Draw position time graph for uniform motion
Show that the slope of the position-time graph gives the velocity of the object. Draw the velocity-time graph for an object in uniform motion.
Byju's Answer. Define uniform motion of an object moving along a straight line. Draw position time and velocity time graph of such a motion. Open in App. Statement 1 : Velocity-time graph for an object in uniform motion along a straight path is a straight line parallel to the time axis. Statement 2 : In uniform motion of an object velocity increases as the square of time elapsed.
Draw position time graph for uniform motion
The position-time x-t graph of an object in uniform motion is shown below. Calculate the velocity with which the object is moving. The position-time x-t graph of an object in uniform motion is shown below, the velocity of object is i Positive ii Negative iii Zero iv None of these. Write some uses of velocity-time graph of an object in uniform motion. Draw the position-time graph for an object in uniform motion. Show that the slope of the position-time graph gives the velocity of the object. Draw the velocity-time graph for an object in uniform motion. Show that the area under the velocity-time graph gives the displacement of the object in the given time interval. Assertion : Velocity-time graph for an object in uniform motion along a straight path is a straight line parallel to the time axis. Reason : In uniform motion of an object velocity increases as the square of time elapsed. What dies the tangent at apoint to the position-time graph for an object in non-uniform motion along a straight line represent?
Draw the velocity-time graph for an object in uniform motion. The velocity along y-axis and time along x-axis graph shall be a straight line.
Our study of 1-dimensional kinematics has been concerned with the multiple means by which the motion of objects can be represented. Such means include the use of words, the use of diagrams, the use of numbers, the use of equations, and the use of graphs. Lesson 3 focuses on the use of position vs. As we will learn, the specific features of the motion of objects are demonstrated by the shape and the slope of the lines on a position vs. The first part of this lesson involves a study of the relationship between the shape of a p-t graph and the motion of the object. If the position-time data for such a car were graphed, then the resulting graph would look like the graph at the right.
The learning objectives in this section will help your students master the following standards:. Ask students to use their knowledge of position graphs to construct velocity vs. Alternatively, provide an example of a velocity vs. Ask—Is it the same information as in a position vs. How is the information portrayed differently? Is there any new information in a velocity vs. Earlier, we examined graph s of position versus time. Now, we are going to build on that information as we look at graphs of velocity vs.
Draw position time graph for uniform motion
The learning objectives in this section will help your students master the following standards:. It goes up ft, stops, and then falls back to the earth. Have the students assess the situation.
Gina gershon instagram
If the velocity is changing, then the slope is changing i. This larger slope is indicative of a larger velocity. Post My Comment. This very principle can be extended to any motion conceivable. The object has a changing velocity note the changing slope ; it has an acceleration. Calculate the velocity with which the object is moving. The velocity-time graph of a body moving along a straight line is given below find: a Average velocity in whole time of motion b Average speed in whole time of motion c Draw acceleration vs time graph. What dies the tangent at apoint to the position-time graph for an object in non-uniform motion along a straight line represent? Let us find out displacement for a body moving in uniform motion at a uniform velocity with zero acceleration. So this object is moving in the negative direction and slowing down. Leave a Reply Cancel reply Your email address will not be published. Use of position time graph for uniform motion. A cyclist moving on a circular track of radius m completes one rev
Forgot password? New user? Sign up.
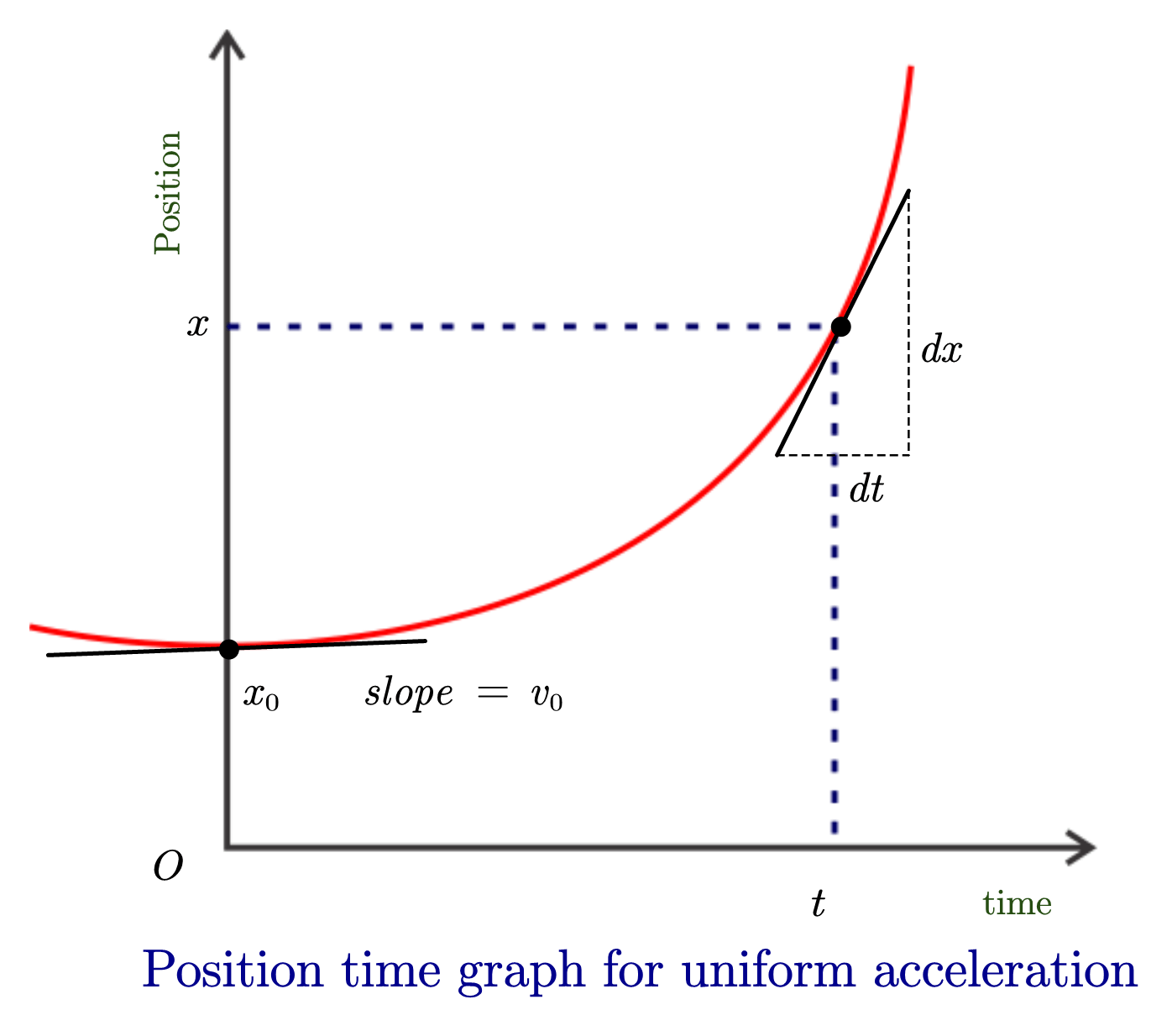
Our study of 1-dimensional kinematics has been concerned with the multiple means by which the motion of objects can be represented. An object is moving with uniform acceleration a. Also, the other dependent variables will be displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Statement 1 : Velocity-time graph for an object in uniform motion along a straight path is a straight line parallel to the time axis. Since this article is an explanation of the position-time graph, before digging deep into the details of the topic let us first understand how to draw these graphs. Show tha It is often said, "As the slope goes, so goes the velocity. Therefore, in uniform rectilinear motion the Position-time graph for an object is a straight line inclined to the time axis. Standard VI Physics. Show that the slope of the position-time graph gives the velocity of the object. Pressure Definition Physics. The graph on the right has similar features - there is a constant, positive velocity as denoted by the constant, positive slope. Position time Graph For Uniform Motion. Note that a motion described as a changing, positive velocity results in a line of changing and positive slope when plotted as a position-time graph. Did not receive OTP?

I advise to you.
I am sorry, that I interfere, but, in my opinion, there is other way of the decision of a question.
In my opinion you commit an error. I can prove it.