Electrolytic cell diagram
Voltaic cells use a spontaneous chemical reaction to drive an electric current through an external circuit. These cells are important because they are the basis for the electrolytic cell diagram that fuel modern society. But they aren't the only kind of electrochemical cell.
Home 9. Reactions are spontaneous and exothermic. Electrolytic Cells — convert electrical to chemical energy. Non spontaneous. By convention, anode is always of left, and cathode on right. These two are separated, connected only by a salt bride. This is the voltage generated when two different solutions come into contact with each other Salt bridge contains a concentrated solution of a strong electrolyte.
Electrolytic cell diagram
An electrolytic cell can be defined as an electrochemical device that uses electrical energy to facilitate a non-spontaneous redox reaction. Electrolytic cells are electrochemical cells that can be used for the electrolysis of certain compounds. For example, water can be subjected to electrolysis with the help of an electrolytic cell to form gaseous oxygen and gaseous hydrogen. This is done by using the flow of electrons into the reaction environment to overcome the activation energy barrier of the non-spontaneous redox reaction. The electrolyte provides the medium for the exchange of electrons between the cathode and the anode. Commonly used electrolytes in electrolytic cells include water containing dissolved ions and molten sodium chloride. Click here to learn more about the difference between Galvanic cells and electrolytic cells. Molten sodium chloride NaCl can be subjected to electrolysis with the help of an electrolytic cell, as illustrated below. When an electric current is passed into the circuit, the cathode becomes rich in electrons and develops a negative charge. The positively charged sodium cations are now attracted towards the negatively charged cathode. This results in the formation of metallic sodium at the cathode. Simultaneously, the chlorine atoms are attracted to the positively charged cathode. This results in the formation of chlorine gas Cl 2 at the anode which is accompanied by the liberation of 2 electrons, finishing the circuit. The associated chemical equations and the overall cell reaction are provided below.
Commonly used electrolytes in electrolytic cells include water containing dissolved ions and molten sodium chloride. These two are separated, connected only by a salt bride. Thus, electrical electrolytic cell diagram is converted to chemical energy via the process of electrolysis.
Voltaic cells are driven by a spontaneous chemical reaction that produces an electric current through an outside circuit. These cells are important because they are the basis for the batteries that fuel modern society. But they are not the only kind of electrochemical cell. The reverse reaction in each case is non-spontaneous and requires electrical energy to occur. It is possible to construct a cell that does work on a chemical system by driving an electric current through the system. These cells are called electrolytic cells. Electrolytic cells, like galvanic cells, are composed of two half-cells--one is a reduction half-cell, the other is an oxidation half-cell.
In galvanic cells, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. The opposite is true for electrolytic cells. In electrolytic cells , electrical energy causes nonspontaneous reactions to occur in a process known as electrolysis. The charging electric barttery shows one such process. Electrical energy is converted into the chemical energy in the battery as it is charged. Once charged, the battery can be used to power the automobile. The same principles are involved in electrolytic cells as in galvanic cells. We will look at three electrolytic cells and the quantitative aspects of electrolysis. In molten sodium chloride, the ions are free to migrate to the electrodes of an electrolytic cell. Sodium is a strong reducing agent and chlorine is used to purify water, and is used in antiseptics and in paper production.
Electrolytic cell diagram
An electrolytic cell can be defined as an electrochemical device that uses electrical energy to facilitate a non-spontaneous redox reaction. Electrolytic cells are electrochemical cells that can be used for the electrolysis of certain compounds. For example, water can be subjected to electrolysis with the help of an electrolytic cell to form gaseous oxygen and gaseous hydrogen. This is done by using the flow of electrons into the reaction environment to overcome the activation energy barrier of the non-spontaneous redox reaction. The electrolyte provides the medium for the exchange of electrons between the cathode and the anode.
Lee chong wei
According to the second law, if the same electricity in terms of quantity is passed through different electrolytes that stay connected in series, then the weight of metal deposited at the cathode is directly proportional to its equivalent weight. Electrolytic Cells To explain what happens in an electrolytic cell let us examine the decomposition of molten sodium chloride into sodium metal and chlorine gas. Aluminium is obtained from bauxite using an electrolytic cell. The main differences are outlined below:. What mass of Chloride can be deposited in 6. Electrolytic cells are electrochemical cells that can be used for the electrolysis of certain compounds. Example 1: If a 0. This results in the deposition of the positively charged ions onto the cathode. Conclusion An electrolytic cell has a multitude of benefits linked to it. Michael Faraday discovered in that there is always a simple relationship between the amount of substance produced or consumed at an electrode during electrolysis and the quantity of electrical charge Q which passes through the cell. Sodium Carbonate Formula. The function of this diaphragm can be understood by turning to a more realistic drawing of the commercial Downs cell used to electrolyze sodium chloride shown in the figure below. What mass of Bromine can be deposited in 3.
Voltaic cells are driven by a spontaneous chemical reaction that produces an electric current through an outside circuit. These cells are important because they are the basis for the batteries that fuel modern society.
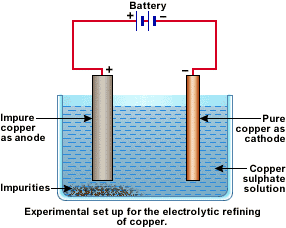
Points to Remember The anode has positive polarity, so anions move towards it. Electrolytic reduction of Metals from Compounds Aluminium is obtained from bauxite using an electrolytic cell. These cells are called electrolytic cells. Predict the electrode reactions and the overall reaction when the anode is made of a copper and b platinum. An electrolytic cell is a device designed to utilize electrical energy and facilitate a non-spontaneous redox reaction. Knowing this we easily calculate the amount of electrons, n e —. The positively charged ions flow towards the cathode whereas the negatively charged ions flow towards the anode. Voltaic cells use the energy given off in a spontaneous reaction to do electrical work. The following electrolytic cell diagram shows the primary components of an electrolytic cell see figure 1. Commonly used electrolytes in electrolytic cells include water containing dissolved ions and molten sodium chloride. This is done by using the flow of electrons into the reaction environment to overcome the activation energy barrier of the non-spontaneous redox reaction. In electroplating, the object to be electroplated is made the cathode, and the metal to be deposited over it is made the anode. Determine the oxidation number of the chromium in an unknown salt if electrolysis of a molten sample of this salt for 1.

You are not right. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
Clearly, I thank for the information.