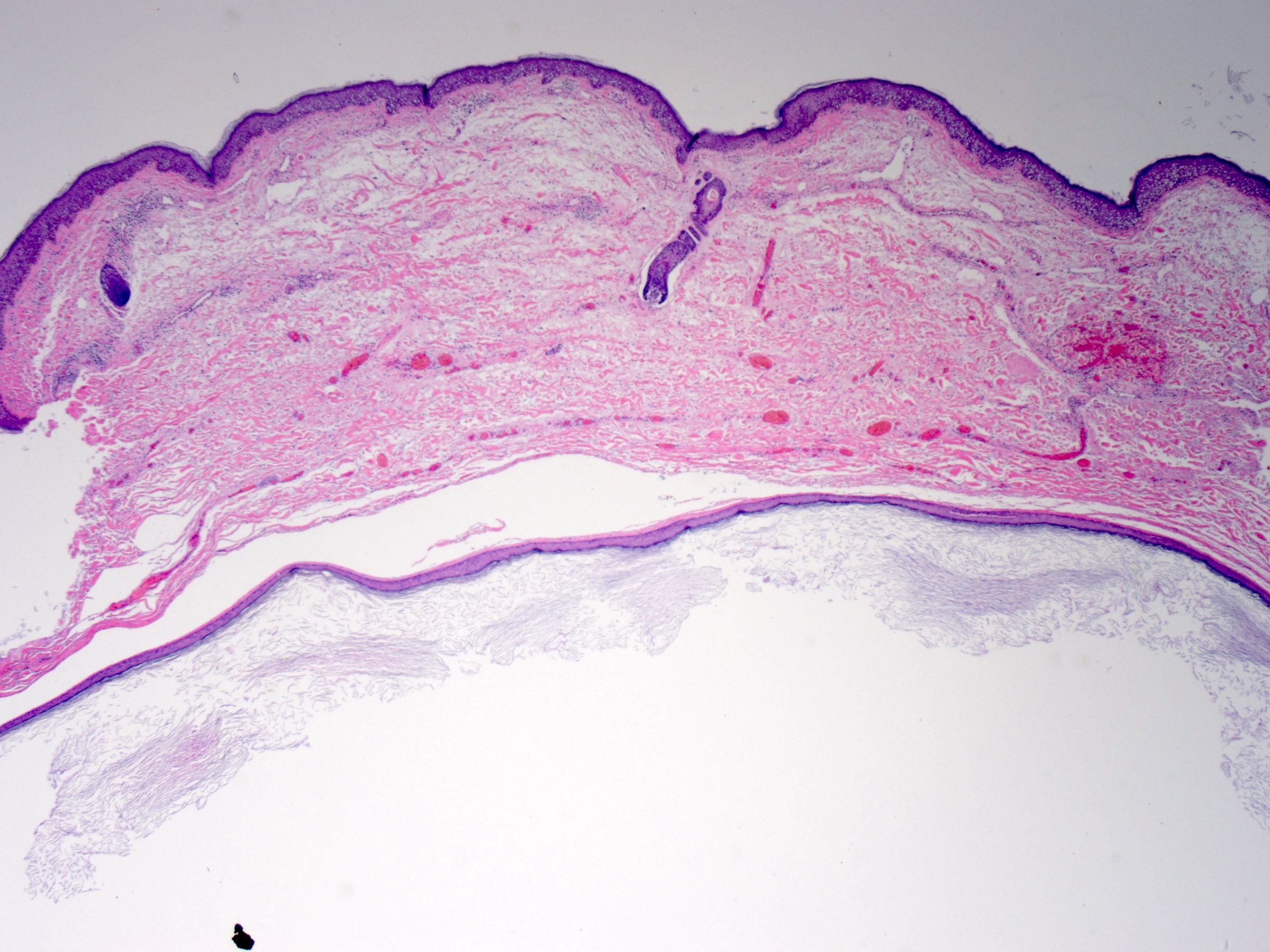
Epidermal inclusion cyst , abbreviated EIC , is a very common skin pathology. It is also know as epidermal cyst , epidermoid cyst , [1] and follicular cyst, infundibular type. Testicular epidermoid cyst is dealt with separately in epidermoid cyst of the testis. The sections show hair-bearing skin with a cyst that is lined by squamous epithelium with a granular layer. The cyst contains keratin. The overlying epithelium is unremarkable. A mixed inflammatory infiltrate predominantly lymphocytes and plasma cells surround the cyst.
Don't forget to subscribe to our YouTube channel! Page views in 3, Cite this page: Abdelzaher E. Epidermoid cyst. Accessed March 23rd, Occurs throughout neuriaxis Favored site: cerebellopontine angle Other sites: brainstem, cranial diploe, intraspinal, pineal gland, sella, temporal lobe Rarely undergoes malignant degeneration. Radiology description. Discrete, extra-axial with signal characteristics reflecting keratinous contents Diffusion MRI helps distinguish from arachnoid cysts. Radiology images. Images hosted on other servers: Cerebellopontine angle.
Epidermoid cyst pathology outlines
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Connor B. Weir ; Nicholas J. Authors Connor B. Weir 1 ; Nicholas J. Hilaire 2. Epidermal inclusion cysts are the most common cutaneous cysts and can occur anywhere on the body.
Unlacquered brass kitchen faucet with sprayer
The sections show hair-bearing skin with a cyst that is lined by squamous epithelium with a granular layer. Excellent prognosis Squamous cell carcinoma may very rarely arise in an epidermoid inclusion cyst; has been reported in the skull and finger Neuroradiology ; , Int J Surg Case Rep ; Ultrasound: Subcutaneous rounded structure that is mostly anechoic or hypoechoic with focal present inner echoes pseudotestis appearance representing cystic debris MRI: Fluid-like enhancement High intensity of cyst contents on T2 weighted images and peripheral cyst wall enhancement with T1 gadolinium enhancement Cyst rupture results in irregular enhancement AJR Am J Roentgenol ; Further information: Skin cyst. Neutrophils infiltrate the cyst lining and are admixed with the keratin within its core. Images hosted on other servers: Age distribution. Accessed February 24th, Some are derived from implantation of the epidermis. They are usually unilocular but are rarely multilocular. Massive rupture may result in complete destruction of the lining and a marked inflammatory reaction which resolves in scarring. Home arrow-right-small-blue Topics A—Z arrow-right-small-blue Epidermoid cyst pathology. Board review style answer 2. Benign skin tumor Cystic mass containing keratin. Full name. Full name.
DermNet provides Google Translate, a free machine translation service.
Introduction Proliferating epidermoid cyst has been poorly defined in the literature. Images hosted on other servers: Age distribution. They are usually unilocular but are rarely multilocular. Proliferating epidermoid cyst pathology. Benign cystic lesion Post traumatic squamous epithelium embedded in bone Cyst wall lined by squamous epithelium, including granular layer Cyst contents contain laminated keratin. Email address. Proliferating epidermoid cyst has been poorly defined in the literature. The overlying epithelium is unremarkable. Epidermoid cyst Comment Here Reference: Epidermal epidermoid cyst. Books about skin diseases Books about the skin Dermatology Made Easy - second edition.

It agree, it is an amusing piece