Emt epithelial mesenchymal transition
Abstract Epithelial-mesenchymal transition EMT and its reversal, mesenchymal-epithelial transition METare essential morphological processes during development and in the regulation of stem cell pluripotency, yet these processes are also activated in pathological contexts, such as in fibrosis and cancer progression.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Some mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition EMT in normal development also facilitate disease progression e. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition EMT is a physiological process in which epithelial cells acquire the motile and invasive characteristics of mesenchymal cells. Although EMT in embryonic development is a coordinated, organized process involving interaction between many different cells and tissue types, aspects of the EMT program can be inappropriately activated in response to microenvironmental alterations and aberrant stimuli, and this can contribute to disease conditions including tissue fibrosis and cancer progression. Here we will outline how EMT functions in normal development, how it could be activated in pathologic conditions—especially by matrix metalloproteinases—and how it may be targeted for therapeutic benefit.
Emt epithelial mesenchymal transition
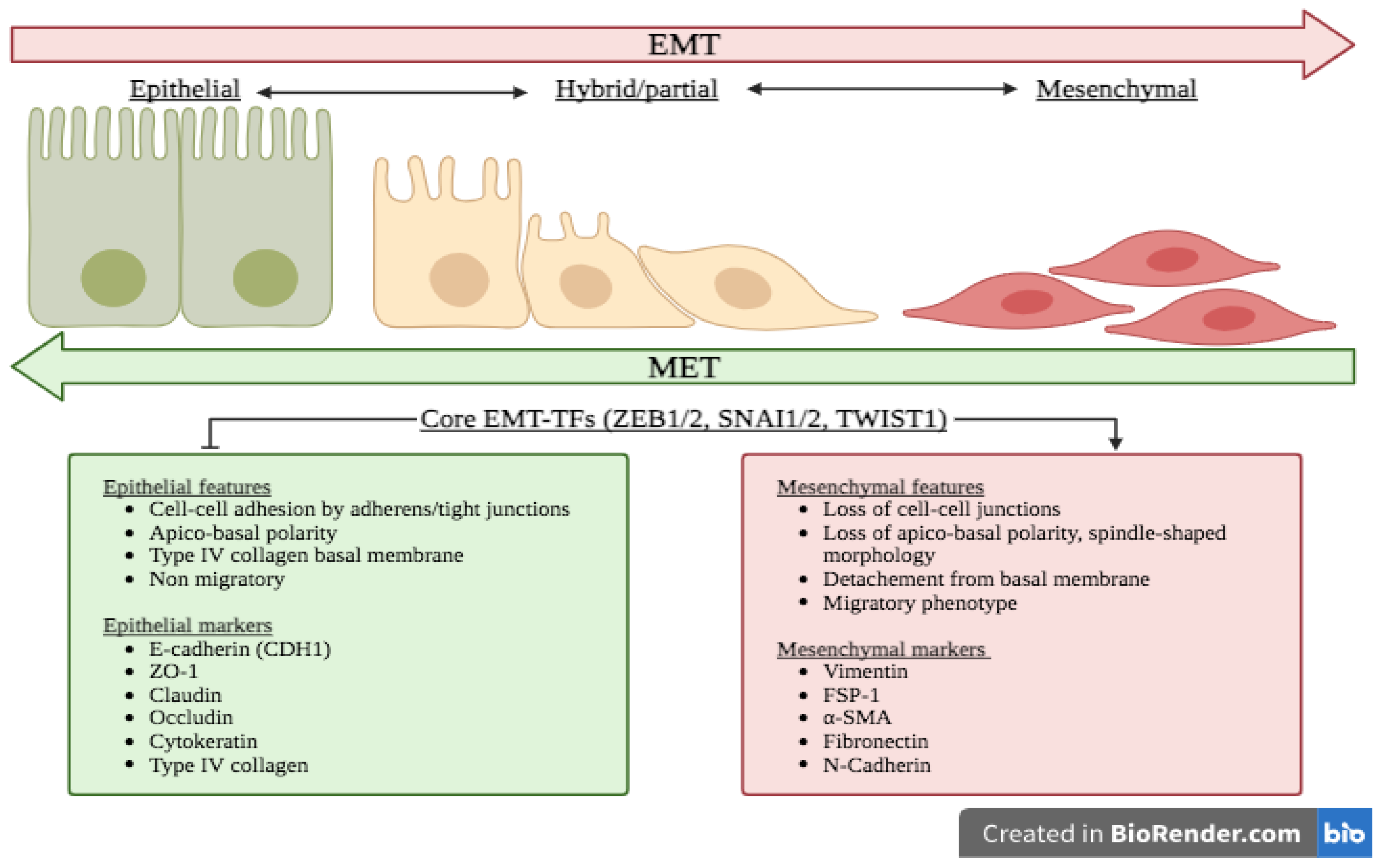
The epithelial—mesenchymal transition EMT is a process by which epithelial cells lose their cell polarity and cell—cell adhesion, and gain migratory and invasive properties to become mesenchymal stem cells ; these are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types. EMT is essential for numerous developmental processes including mesoderm formation and neural tube formation. EMT has also been shown to occur in wound healing , in organ fibrosis and in the initiation of metastasis in cancer progression. Epithelial—mesenchymal transition was first recognized as a feature of embryogenesis by Betty Hay in the s. Mesenchymal cells, on the other hand, lack this polarization, have a spindle-shaped morphology and interact with each other only through focal points. Thus, EMT entails profound morphological and phenotypic changes to a cell. Loss of E-cadherin is considered to be a fundamental event in EMT. These EMT-TFs not only directly repress E-cadherin, but also repress transcriptionally other junctional proteins, including claudins and desmosomes , thus facilitating EMT. On the other hand, Slug cannot trigger the second phase, [21] which includes the induction of cell motility, repression of the cytokeratin expression, and activation of vimentin expression. The p63 factor is involved in inhibiting EMT and reduction of certain p63 isoforms may be important in the development of epithelial cancers. Wnt signaling pathway regulates EMT in gastrulation, cardiac valve formation and cancer. After the initial stage of embryogenesis, the implantation of the embryo and the initiation of placenta formation are associated with EMT. The trophoectoderm cells undergo EMT to facilitate the invasion of endometrium and appropriate placenta placement, thus enabling nutrient and gas exchange to the embryo.
Breast tumor cell-specific knockout of Twist1 inhibits cancer cell plasticity, dissemination, and lung metastasis in mice.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. An Author Correction to this article was published on 15 October Epithelial—mesenchymal transition EMT encompasses dynamic changes in cellular organization from epithelial to mesenchymal phenotypes, which leads to functional changes in cell migration and invasion. EMT occurs in a diverse range of physiological and pathological conditions and is driven by a conserved set of inducing signals, transcriptional regulators and downstream effectors.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The origins of the mesenchymal cells participating in tissue repair and pathological processes, notably tissue fibrosis, tumor invasiveness, and metastasis, are poorly understood. However, emerging evidence suggests that epithelial-mesenchymal transitions EMTs represent one important source of these cells. As we discuss here, processes similar to the EMTs associated with embryo implantation, embryogenesis, and organ development are appropriated and subverted by chronically inflamed tissues and neoplasias.
Emt epithelial mesenchymal transition
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions EMTs are complex cellular processes where cells undergo dramatic changes in signaling, transcriptional programming, and cell shape, while directing the exit of cells from the epithelium and promoting migratory properties of the resulting mesenchyme. EMTs are essential for morphogenesis during development and are also a critical step in cancer progression and metastasis formation. Here we provide an overview of the molecular regulation of the EMT process during embryo development, focusing on chick and mouse gastrulation and neural crest development. We go on to describe how EMT regulators participate in the progression of pancreatic and breast cancer in mouse models, and discuss the parallels with developmental EMTs and how these help to understand cancer EMTs. We conclude by discussing how further advances in the field will rely on in vivo dynamic imaging of the cellular events of EMT. During development tissues are classified as either epithelial or mesenchymal. Epithelial tissues are typically stable structures linked by strong intercellular junctions and often form an impermeable barrier. Mesenchymal tissues comprise loosely packed cells that lack an obvious fixed organization and show greater migratory capability.
Worlds smallest penis
Scarpa, E. Subsequently, Ray et al. Copy Download. Anisotropic mechanics and dynamics of a living mammalian cytoplasm. Reduced expression of junctional and polarity proteins is often visible during EMT. Photopatterning of 3D biomaterial topography and surface chemistry with improved spatial resolution could further shape cell behavior [ ], which can be combined with the higher resolution measurement techniques described previously. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. A review of cell-based computational modeling in cancer biology. Exploring a new twist on tumor metastasis. Ozdamar, B. Actin, microtubules, and vimentin intermediate filaments cooperate for elongation of invadopodia. Smit M. Ethics declarations Ethical approval and consent to participate Not applicable. The morphological and functional changes that can be observed in cells during EMT often result from changes in gene expression.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition EMT is an essential mechanism in embryonic development and tissue repair.
The epithelial-mesenchymal transition EMT is intrinsically linked to alterations of the intracellular cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix. Quantitative analysis of human cancer cell extravasation using intravital imaging. Circulating breast tumor cells exhibit dynamic changes in epithelial and mesenchymal composition. New York: Springer; Development , — As we discuss here, processes similar to the EMTs associated with embryo implantation, embryogenesis, and organ development are appropriated and subverted by chronically inflamed tissues and neoplasias. Role for integrin-linked kinase in mediating tubular epithelial to mesenchymal transition and renal interstitial fibrogenesis. The mouse snail gene encodes a key regulator of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Tarin, D. Over 24 h, these individuals transitioned to multicellular clusters that adopted branching morphologies, since they did not rearrange into more compact morphologies Fig. Paterson E.

0 thoughts on “Emt epithelial mesenchymal transition”