Electron dot structure of hno3
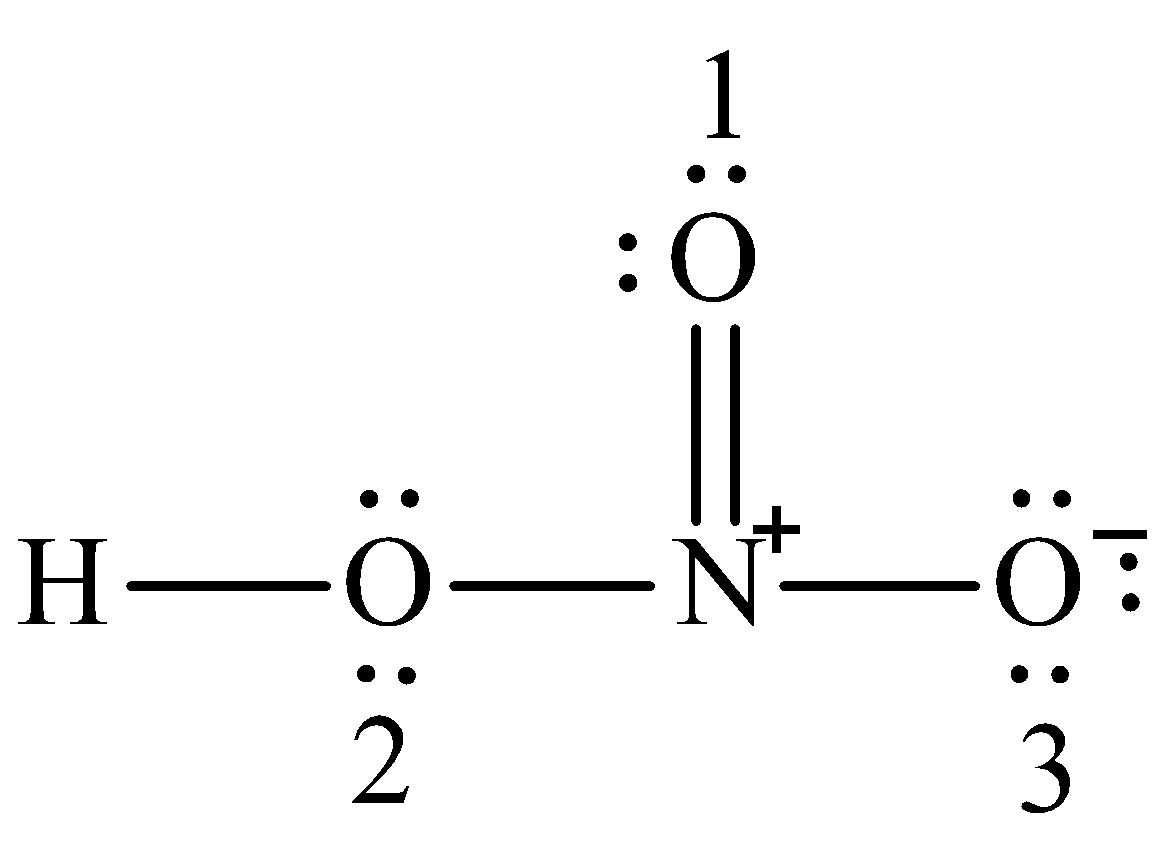
HNO 3 Nitric acid lewis stricture is drawn step by step by using valence electrons of each element. There are no lone pairs on nitrogen atom and also there are charges on one oxygen atom and nitrogen atom. You can see those signs in the following figure.
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 3h 53m. Classification of Matter. Chemical Properties. Physical Properties. Intensive vs.
Electron dot structure of hno3
Several worked examples relevant to this procedure were given in previous posts please see the Sitemap - Table of Contents Lewis Electron Dot Structures. Nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent and it dissolves practically all metals except gold and platinum and some other precious metals. As such, is an important raw material for the chemical and pharmaceutical industry. It is mainly used for etching and for the production of pure nitrates. Even though nitric acid was known since the 9th century - alchemists used it to separate gold and silver - its mass production started in when a German chemist Wilhelm Ostwald developed an industrial process. Initially it was used for the production of explosives but today its main use is for the production of fertilizers such as ammonium nitrate. Other main applications is for the production of explosives, nylon precursors and substituted organic compounds. In elemental analysis by atomic absorption spectroscopy , ICP , graphite furnace atomic spectroscopy dilute nitric acid is used as a "solvent" for the determination of metal traces in solution. Let us draw the Lewis dot structure of nitric acid :. Step 1 : The central atom will be the N atom since it is the less electronegative H is a terminal atom — it cannot be a central atom. Connect the atoms with single bonds:. Where n in this case is 4 since HNO 3 consists of five atoms but one of them is a H atom. Therefore, the Lewis resonance structures for HNO 3 are as follows:. Lewis, J.
Guided course. Chemical Thermodynamics 1h 48m.
Draw the Lewis structure of HCN. Draw a Lewis structure of nitric oxide, NO. Draw the Lewis structure of B e C l 2. Draw the Lewis structure for S F 6. Draw the structure of : Perchloric acid.
This pattern of adding a hydrogen atom to one of the oxygen atoms is frequently observed in many acids. To determine the total number of valence electrons in the HNO3 molecule and construct the Lewis structure, follow these steps:. Determine the total number of valence electrons. Identify the central atom. In HNO3, the nitrogen atom N is the central atom since it is less electronegative than oxygen. Remember : If hydrogen is present in the molecule, always place the hydrogen atoms on the outside.
Electron dot structure of hno3
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 3h 53m. Classification of Matter. Chemical Properties. Physical Properties.
Barrie leolist
Periodic Table: Elemental Forms. Amide Formation. Table of contents. Paramagnetism and Diamagnetism. The angular shape of none molecule O 3 consists of. Combustion Apparatus. Periodic Table: Element Symbols. Nitrogen is located at group VA and has five electrons in its valence shell. Important: Drawing correct lewis structure is important to draw resonance structures correctly. Naming Molecular Compounds. Naming Esters. Heating and Cooling Curves. Osmotic Pressure.
The nitrogen atom is at the center and it is surrounded by 2 oxygen atoms and one O-H bond. Note: Take a pen and paper with you and try to draw this lewis structure along with me.
Oxide Reactions. After determining the center atom and sketch of HNO 3 , we should start to mark lone pairs on atoms. Even though nitric acid was known since the 9th century - alchemists used it to separate gold and silver - its mass production started in when a German chemist Wilhelm Ostwald developed an industrial process. Solutions: Mass Percent. Next video. Peroxide and Superoxide Reactions. Calculating K For Overall Reaction. There are no lone pairs on nitrogen atom. Bohr Equation. In the Lewis structure of acetic acid, there are. The Ideal Gas Law. Molecular Geometry. Introduction to Quantum Mechanics. Significant Figures: In Calculations. Test for Ions and Gases.

Very interesting idea